PHYSICAL EDUCATION OF MEDICAL STUDENTS BASED ON INTEGRATION OF ORIENTATION AND FORMS OF ORGANIZATION
Фотографии:
ˑ:
O.A. Breikina, postgraduate student.
L.E. Pakhomova, associate professor, Ph.D.
Belgorod State National Research University, Belgorod
Key words: physical education, medical professions, orientation, forms of organization, integration.
Introduction. The goal of physical culture of university students is associated with formation of personal physical culture and skill in using variety means of physical culture, sports and tourism to preserve and strengthen health, for psychophysical training and self-training for future professional activity. As follows from the dedicated analysis, integrated approach is required as a basis of students’ physical education.
However, most of researches are devoted to solution of the problem of improving efficiency of educational process in students’ physical education, in particular health professions, using a differentiated approach. Some teachers pay their attention mainly to future doctors’ physical fitness [2; 3], while others focus on training of students’ skills in preventive work with patients by means of physical culture [5].
Both of the directions of students’ physical education (conditioning and professionally-applied) are topical and regulated by public documents.
One of the requirements to mastering the discipline “Physical culture” is the students’ skill for applying means of physical culture, hygiene and environmental factors for their health improvement, professional and physical development all life long (government program). According to the federal state educational standard of higher vocational education on the specialty “Medical care”, graduate is to be able and ready to carry out preventive measures with people to prevent the most common diseases, organize recreational activities aimed at forming healthy way of life in view of age and sex groups and state of health, to advise on healthy food, motor regimen and classes of physical culture (professional competence-12).
Consequently, the content area on the discipline “Physical Culture” is quite similar to the one on the disciplines of student vocational training on the specialty "Medical care", stipulated by public documents.
It is to be noted that many modern researchers already associate competency approach with these very ideas of integration of modern education. Particularly, as stated by O.V. Shemet: “Competence is a person’s skill for integrating in the mind all-round knowledge; various types of activity, scientific knowledge and personal experience, theory and practice… Integrated educational environment can be considered as a basic organizational unit of the competence-focused university educational process…” [7, p. 41]. “In view of the integrative nature of professional competence, future specialist is assumed to be able to acquire it in case of continuous involvement in the educational process where interdisciplinary relations are actualized” [6, p. 22].
The purpose of the present research is development and experimental verification of efficiency of the technique of physical education of female medical students based on the integration of conditioning and professionally-applied orientations within academic and extra-curricular classes.
Materials and methods. The experimental part of the research consisted of two stages: pilot survey and forming pedagogical experiment. 2-course female medical students of the basic medical group of Belgorod State University studying on the specialty 060101-“Medical Care” were involved in the research and divided into two groups: experimental (EG) and control (CG).
The methods of acquiring actual material on the first stage included questionnaire of students (230 pers.) and practitioners of all age and work experience (159 pers.), pedagogical test of knowledge, physical fitness and exercise performance, anthropometry and methodology of estimation of health level by G.L. Apanasenko [1].
The experimental technique was developed in view of the pilot survey results of medical students (NRU BSU) and practitioners along with specialized literature and document materials.
The educational experiment has been carried out within the academic years 2010-2011 on the department of physical education № 1 NRU BSU. The specifics of the experimental technique is in the integration of the following aspects: firstly, content area of the discipline “Physical culture” and vocational training on the specialty “Medical Care”; secondly, conditional and professionally-applied directions of physical education; thirdly, compulsory academic and extra-curricular classes. Thus, intra and interdisciplinary integrations take place in the present educational experiment. The model of construction of physical education for students of the experimental group is adduced in the paper (Fig.).
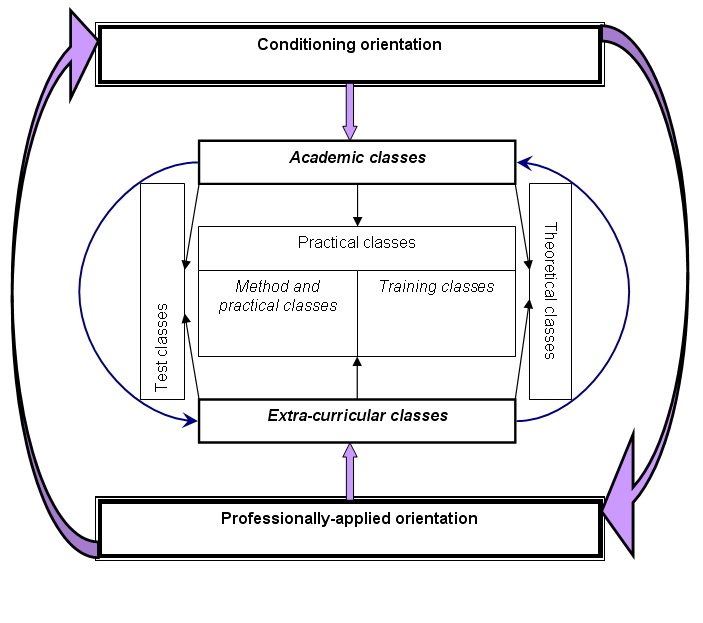
Fig. The model of physical education for female students of experimental group
The experimental procedure was realized within 90-minute-academic classes twice a week and regular extra-curricular classes at least 4-5 times a week (Table 1).
Table 1. Distribution of academic hours for basic academic and extra-curricular classes
|
Semester |
Theory |
Practice |
test |
Total of hours |
Extra-curricular |
|
|
Methods and practical |
Training |
|||||
|
I |
8 |
5 |
51 |
4 |
68 |
44 |
|
II |
10 |
5 |
49 |
4 |
68 |
44 |
|
total |
18 |
10 |
100 |
8 |
136 |
88 |
Theoretical training of female students was carried out in the beginning of practical classes in the form of short messages (10-15 min.), at self-training using the literary sources recommended by teacher and an essay. Relative to the content area theoretical classes are correlated with methodological aspects of conditioning and professionally-applied trainings.
Theoretical material on the discipline “Physical culture” for the 2nd-year medical students was based on program documents of reforming of health care system, modernization of education, modern concepts of health assessment, healthy way of life, personal culture and its determinants, along with sample public program of physical culture for universities. Therefore, the researchers tried to organize and distribute consistently the material into the topics: “Fundamentals of healthy way of life” (semester I) and “Health and fitness technologies” (semester II) (Table 2).
Table 2. The content of theoretical classes for female students of the experimental group
|
№ |
Semester I “Fundamentals of healthy way of life” |
|
1 |
Fundamentals of student’s healthy way of life. The role of means of physical culture in health improvement. |
|
2 |
Focus of human behavior on ensuring personal health, his self-assessment. |
|
3 |
Means and methods of self-training |
|
4 |
Planning and control of self-training. Features of independent physical exercises for women. |
|
5 |
Control and self-control during physical exercises. |
|
6 |
Physiological characteristic of body functions at physical activity |
|
7 |
Physical fatigue, basic recovery solutions. |
|
8 |
Means of physical culture to provide stable mental and exercise performances |
|
Semester II “Health and fitness technologies” |
|
|
1 |
Physical culture as a basis of initial and secondary preventive health care |
|
2 |
Health and fitness methods |
|
3 |
Psychophysiological characteristics of modern recreational workouts |
|
4 |
Individual selection of workout. Body weight correction by means of physical culture |
|
5 |
Preventive and sanitary values of different types of physical activity |
|
6 |
General health level assessment. Diagnostics and self-diagnostics of health status, assessment of human exercise performance |
|
7 |
Physiological basis of the use of means of physical culture for health improvement |
|
8 |
Adaptive processes at regular classes of physical culture |
|
9 |
Physiological characteristics of adaptation to physical loads. Dynamics of body functions at adaptation and stages of adaptation |
|
10 |
Body functional changes after physical exercises |
Since the methods and practical part of the class was preceded by brief theory, numerous methods and techniques were used which are the following:
- discussion or dialogue with female students as relatively simple ways of involvement of girl students in the educative process, promoting drawing their attention to acute aspects of the topic and setting the pace of report;
- group consultations - a specific form of studies mainly focused on explanation to girl students of single, most complicated or practically significant issues of material they study. Group consultations were mainly conducted in case of required detailed study of practical matters, especially difficult for them while planning recreational workouts without assistance, determining adequate load, at self-diagnostics, to help them to make reports or get ready for tests.
Methods and practical studies were focused on mastering of means and methods promoting independent use of means of physical culture for professional purposes and self-improvement. Considerable attention was given to assessment of individual health, physical development, physical fitness, work of individual exercise sets in view of future professional activity.
Girl students were offered exercise sets, the effects from which were defined, along with application conditions and methods of graduation of physical loads. They were given creative topical tasks to do on their own on the methods and practical classes.
Training classes are aimed at training motor skills and abilities, development of girl students’ physical properties. The content area was defined by the sample public program on the discipline “Physical culture”. The classes were carried out using such methods as self-control and mutual control of the effect of exercises on the body of the ones who trained by means of heart rate monitor (to register heart rate) and self-analysis of sensations after physical loads. Girl students were to rate the data received and if needed correct the dose of loads, as well as to use the methods of self-control of the amount of physical load on their body during self-training.
Test classes are aimed at:
- reaching the qualifying standards provided by the sample public program;
- holding presentations of creative methodological manuals of exercise sets, selected by students in accordance with the previously developed topic;
- analysis and evaluation of self-control journal.
Specifically, during presentation each girl student presented the designed exercise set and showed theoretical and methodological knowledge she used to make it, resulting in an undifferentiated pass-fail evaluation in accordance with the presentation results. Girl student is to show at least basic theoretical and methodical knowledge to pass the test.
Self-control journal was analyzed in view of its regular infill, records of results of self-monitoring and health self-evaluation (once a month) by the method of L.G. Apanasenko.
One of the evaluation criteria was girl students’ ability to associate the content of the discipline they study with the content of future professional activity. Moreover, activity in studies within the semester was taken into account, that is, interest in discussions of the material, the number and content of questions asked and attendance.
Test classes were finished by undifferentiated pass-fail evaluation based on the results of the control in the three aspects mentioned above.
Self-training. Compulsory classes of physical culture twice a week are not enough to settle all the tasks due to the failure to comply the principle of consistency. Therefore, girl students had to have extra-curricular trainings at least 4-5 times a week.
Proceeding from the analysis of theoretical and methodological recommendations of the leading researchers on organization of independent recreational classes of physical exercises, the core requirements to work of individual workouts for university students were allocated, including: training 4-5 times a week; exercise intensity - 65-85% of maximum heart rate (HR); introduction of “peak” loads - 90-95% of maximum HR; training interval of 30-50 minute continuous aerobic workout with HR 140-150 beats/min; application of integrated approach with the use of both aerobic and anaerobic loads; type of exercises: continuous, uninterrupted workout with large muscle groups working; use of exercises with external resistance of moderate intensity enough to train and maintain body muscle mass; exercises combined with natural recreational effects, provoking activation of biological processes and improvement of overall body performance.
K. Cooper’s aerobic training was chosen for self-training of girl students from the experimental group in view of easiness in organization, simplicity of load graduation, unnecessary additional equipment and due to training outdoors [4].
Results and discussion. Effectiveness of the experimental technique was determined in accordance with the following criteria: theoretical knowledge and teaching skills on the subject “Physical culture”; physical development; physical fitness; somatic health (by to G.L. Apanasenko).
The educational experiment was finished by the questionnaire of girl students from both of the groups to determine self-evaluation of their knowledge and skills for using results of interdisciplinary integration while studying on the medical department (Table 3). As follows from the data, the girl students from the experimental group have an absolute advantage over the control group.
Table 3. Indices of self-evaluation of knowledge and skills of using results of interdisciplinary integration by female students, %
|
№ |
Indices |
Groups |
|
|
CG |
EG |
||
|
1 |
Act of will, insistence in attainment of goals set within studies |
29,5 |
34,2 |
|
2 |
The use of knowledge on the subject “Physical culture” in answers |
43,6 |
67,1 |
|
3 |
Understanding of interdisciplinary correlations in the studying process and awareness of their role and necessity |
64,1 |
89,5 |
|
4 |
Skill for making their personal recreational program |
75,6 |
96,1 |
|
5 |
Skill for analysis of health indices and new goal-setting |
51,3 |
90,8 |
|
6 |
Work focused on development of skills for self-training and preventive health care by means of physical culture |
12,1 |
84,2 |
|
7 |
Knowledge of methods, means and techniques of health and fitness work based on the principles of interdisciplinary correlations |
30,8 |
63,2 |
|
8 |
Strong desire to continue independent trainings |
21,8 |
72,9 |
To determine the level of development of theoretical knowledge a test by the 10-point scale was carried out. It revealed the quality of theoretical knowledge before and after the experiment.
Based on the pre-test results, the mean level of theoretical knowledge in the control and experimental groups was 2.78 points (p>0,05), whereas by the end of the educational experiment the level of knowledge in the experimental group increased by 5.82 points and totaled 8.52 points. In the control group, this rate changed by 1.16 points and amounted to 3.36 points. It proves effectiveness of the use of theoretical material in the process of methods and practical studies and girl students’ extra-curricular work with specialized literature.
Physical development of students from both of the groups was estimated by the following indices: height, weight, chest excursion, lung vital capacity, carpal dynamometry, body mass index (BMI), Stange’s test and Roufier-Dixon index. The test preceding the experiment showed the lack of significant variance in the tested indices of female students from these two groups (p> 0,05).
The use of the experimental technique promoted significant changes in the majority of indices of girl students from the experimental group (p < 0,05). As for dynamics in the control group, their indices changed very slightly and insignificantly.
Indices of physical properties were allocated on test classes in the compulsory test at the beginning and end of the academic year, under the public program on the subject “Physical culture”. The test program consisted of 60 m run, standing long-jump, falling leaf, 2000 m run. The studies failed to reveal any significant variance between test indices of physical properties of girl students from the control and experimental groups, except for the results in 2000 m run: here the results of female students from the experimental group are significantly higher (p> 0,05). And the value of increase of absolute results in all exercise is more notable in the experimental group than in the control one.
Conclusion. On the modern stage modernization of physical education of university students is mainly based on the principles of differentiation and less on the use of the integrated approach.
The worked experimental technique of physical education for university students of the specialization “Medical Care” is based on interdisciplinary and intradisciplinary integration, due to, firstly, quite similar subject area and requirements to future expert training, stipulated in public documents on physical culture and doctors’ vocational training; secondly, rational integrated solution of the tasks of physical education with conditioning and professionally-applied orientation; thirdly, required use of compulsory academic classes and self-training guided by a teacher for the complete solution of the tasks of physical education.
Factual evidence resulted from the experiments prove high efficiency of the worked technique.
Bibliography
- Apanasenko, G.L. Medical valeology / G.L. Apanasenko, L.A. Popova. – Rostov-on-Don: Fenix, 2000. – 248 P. (In Russian)
- Varennikov, Yu.T. Means and methods of control of physical training of university students: abstract of Ph.D. thesis / Yu.T. Varennikov. – Мoscow, 1995. – 24 P. (In Russian)
- Erofeeva, T.M. Physical culture in the university educational process /T.M. Erofeeva // Fizicheskaya kultura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka.– 1995. – P. 27–35. (In Russian)
- Cooper, K. Aerobics for feeling good / K. Cooper. – Мoscow: Fizkultura i sport, 1989. – 224 P. (In Russian)
- Mandrikov, V.B. Technologies of optimization of health, physical training and education of medical university students: monograph / V.B. Mandrikov. – Volgograd: VSTU, 2001. – 332 P. (In Russian)
- Shemet, O.V. Didactic basics of competence approach in higher vocational training / O.V. Shemet // Pedagogika. – 2009. – № 10. – P. 16–22. (In Russian)
- Shemet, O.V. Three-dimensional organization of the competence-focused educational university process / O.V. Shemet // Pedagogika. 2010. № 6. – P. 40–44. (In Russian)
Author’s contacts: pakhomova@bsu.edu.ru



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE