Specifics of methodology of professional physical training of cadets of engineering institutes
Фотографии:
ˑ:
A.V. Klyuchnikov
Lyceum under Gomel Engineering Institute of the Emergency Ministry of the Republic of Belarus
G.I. Narskin, professor, Dr.Hab., Honored worker of physical culture and sport of the Republic of Belarus
A.G. Narskin, associate professor, Ph.D.
Skorina Gomel state university, Gomel, Belarus
Key words: cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry, professional physical training, fire and rescue double event.
Introduction.
In connection with the recent negative trend to increase of the number of emergency situations, growth of material damage and casualties, natural and anthropogenic disasters are to be the global problems, and ensuring of life safety is one of the crucial ones for all mankind [3].
Due to diversity of emergency situations and working conditions on their management high demands are made to the rescuers’ professional skills and their efficiency is directly correlated with the specialized knowledge they possess, the level of development of professional qualities, skills and abilities [4, 7].
Firemen are often subject to high physical and mental loadings when performing operational missions in extreme conditions: they have to take prompt decisions in critical situations, perform various kinds of work associated with people and property rescuing efficiently and consistently along with other activities. Thus, cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry can be considered athletes involved in combined sports (double events) according to the overall and special fitness criteria. However, it is to be taken into account that they work in emergency, sometimes extreme and unpredictable situations [1, 8].
Expert training in the institutes of the Emergency Ministry of the Republic of Belarus is being realized in accordance with the educational standard “AD RB 02100.5.233-2002 Educational standard. Higher education. Speciality 1-94.01.01 – “Emergency management” and the qualification “Emergency management engineer”. Here high demands of the present economic and social environment to physical education and first of all to applied professional physical training of experts of the Emergency Ministry, associated with training of physical qualities, enhancement of physical working capacity and formation of professional skills and abilities are to be taken into account [5, 11]. Meanwhile, according to the analysis of the scientific and methodological literature dedicated to the theory and methodology of vocational training of cadets of paramilitary higher educational establishments, along with synthesis of the practical professional experience, the methodology of physical education at the phases of long-term training of cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry of the Republic of Belarus in view of initial physical state and demands of the future professional activity has not been established so far. The facts on the combination of methods of physical education at the phases of the educational process are contradictory [6, 9, 10].
All the abovementioned predetermines the relevance of the present study and indicates to the required optimization of the educational process on the discipline “Physical culture” for cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry in view of initial physical state and demand of the future career.
The paper is devoted to the problem of professional physical training, due to complicacy and versatility of the applied professional physical training of cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry, which is intended for acquiring, training and forming of applied knowledge, applied mental and personal qualities [2, 4, 5, 9], but not only for formation of applied physical qualities, skills and abilities.
The purpose of the study was to enhance professional physical training of cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry of the Republic of Belarus in view of the initial physical state and demands of the future professional activity.
Materials and methods. The main research methods involved were as follows: theoretical analysis of scientific and methodological literature; synthesis of the leading educational experience; pedagogical follow-ups; studies within natural educational process, ascertaining and “forming” educational experiments with the use of instrumental methodologies (study of morphological characteristics, estimation of development of motor abilities, technical skills and functional vigor); mathematical and statistical methods of analysis of facts.
The educational experiment was made based on the Gomel engineering institute of the Emergency Ministry of the Republic of Belarus and included several phases.
At the first phase we made several studies to define the most informative and obtainable indices of the integrated estimation of cadets’ professional skills (including the tests of physical, technical and functional skills and abilities), where we studied the indices of physical fitness (level of development of motor abilities) – 25 indices; functional vigor – 8 indices; morphological characteristics - 8 indices. In addition, the competitive results in 100-m obstacle course competition, assault-ladder climbing onto the 4th floor of a training tower and the total of fire and rescue double event were analyzed. Over 300 cadets were involved in the study.
The findings were examined in two aspects. In the first case the correlation of the indices of single aspects of fitness (physical, technical and functional) with the 100-m obstacle course competition and assault-ladder climbing onto the 4th floor of a training tower was considered. In the second case, reliability and information value of the tests were determined to define the minimum of reliable and informative tests for the integrated monitoring of cadets’ professional skills.
The second phase of the studies was dedicated to the analysis of the overall physical fitness of the first-year cadets (n=77) on the basis of tests, having been selected at the first phase.
At the third phase of the study we made a year-long educational experiment to reveal efficiency of educational classes of various dominant orientations within the discipline “Physical culture” for cadets of the Gomel engineering institute of the Emergency Ministry. The orientation of classes in experimental groups was as follows:
1) type of integrated training aimed at the even proportional development of motor abilities;
2) dominant orientation to training of lagging motor abilities;
3) orientation to enhancement of individual key motor abilities, mainly specialized technical training in the kinds of fire and rescue double event.
At the fourth phase of the study we organized and made the main educational experiment to validate the methodology of professional physical training of cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry with 54 first-year cadets involved.
The worked methodology includes five correlated blocks (Fig.):
1. Input data collection;
2. Planning of educational process;
3. Determination of the content of the program;
4. Integrated monitoring;
5. Correction of educational process.
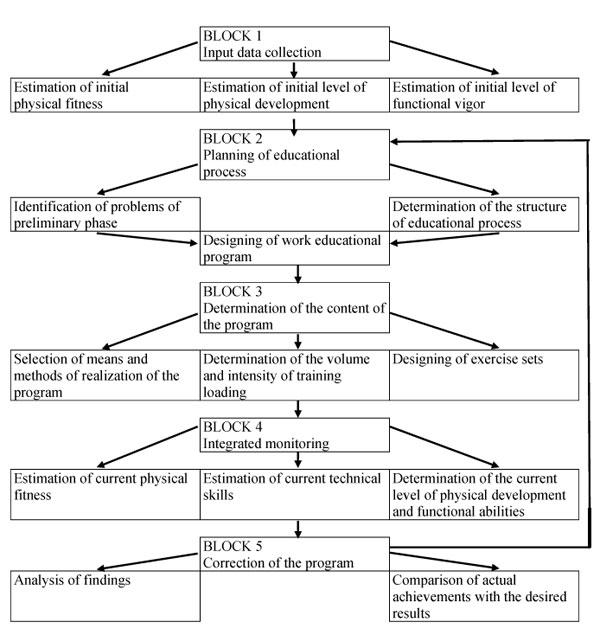 Figure. Methodology of professional physical training of cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry
Figure. Methodology of professional physical training of cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry
The methodology was approved in the main educational experiment. Different organization of the educational process of cadets by orientation of training methods and their percentage served the key experimental factor. The first-year cadets were distributed into two homogenous groups: control and experimental ones. The control group (n=28) trained in accordance with the program on the discipline ”Physical culture” for the speciality 1-94.01.01 - “Emergency management”, based on:
1) all-round training using the main methods from such sports as athletics, gymnastics, skiing, sports games, body-building (to the extent of 65% of the total time of classes);
2) special training – swimming and water rescue training, self-defense (to the extent of 16% of the total time of classes);
3) sports technical training – kinds of fire and rescue double event (to the extent of 19% of the total time of classes).
The educational process in the experimental group (n=26) was arranged based on the results of preliminary studies and involved:
1) all-round physical training using the methods of gymnastics, athletics, sports games, skiing, intended for the dominant development of the key motor abilities (to the extent of 43% of the total time of classes, where approximately 30% of time was dedicated to further enhancement of the overall physical fitness and development of key physical qualities and approximately 13% of time – for two-three components of motor abilities);
2) special training – swimming, self-defense (to the extent of 6% of the total time of classes);
3) sports technical training - kinds of fire and rescue double event (to the extent of 51% of the total time of classes with approximately 40% - for integral performance of kinds of fire and rescue double event and about 11% - to enhancement of technical skills in kinds of fire and rescue double event).
Results and discussion. According to the results of the main experiment, the influence of the applied programs on efficiency of kinds of fire and rescue double event varies in both of the groups (Tab. 1).
Table 1. The dynamics of the total of fire and rescue double event and its single kinds for cadets of the control and experimental groups within the educational experiment
|
Group |
Input data |
Finite data in the end of the main experiment |
Significance of differences, t / Р |
Rates of increase, % |
|
X±δ |
X±δ |
|||
|
Total of fire and rescue double event, sec |
||||
|
Control |
57,04±1,94 |
50,71±1,83 |
2,37 < 0,05 |
11,09 |
|
Experimental |
56,81±1,92 |
45,25±1,85 |
4,34 < 0,001 |
20,35 |
|
Intra-group differences, t / Р |
0,08 > 0,05 |
2,09 < 0,05 |
|
|
|
100-m obstacle course competitions, sec |
||||
|
Control |
27,79±1,26 |
23,81±1,18 |
2,30 < 0,05 |
14,32 |
|
Experimental |
27,28±1,29 |
22,51±1,12 |
2,79 < 0,01 |
17,49 |
|
Intra-group differences Р |
0,28 > 0,05 |
0,80 > 0,05 |
|
|
|
Assault-ladder climbing onto the 4th floor of a training tower, sec |
||||
|
Control |
29,27±1,22 |
26,95±1,19 |
1,36 > 0,05 |
7,93 |
|
Experimental |
29,63±1,21 |
23,41±1,17 |
3,69 < 0,001 |
20,99 |
|
Intra-group differences Р |
0,21 > 0,05 |
2,12 < 0,05 |
|
|
|
Efficiency of technical skills in 100-m obstacle course competition, sec |
||||
|
Control |
10,67±0,20 |
10,09±0,19 |
2,10 < 0,05 |
5,59 |
|
Experimental |
10,62±0,23 |
9,75±0,21 |
2,79 < 0,01 |
8,54 |
|
Intra-group differences Р |
0,16 > 0,05 |
1,20 > 0,05 |
|
|
|
Efficiency of technical skills in assault-ladder climbing onto the 4th floor of a training tower, sec |
||||
|
Control |
8,92±0,19 |
8,56±0,23 |
1,21 > 0,05 |
4,12 |
|
Experimental |
8,79±0,20 |
7,81±0,18 |
3,64 < 0,001 |
11,81 |
|
Intra-group differences Р |
0,47 > 0,05 |
2,59 < 0,01 |
|
|
The total of the fire and rescue double event served an integrated index of cadets’ professional physical fitness when analyzing the obtained experimental data. The estimation of the rates of increase of result in the total of fire and rescue double event revealed the annual growth by 11,09% in the control group (stipulating for enhancement of result from 57,04±1,94 sec to 50,71±1,83 sec, at t=2,37, Р < 0,05) and by 20,35% in the experimental group (from 56,81±1,92 sec to 45,25±1,85 sec, at t=4,34, Р < 0,001). The significance of intra-group differences was t=2,09, Р < 0,05. The allocated tendency is caused by the dynamics of specific kinds of fire and rescue double event, where cadets of the experimental group surpassed their coevals by the end of the main educational experiment in the test “Assault-ladder climbing onto the 4th floor of a training tower” (t=2,12, Р < 0,05) and the index of efficiency of technical skills in assault-ladder climbing onto the 4th floor of a training tower (t=2,59, Р < 0,01).
A significant increase of the studied indices was marked in both of the groups in the results of the tests characterizing development of key motor abilities. Meanwhile, in the experimental group the most pronounced statistical fluctuations (Р < 0,01 versus Р < 0,05) were marked in the test “100-m run from start”, “Shuttle run 10 х 10 m”, “Standing long jump”, “Grip pull-up” and “Powerlifting (Combined Weightlifting Exercises)”.
Concerning the total score in five control tests the growth in the control group was by 61,30 % (at statistical difference between the input and finite data Р < 0,05), while in the experimental group – by 67,09 % (at statistical difference between the input and finite data Р < 0,01).
Proceeding from the experimental results, both variants of organization of the educational process within the year-long educational experiment stipulated for enhancement of physical development of cadets, with the statistically unreliable annual growth of the studied inter- and intra-group indices (P > 0,05).
Herewith, proceeding from the study of the dynamics of the functional vigor of cadets of the control and experimental groups, in spite of the higher rates of increase of the studied indices among cadets of the control group, no significant difference was traced between the groups both in the beginning and in the end of the experiment (P > 0,05). Moreover, the compared input and finite intra-group indices revealed the statistically significant growth of the functional vigor in both of the groups, at P < 0,05.
Conclusion. As follows from the results of the study, the methodology of professional physical training of cadets of engineering institutes of the Emergency Ministry, we had designed and realized in view of the demands of the future career, facilitated more efficient learning of specific kinds of fire and rescue double event and enhanced technical skills in the experimental group.
The suggested methodology of professional physical training intended for development of key physical qualities (to the extent of 30% of the total time of classes) and integral performance of kinds of fire and rescue double event (to the extent of 40% of the total time of classes) facilitates development of the basis for enhancement of physical and technical skills, capabilities, obtaining of high results in professional motor activity and lays the basis of high professional efficiency.
The methodology of professional physical training of cadets was proved efficient by the results of the educational experiment, testifying to the statistically significant dominance of the cadets of the experimental group, promoting enhancement of their total results in the fire and rescue double event to 45,25 sec versus 50,71 sec in the control group (the 5,46 sec variance at the statistical validity of differences Р < 0,05).
References
- Bondarenko, K.K. The use of the differentiated approach to estimate special training of firemen / K.K. Bondarenko, D.N. Grigorenko // Pozharnaya bezopasnost’. – Moscow: ARRIIPE, 2005. – № 2 – P. 83–89. (In Russian)
- Bondarenko, L.Yu. Firemen and rescuers’ training / L.Yu. Bondarenko. – Moscow: Meditsinskaya podgotovka, 2008. – 254 P. (In Russian)
- Vladimirov, V.A. Natural dangers and society /V.A. Vladimirov, Yu.L. Vorob’ev, V.I. Osipov, S.K. Shoigu. – Moscow: Kruk-Prestizh, 2002. – 245 P. (In Russian)
- Gavrilenko, E.S. Psychological educational characteristics of applied professional physical training of rescuers of the Emergency Ministry of Russia / E.S. Gavrilenko // Psikhologiya obucheniya. – Moscow, 2007. – Iss. 3. – P. 100–107. (In Russian)
- Dinaev, B.M. Applied professional physical training of cadets in fire-engineering universities / B.M. Dinaev // Vestnik gosudarstvennogo universiteta upravleniya, 2009. – № 11. – P. 13–16. (In Russian)
- Dinaev, B.M. The ways of development of the applied vocational physical training and sport in the Academy of Public Fire Service of the Emergency Ministry of Russia / Ch.T. Ivankov, B.M. Dinaev // Man, health, physical culture and sport in the changing world: XVIII Inter-university theor.-pract. conf. on the issues of physical education of pupils: Proceedings. – Kolomna, 2008. – P. 186–188. (In Russian)
- Zaytsev, A.N. Methodology of evaluation of readiness of the worker of the Emergency Ministry for acting in extreme situations / A.N. Zaytsev // III inter-departmental theor.-pract. conf. “Acute safety issues in the Russian Federation”: Proceedings of the conference. – Yekaterinburg, 2009. – V. 1. – P. 147–150. (In Russian)
- Kovalevsky, Yu.N. Rescue work in the regions of natural disasters / Yu.N. Kovalevsky. – Riga: Lesma, 1976. – 207 P. (In Russian)
- Murovitsky, A.I. The innovative methodology of training of physical qualities of rescuers and firemen within applied vocational training: abstract of Ph.D. thesis / A.I. Murovitsky. – Smolensk, 2004. – 20 P. (In Russian)
- Mysiv, V.M. Development of the content of physical training of future rescuers and perspective directions of its optimization / V.M. Mysiv // Fizicheskoe vospitanie studentov. – 2011. – № 1. – P. 99–101. (In Russian)
- Sukmanov, S.V. Methodology of securing of operational readiness of departments of the state fire service of the Emergency Ministry Russia: abstract of Ph.D. thesis / S.V. Sukmanov. – St.Petersburg, 2005. – 21 P. (In Russian)
Author’s contacts: iri6432@yandex.ru



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE