Validation of the strategy of modernization of physical education of higher school students in ukraine
Фотографии:
ˑ:
S.I. Belykh, professor, Ph.D.
Donetsk national university, Ukraine
Key words: physical education, non-professional physical education of students, strategy.
The relevance of the study and the problem statement is defined by the situation of long-term selection of the way of development of university physical education taking place on the territory of the former USSR.
In the Russian Federation bodily-centered, environment-centered and personality-centered approaches are implemented in practice. Belarus holds the concept, which has been worked out in the USSR, intended for bodily-centered approach and physical training, remarkable by the conversion of ideas generated to the theory of sport. Whereas in Ukraine, it is impossible to distinguish the concept, which performs here the role of a guide for improving students’ physical education.
The university subject "Physical education" will be clearly incapable of accomplishing its mission, until it faces the solution of the issue of formation of a personality taking care of his health, by its content, not only in intentions. And what it requires, has been known for a long time, because in the late 1980s V.V. Prikhod’ko introduced in the theory and practice of physical culture the concept of non-professional (non-special) physical education [6], and L. I. Lubysheva - the concept of physical education of students [5], which made it possible to solve this problem in practice.
The purpose of the study was to validate the strategy of modernization of university physical education in Ukraine.
By the early 1990s, two strategies of improving students’ physical education were formed. One of them we conventionally call "traditional", it is historically the first by the time of occurrence. This strategy is based on the idea of solving existing problems via high personal activity of physical education teachers and it is intended to improve the means of bodily-centered approach that relate to the methodology [6].
Without questioning the importance of this approach for improving the bodily component of the personality during the classes on the university subject "Physical education" (as it is called in Ukraine - auth.) as its essential basis, we question the perspectives of the approach in the XXI century, in which the mere corporality condition remains the object of teachers' efforts. Especially because in the early 1990s a qualitatively different strategy was actually formed, which was first developed by L.I. Lubysheva and V.V. Prikhod’ko [5, 8] in their doctoral theses, we call it "modern".
Preparation for the development of the modernization project required the ascertaining studies to assess the progress of the implementation of bodily-centered approach. Their general direction is determined by the desire to deeply explore the formulation of physical education of university students in the part, which is associated with the formation of personality physical culture and healthy way of life. And we were interested not so much in whether students have different knowledge and skills or not, but also the features of promotion of healthy way of life. In addition, since the situation in the university physical education is estimated by both teachers and students, we needed to consider the opinion of bachelor students attending classes in this subject about its current state and prospects of development of the subject "Physical education".
Materials and methods. In order to assess the actual results of the first strategy, we will refer to our special research. Devoted to the study of self-estimation on the topic of maintaining health, it was conducted at three universities in Ukraine: Donetsk National University (DonNU), Zaporizhzhya National Technical University (ZNTU) and National Mining University in Dnipropetrovsk (NSU). 650 first and fourth-year students (324 boys and 326 girls) were surveyed.
As a result of responses to the questionnaire student could earn a certain number of conventional points, namely: 3 - 22 - bad, 23 - 53 – average, 54 - 84 - good and 85 - 115 points - excellent. In this case, "excellent" mark matched with active participation in self-care, which is reliably qualified as sports activity. It is a state (not just "know" and "know how", but also regularly "do" what is important to maintain health), regarded as the desired end result of the efforts of physical education departments and the staff of three mentioned universities.
Results and discussion. According to the data, it was found in a survey that the maximum number of points, corresponding to a full featured sports activity, among young men of the National Mining University was reached by: 14.06 % of first-year students, 6.38 % of fourth-year students; ZNTU - 7.50 % - first-year, 26.47 % - fourth-year; Donetsk National University - 15.55 % - first-year, 4.26 % fourth year. As can be seen, physical activity of these university students is not of the nature of the phenomenon, which has a general tendency to develop as they get older (i.e., moving to the next course of study). We can assume that this situation, namely, the low popularity and even the loss of sports activity is characteristic for all universities of Ukraine and indicates the random reasons for inclusion and "the drop out" of students from the state, which is characterized as a full-fledged physical activity.
Among the girls of NSU the maximum number of points corresponding to the features "sports activity" was obtained by the 1.82% of first-year students, 0.00% of fourth-year students; in ZNTU - the first-year - 6.25%, the fourth – 7.50%; Donetsk National University - the first - 5.56%, and the fourth - 1.45% of students. Table 1 shows the results separately for each university according to year and gender.
Self-estimation by the students of the degree of involvement in sports activity in different universities (in %).
|
Points |
NSU |
ZNTU |
DonNU |
|||||||||
|
Boys |
Girls |
Boys |
Girls |
Boys |
Girls |
|||||||
|
1 y. |
4 y. |
1 y. |
4 y. |
1 y. |
4 y. |
1 y. |
4 y. |
1 y. |
4 y. |
1 y. |
4 y. |
|
|
3 – 22 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
23 -53 |
4,69 |
18,09 |
12,73 |
23,08 |
17,50 |
- |
25,00 |
2,50 |
8,89 |
6,38 |
12,5 |
18,84 |
|
54-84 |
81,25 |
75,53 |
85,45 |
76,92 |
75,00 |
73,53 |
68,75 |
90,00 |
75,56 |
89,36 |
81,94 |
79,71 |
|
85-115 |
14,06 |
6,38 |
1,82 |
- |
7,50 |
26,47 |
6,25 |
7,50 |
15,55 |
4,26 |
5,56 |
1,45 |
Obviously, the results shown in the table create only the illusion of well-being (we see a significant number of evaluations corresponding to the mark "good" among boys and girls). But the survey is specific for the fact that we select as expected only those evaluations which correspond to the position of "excellent": it is this evaluation that indicates the fact of sports activity.
Thus, 11.11 % among the first and fourth-year male respondents and 3.99 % among the girls gained the maximum number of points that reflect the level of sports activity (Fig. 1). The points of others are not enough to this important state of a mature man.
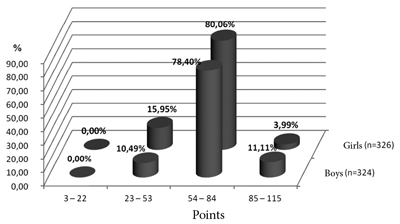
Fig.1. Summary figures of university students’ self-estimation of the degree of involvement in sports activity (boys and girls).
One of the objectives of the study was to determine the degree of participation and influence of physical education teachers on the student's decision to do chosen kinds of physical activity and sport. The results were unexpected. The influence of teachers on student's decision to do chosen kinds of physical activity and sport at NSU among the male first and fourth-year students and the female fourth-year students was - 0.00%, first-year girls - 3.64%. The greater part of the students made their choices of physical activity and sport independently. Namely: first-year boys - 70.31%, fourth-year boys - 62.77%; first-year girls - 78.18%, fourth-year girls - 80.77%.
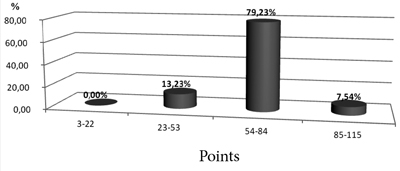
Fig. 2. Summary figures of students’ self-estimation of the degree of involvement in sports activity (regardless of gender).
In DonNU the situation is similar, as the impact of teachers on student's choice of type of physical activity remains negligible: 4.44% and 0.00% for first and fourth-year boys respectively, 8.33% and 1.45% for first and fourth-year girls. The highest percentage of students surveyed took part in choosing the type of physical activity independently. 68.89% and 74.47% for male first and fourth-year students respectively and 79.17 and 85.51% for female first and fourth-year students correspondingly.
In ZNTU the situation is somewhat different. The decision to do chosen kind of physical activity and sport was influenced by physical education teachers the following way: for the boys of the first year - in 22.50% and 14.71% cases for male first and fourth-year students respectively; 26.56% and 20.00% for female first and fourth-year students respectively. But even here, student is first to choose himself a kind of physical activity. 60.00% and 55.88% of male first and fourth-year students respectively, 62.50% and 52.50% of female first and fourth-year students respectively.
In general, the teacher's role in the choice of a certain kind of physical activity is 26.94% and 14.71% of cases among male first and fourth-year students respectively; 38.53% and 21.45% among female first and fourth-year students respectively, i.e. while studying in a university the teachers’ influence is remarkably reduced.
Based on the data, it is clear that physical education teachers have little influence on healthy way of life promotion and don't take a noticeable part in attracting young students to various kinds of sports activity. It leads to the fact that students are often on their own, not interrupted by teachers, through trial and error trying to choose their kind of physical activity and sport.
The next objective of the study was to determine whether it is the satisfying amount of theoretical and practical knowledge and skills on rehabilitation, physical development and physical training, what students acquire during the course of the subject "Physical education". Students were asked to choose one of the following answers: quite satisfied, not very satisfied or satisfied. From these results, we present the data that in our opinion is critical, indicating the students’ high demands to the subject "Physical education" itself. For this analysis we combined the following options for students' answers - "not very satisfied" and "not satisfied." Consider the generalized results obtained for each of the three universities and in general.
In DonNU 26.66% male and 12.45% female first year students and 25.53% male and 37.68% female fourth-year students are not satisfied with the amount of obtained knowledge. The total of male and female first and fourth-year students - 26.09% and 24.82% respectively.
In NSU boys - 37.51% male and 38.18% female first year students and 52.13% male and 42.31% female fourth-year students are not satisfied with the amount of theoretical and practical knowledge and skills. The total of male and female first and fourth-year students - 46.20% and 39.51% respectively.
In ZNTU students are even more demanding to theoretical and practical knowledge. The amount of obtained knowledge doesn't satisfy in the first year : boys - 70,00 % , girls - 54.69 %; in the fourth year: boys - 67.65 % , girls - 50.00%. Total not satisfied with the level of knowledge boys of the first and fourth years - 68.92 %, and the girls - 52.88 %.
45.68 % of the total respondents-boys of the first and fourth years (n = 324 ) are not satisfied with the amount of theoretical and practical knowledge and skills on rehabilitation, physical development and physical training during the course of the "Physical education"; and for the girls - 37.42 %( n = 326). From a total of 650 students surveyed 41.54 % (270 people) are not satisfied with the amount of theoretical and practical knowledge.
It should be noted the important fact that most of the respondents set goals in the preservation and strengthening of health: boys of the first year - 87.25%, of the fourth year - 90.29%; girls - of the first year 87.96 %,of the fourth year- 89.63%. Notably that at ZNTU the boys and girls of the fourth year set goals in the preservation and strengthening of health in 100% of cases.
Consider the following position, namely: are students ready to take responsibility for the preservation and strengthening of their health?
For the question: "What determines the health of a person ?" students were offered a number of responses , some of which meant that the person himself must take responsibility for his health. For example: for the quality and the regimen of nutrition, lifestyle and daily routine, the lack of bad habits, the amount of motor (physical) activity and more. Other responses meant that a person is ready to shift responsibility to others, to the circumstances. For example, the activities of health institutions, the environmental conditions or the heredity.
During the survey it was found that boys and girls of the first and fourth year believe that human health depends on: the environmental conditions of life - boys: of the first year - 61.07%, the fourth year - 70.86%, girls: of the first year - 70 , 68%, the fourth year - 74.07%; the heredity - boys: of the first year - 40.94%, the fourth year - 45.14%, girls: of the first year - 43.98%, the fourth year - 49.63%; the healthcare - boys: of the first year - 16.78%, the fourth year - 23.43%; girls: of the first year - 19.9%, the fourth year - 14.81%.
The study generally allows to conclude that:
- There are no any noticeable participation and influence of physical education teachers on students' decision to engage in certain kinds of physical activity and sport, that hardly justified at the step of forming a healthy way of life of a young man;
- The amount of theoretical and practical knowledge and skills on rehabilitation, physical development and physical training, obtained during the course of the "Physical education" doesn't satisfy the 41.54 % of the students surveyed;
- While the majority of respondents set goals in the preservation and strenghtening of health, namely : boys of the first year - 87.25%, of the fourth year - 90.29% girls - first year 87.96%, of the fourth year - 89 63%.
Due to the weak participation of teachers in the initiation and organization of physical activity of students, as well as insufficient knowledge obtained in the field of physical culture, 60% of young people try to choose for themselves a type of physical activity. Eventually, however, this brings to the sports activity expansion only 7.54% of the total number of students surveyed.
The following 'modern' modernization strategy of physical education is distinguished by, firstly, the desire to move from the subject - object relationship between teacher and student to subject - subject relationship (ie , from the pedagogical supervision to a style of pedagogical management). Secondly, the desire to change the student state from the object of teaching manipulation to the subject position of teaching and learning activities, due to which he has a full-fledged educational activity, which in terms of the traditional teaching of "Physical education " simply doesn't exist, it all comes down to exercises and training. Thirdly , the authors of the strategy shift their efforts from physicality exercises to the state of consciousness of the students involved, bringing to the fore the questions of values and motives, knowledge, skills and competencies necessary for students to plan and conduct their own physical training events.
Fourthly, only within the framework of commitment to this strategy it is possible to provide a truly individually oriented educational and learning process that opens up new horizons for the development of "Physical education" as a full-fledged university subject. What distinguishes this approach is not so much the familiar exercise and sports orientation, but the desire to spread the values of physical education and healthy way of life, and the formation of the students' strong motivation to continue sports and sporting activities even after the date of last test on the "Physical education". It is also the attention to developing the necessary variety of knowledge and skills. Thus the conditions for the mutual concerned activities of teachers and students, that opens up new prospects for the modernization of the "Physical education".
Existing educational technologies also support the above two approaches to the student learning and development in the field of physical culture. The first ensures the formation of the normative standard of knowledge and skills. In physical education of students, it is realized through the applied professional physical training. The second way is related to the search of the answers to such issues (problems) of the self-education technology and personal development, which in principle don't have a unique solution" [3, p. 72-73 ].
Physical education of a person involves the integration of physical training and physical education, the physical development and saving of physical health, providing a high level of person's physical culture. As for priorities, they can be understood only in the personality-centered model of educational process , as those related to the creation of conditions for the manifestation and development of the characteristics of each individual, his personality , with the idea of free choice of the person's development path in the educational process.
Structural components of organizational and pedagogical conditions of the formation and preservation of health and physical education of students are:
- The formation of self-educational motives, the development of knowledge and skills for healthy way of life;
- The maintenance and development of physical condition, the training sessions for the development and self-development of physical training, the propagandistic-educational work on the formation of personally significant values of healthy way of life;
- The teacher's activities to promote self-development of physical culture of the person;
- The students' activities on self-development of physical culture;
- The pedagogical means(training exercises , creative tasks, technical means to maintain the health and development of physical condition);
- The quality of training and methodological support, including the individual programs, tutorials, guidelines.
We believe that: "Knowledge has become a professionally-personal only when there was a systematization ( self-reflection ) of the experience, when a person can adapt it to other tasks (task orientation), make it a working tool ( technology) " [3, p. 37]. Anthropic educational technologies allow to switch from the qualification ( subject- disciplinary ) approach in higher education to professionally-competentive. The perspective of the specialist development the higher, the wider ( while maintaining the specialization ) his horizons , how fully he can use the achievements of human culture and the diverse areas of knowledge, including the achievement of physical culture for self-improvement.
Conclusions. Proceeding from the study, the further use in higher schools of the traditional, body-centered strategy gives no hope for efficient settlement of the problem of formation in students of the phenomenon of personal physical culture, visually being realized via the phenomenon of physical activity.
We take physical activity as an acute educative and training result of the distribution of physical culture in the higher school. As an integral part of vocational training sports activity and a flash of personal physical culture, physical activity acts as a reliable base of self-care (including personal readiness for readaptation in the constantly changing conditions of productive activity, ensuring of high efficiency and optimal health level).
Only the "modern" strategy based on the personality-centered approach to education and training is assumed a reliable base in solution of the issue of formation of the personality active in sports.
References
- Dmitriev, S.V. Anthropic university technologies – it is a developing professional, but not a trained specialist who is important / S.V. Dmitriev // Fizicheskoe vospitanie studentov. – 2011. – № 3. – P. 37–41. (In Russian)
- Dmitriev, S.V. Educational technologies – from logics of interaction to the logics of creativity / S.V. Dmitriev, S.D. Neverkovich // Sportivny psikholog. – 2011. – № 2 (23). – P. 72–77. (In Russian)
- Lubysheva, L.I. Theoretical and methodological basics of formation of students’ physical culture: abstract of doctoral thesis (Hab.) / L.I. Lubysheva. – Moscow, 1992. – 53 P. (In Russian)
- Oleksenko, V.M. Theoretical and methodological basics of realization of innovation technologies in training of future engineers: doctoral thesis (Hab.)/ V.M. Oleksenko. – Kiev, 2008. – 463 P. (In Russian)
- Prikhod’ko, V.V. Educational basics of physical education of students (Experience of gaming simulation and expert design planning and expert examination): doctoral thesis (Hab.)/ V.V. Prikhod’ko. – Moscow, 1991. – 416 P. (In Russian)
- The European health report 2009: health and health systems. http://www.euro.who.int/PubRequest?language=Russian. (In Russian)



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE