Modular method of selfcontrol of student studies within faculty of physical culture
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Relevance of the study. In the university discipline "Physical culture", "Physical education" in Ukraine, formation of the habit of physical education and sports classes, encouragement and punishment are traditional for the current practice and clearly not the most effective. However, "Concerning the genetic predecessor, for example, on the existing need for self-assertion, it is necessary to create such conditions so that the implementation of some aspects of learning activity could provoke the feelings of success, potential recognition, higher social status, prestige, was perspective, contributed to the realization of the self-affirmation need. In this case a student considers his learning operations and actions during studies, which continuously promise positive emotions, not just as studies, but a source of satisfaction, so he has a new positive attitude to learning [4, P. 55–56].
The traditional system of totalitarian, precisely programmed physical education brings a temporary, usually only visible effect, displayed in passing of qualification standards for physical training. However, the evidence suggests that after passing a final test, a student, whose health values have not been actualized yet, is not aware of the motives of fitness classes due to his undeveloped system of competencies that ensure working capacity and health control and the lack of first experience of self-tuition. That is why he remains a personality with a passive attitude to sports.
The deep goal of educational technologies, including in the field of physical education, is improvement of the inner subject world of a person as a creator - "personality formation", "activity formation" and "competency formation", but not mastering of knowledge and skills. University is to create the educational environment and the personality-developing sphere for self-organization of the consciousness, thinking and activity spheres [3, P. 75].
The purpose of the study was to substantiate the necessity of using the modular technology of self-management of learning activity while training future physical education teachers as an acute condition of enhancement of their vocational training.
Results of the study. Anthropic educational technologies contribute to changing from the simplified approach to high school “physical culture”, intended to train a given set of psychophysical qualities, to the personality developing approach, i.e. professional-competency approach.
We proceed form the fact that not only knowledge and skills enabling teacher’s effective activity within the chosen specialization, but the personality of the physical education teacher itself, the values and way of life he has accepted directly affect the world outlook and formation of physical activity of his students.
Physical activity is one of the types of human activity, associated with cultivating (formation and establishment) of a personality and development of social relations generally of the social-cultural nature. It can be considered at the level of individual, group or social activity. It is characterized by the spirituality priority as integrity of human inner mental life when forming his physical conditions. Various types of physical activity are distinguished by the need-motivation unit, i.e, their spiritual aspect and the social status of activity in general [5, P. 22].
Human physical activity is such a state of vital activity, when physical culture exists in the form of involved standards, patterns and models of physical culture being implemented by a person. This is also an environment where search, development and first check of actions worked by humans take place while creating new, vital fitness practices [6, P. 111].
Hence, physical activity acts as a reliable vector, which if chosen can be used to determine the requirements to design and formation of the system of personality-centered physical education of university students.
The meaning of introducing of a university student to physical culture regardless his specialization consists in the fact that being an independent sphere of human activity, physical culture is aimed at creating a miscellaneous, creative personality, able to achieve spiritual and physical harmony, develop in the unity with culture and society.
It should be marked that physical training, being carried out during standard physical education classes, has no such claims, but the present underestimation of this peculiarity of physical culture in practice violated the unity of three structural components of the human culture (material, spiritual and physical), their indissoluble connection and interdependence.
According to the results of the study of the attitudes of 560 students on the ratio of general and physical culture in the personal and vocational self-determination, only 23,6% recognize the presence of such a relation, while 53,4% deny it blankly and 22% have no opinion [7, P. 17].
Hence, in training of physical education teachers it is important not only to form various skills and abilities, but introduce in the physical activity of teachers themselves. It is a known fact that students of the physical education department, after quitting sport, usually stop their physical activity.
In view of management, the educational process is a combination of teacher’s managerial activity and student’s self-management in the integral management cycle as an interaction of participants of the educational process: the system process of the teacher and students collaboration on design (planning), organization, positioning and correcting of the educational process to achieve specific result providing comfortable environment for its participants. Any teaching technology includes: goal; scientific basis; set of actions of subjects of educational process; evaluation criteria and actually results and limitations.
We are talking about a student as a subject of a doctrine, who determines for himself the final results of his activity and how to achieve them. This forms the full cycle of student’s control of his learning-cognitive physical activity, provided the comfortable operational climate for all subjects of the educational process. Thus, educational technologies are directed to create the conditions for revelation, implementation and development of student’s personal potential. In this regard, we can state that the applied modular technology is meant to teach students of physical education department self-management of the learning-cognitive activity while they master achievements in physical culture.
The measure of the value of technology is not only the operationally fixed final result, but the process itself, and when designing it its stochastic nature is to be taken into account (correlation (stochastic relation) - is an incomplete, probabilistic relationship between indicators that occurs only in the mass of observations). Consequently, the attractiveness of the technological approach within physical education of future teachers of this academic discipline is stipulated by, on the one hand, the benefits of planning (design) and control, while on the other - potential display of individual self-management abilities in the learning-cognitive activity of the subject of the educational process.
The most important characteristics of the educational technology of the operations self-management are: goal-setting, scientific ideas the authors rest upon; set of types of activity; content and organization of educational process [10].
The researches prove the need for using the modular education and organization of operations self-management and active learning technologies in the educational process, including information technologies when mastering physical culture. Modular education with all the workability features is known to ensure the best intensification of the student’s learning-cognitive activity.
Theoretical and methodological approaches to the design of the self-management system contributed to development of the modular-design technology of formation of self-management of the learning-cognitive activity during physical education classes, which we covert for students of the physical education department, which promotes the design and implementation by students of the projects of healthy way of life as a set of tasks with specific didactic purposes.
A motivated student becomes action-oriented in the search for new information, new knowledge, acquiring methodological and practical skills and abilities, settling new creative challenges while learning, which generally changes the social nature of learning, bringing the student to the position of the subject in the educational process. As a result knowledge and skills are not just translated and assimilated with felt motives during studies, but new ones are created.
The modular-design technology of teaching self-management [8] involves didactic goal-setting; allocation of the content of correlated and interacting blocks (theoretical, methodological, practical, input and output data). Students’ subjective representation on the goal of physical activity is a specific feature of operation of the blocks.
The content of the data flow module includes the capabilities and correlations of theoretical and methodological, practical blocks, along with input and output data [9]. They operate in the relationship and dialectic unity at all phases of formation of self-management of the student’s learning-cognitive activity during physical education classes. Each block has a two-level structure and is implemented at the basic (compulsory) and elective (as chosen by students) levels. The block conveys a specific meaning and can be taken as some complete element in view of didactics. The basic level includes compulsory structural units, the elective level – elective knowledge. At this level a student makes a choice himself or guided by a teacher (if he needs a consultation). The units of physical culture can be integrated by various schemes depending on the student’s level.
The data inflow module gives information on the controlled subject, his state after control and self-control actions (feedback). Diagnostics and self-diagnostics, control and self-control are the key source of information.
According to management theories, the requirements to information are as follows: adequate dataflow rate, which needs immediate control commands (urgent information); periodical comparison with set model characteristics of the actual state of the control object (current information) to correct individual impact programs; adequate information content; elimination of excess information, hampering the self-management process (determination of priority information for effective self-management); quantitative (numerical) data.
Theoretical block (Fig. 1). Its integrating function provides for:
– mastering by students of the system of theoretical-practical and specialized knowledge, essential for understanding the natural and social processes of operation of social and personality physical culture;
– formation of skills of adaptive, creative and conscious use of personal knowledge for personality and professional development and self-improvement;
– accumulation of knowledge to design the project of individual programs and their implementation in the learning and vocational activities.
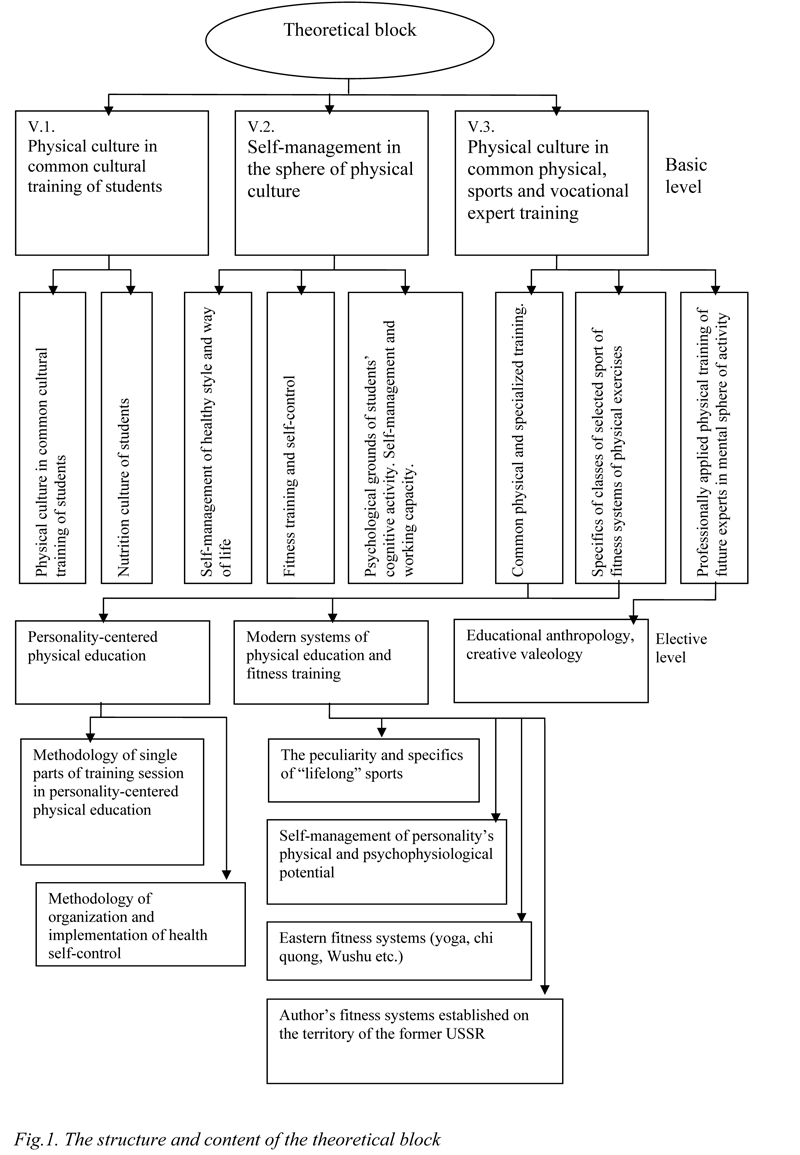
Fig. The structure and content of the theoretical block
Methodological block. Here the content of theoretical data is being completed, aggravated and specified during the learning activity.
The block is aimed at:
– mastering the diagnostics and self-diagnostics of physical health and their control;
– formation of methodological knowledge and skills in the sphere of physical culture, abilities to analyze, compare personal results with the standard, estimate and correct results of personal actions and types of physical activity;
– acquiring managerial and designing abilities;
– development and presentation of the projects of healthy way of life in view of individual peculiarities, motivation, interest in different kinds of physical activity;
– training professionally important personality traits, skills and methods of management of the learning-cognitive activity, self-improvement.
The active teaching methods applied are as follows: project method, case method, mini-conferences etc. Forms of organization: methodological classes, class and extra-curricular work independently from a teacher or under his guidance. Forms of control - test to determine the level of methodological knowledge and presentation of projects of healthy lifestyle to allocate the level of methodological skills.
The examined block consists of three basic and elective structural units. They can be structured as extended didactic units in view of motivation, health state, levels of theoretical, methodological, practical skills and future professional activity of a student.
The programs applied at methodological sports classes on the disciplines “Personality-centered physical education of students” and “Creative valeology” were to diagnose and self-diagnose personal physical health, design a healthy lifestyle program and correct it. So the programs were focused on specific sports and fitness orientations that are of interest.
The modular-design technology can be effectively organized in case of following several psychological-teaching conditions. So the structure and content of conditions, providing for more effective design of the model of student’s learning-cognitive activity in the sphere of physical culture, were developed based on the ideas of M.Ya. Vilensky and S.Yu. Al’kova [2]. Here we distinguish organizational-functional, procedural-conceptual and managerial conditions.
The procedural-conceptual conditions consist in providing student with the information on the operation of body systems, their changes during physical training and sports activity and enable development of individual training programs. The conditions are realized in organizational-cognitive games (theme chosen by students); in discussions; when designing personal programs of healthy way of life.
The created managerial conditions ensure training student’s skills to control personal learning-cognitive activity in the sphere of physical culture using the modular-rating form of holding classes and control curricula on “Educational anthropology”, “Personality-centered physical education of students” and “Creative valeology”, that change the student’s attitude to self-management.
The mechanism of self-management of the learning-cognitive activity is considered as an algorithm of operation, defined as a complex system of regularly unfolding step-by-step instructions, which when performed result in achievement of specific skill levels. Representing the core of this mechanism we base on the understanding of the principle of conversion from educational management to personality self-management as a method of dialectic cognition.
The phases of formation of self-management display the combination of the object’s and subject’s functions, the hierarchy of the structure of teaching processes that consolidate the specificity of the learning-cognitive activity of students in the sphere of physical culture. Every phase during self-management has its purpose and main function. Hence the designed algorithm ensures the conversion from management to self-management.
It is important to form in a student the skill of independent conversion from one phase to another: from accepting the goal to its solution, from setting a goal to defining adequate learning actions, from actions on implementation of the project of healthy way of life to self-control and correctional actions. And finally, mastering not only logical methods and solving problems using standard methods, but the skill to search for a personal best way of solution of unconventional goals.
Hence, the phased control of learning-cognitive activity by a student of the physical education department is assumed to be a rather effective method, providing for the due level of theoretical, methodological and practical skills, along with generated and preserved physical activity while promoting the process of learning information, psychological and teaching impact methods. These teaching methods are enough to implement the personality-centered physical education of students from different universities.
References
- Belykh, S.I. Project approach as a mechanism of innovations in the reform of the university discipline "Physical education" / S.I. Belykh // Fizicheskaya kultura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka. – Moscow, 2012. – № 1. – P. 5–9. (In Russian)
- Vilensky, M.Ya. Differential approach in physical education based on the students' subjective experience / M.Ya. Vilensky, S.Yu. Al'kova // Acute matters of students' physical culture and sport: Proceedings of the II internat. theor.-pract. seminar, April, 22-24 2004; ed. by V.S. Makeeva. – Orel: OrelSTU, 2004. – P. 254–264. (In Russian)
- Dmitriev, S.V. Educational technologies – from the logics of cooperation to the logics of co-authorship / S.V. Dmitriev, S.D. Neverkovich // Sportivny psikholog. – 2011. – № 2 (23). – P. 72–77. (In Russian)
- Kartsev, Ya.B. Psychological-teaching conditions of formation of educational needs of sports university students: Ph.D. thesis / Ya.B. Kartsev. – Moscow, 2003. – 132 P. (In Russian)
- Nikolaev, Yu.M. Theoretical aspects of the integrative content and the human creative essence of "Physical culture" / Yu.M. Nikolaev // Teoriya i praktika fizicheskoy kultury. – 1998. – № 4. – P. 16–23. (In Russian)
- Prikhod'ko, V.V. Creative valeology. The concept and educational technology of formation of technical and humanitarian students as future health creators: study guide / Ed. by A.G. Chichikov / V.V. Prikhod'ko, V.P. Kuz'minsky. – Dnepropetrovsk: NSU, 2004. – 230 P. (In Ukrainian)
- Chernyaev, V.V. Humanitarization of higher education as a precondition of its modernization / V.V. Chernyaev, K.Yu. Akulova, P.A. Khomyak // Kul'tura fizicheskaya i zdorov'e. – 2005. – № 2 (4). – P. 13–17. (In Russian)
- Yamaletdinova, G.A. Modular education as a method of self-control in the sphere of physical culture / G.A. Yamaletdinova// Vysshee obrazovanie v Rossii. 2009. № 7. P. 173–177. (In Russian)
- Yamaletdinova, G.A. Technology of self-control of cognitive activity / G.A. Yamaletdinova // Professional'noe obrazovanie. Stolitsa. – 2009. – № 3. – P. 15–16 (In Russian)
- Yamaletdinova, G.A. The system of self-control of students' learning-cognitive activity in the sphere of physical culture: doctoral theis (Hab.) / G.A. Yamaletdinova. – Moscow, 2009. – 421 P. (In Russian)
Author’s contacts: sportkafedra.donnu@gmail.com



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE