THE EFFECT OF BREATHING EXERCISES ON THE LEVEL OF FUNCTIONAL AND PHYSICAL PREPAREDNESS OF STUDENTS OF BASIC MEDICAL GROUP
Фотографии:
ˑ:
A.G. Zheleznyakov, associate professor, Ph.D.
Kursk branch of the Russian State Trade and Economic University, Kursk
Key words: volitional liquidation of deep breathing (Buteyko method), control pause (CP), health level.
Introduction. Correction of the modern student way of life for improvement of motor activity is one of the main criteria of health preservation. The task can be solved by the continuous search for the most effective methods and technologies stimulating the interest of the ones who study and improving their health level [10]. According to the initial medical examination of functional and motor (physical) indices of first-year students of the Kursk branch of RSTEU, 55% were referred to the basic medical group; 35% - to special medical group; 5,7% - group with reduced load and 4,3% - temporarily free from exercises. Herewith, only 30% of freshmen cope with the primary standards of the university program for the ‘satisfactory” mark, whereas 25% persons referred to special medical group fail it. Especially hard for most of students are: 2000-m stadium flat race (girls), as well as speed and speed-power exercise standards (70% of students show results below 1). Such a situation requires serious reconsideration of the contents of the curriculum, work of standard evaluation tables regarding the quoted university, selection of health-improving methods and technologies of work with students. We selected K.P. Buteyko’s breathing exercises [4,5] out of all the manifold modern methods health-improving technologies subjected by researchers and practitioners [1,2,4,5,6,8,10,11,13,14] to approve it on the classes of physical education with students of the Kursk branch of RSTEU.
The studies have revealed only a fragmentary reference to the use of exercises by the method of volitional liquidation of deep breathing on the classes of physical education in the special medical group [11] not indicating the dynamics of research results. All other methods [2,6,13,14] good for health lack standard evaluation tables of the human health level.
The purpose of our research was to study, approve and introduce into the practice of student physical education the Buteyko’s health-improving breathing exercises [4,5] and trace the effect of breathing exercises on the level of functional and physical (motor) indices of student youth within an academic year.
Methods and organization of research.
Natural pedagogical experiment [3,7] served the basic research method and included the following methods:
- estimation of the conscious attitude to the subject of “Physical culture” in students examined by the results of the anonymous questionnaire (the authors questionnaire – 20 questions, 60 question answers);
- allocation of anthropometric and functional indices;
- allocation of indices of physical (motor) fitness by the tests of the sample university [12];
- determination of health level indices using the VLDB method by K.P. Buteyko (1962).
All the actual numeral material was processed in according with the applied program of statistical processing.
The study was made since September 2010 till May 2011 based on the Kursk branch of RSUEU. The pedagogical experiment was made with 30 female students of the 1-2 of the faculties of Economics and Commerce and marketing, referred to the basic medical group due to state of health. Since we allocated effectiveness of the breathing exercises and the VLDB method in changing functional and physical (motor) indices at occupations twice a week with first-year students, the effectiveness of the subjected technique was estimated by the average increase in the results of the same students, without forming the control group. 24 female students out of the initially declared 30 have passed completely the experimental work within the research.
The female students’ functional and physical (motor) indices were tested on the first and the last five of the occupations. At the occupations from 6 to 9 we introduced the students to the basics of breathing exercises, showed and approved the VLDB method. Herewith special attention was paid to the ability to listen and feel your breath. Students were introduced to the theory and practice of breathing: symptoms of deep breathing; physical exercises, facilitating the decrease of the breathing depth and the increase of the СО2 level.
The volume of physical exercises has been rising gradually from 4 to 20 times within the academic year and the number of exercises has also been gradually increasing from 6 to 24. Moreover, the occupations contained the discussions of the matters of sleep, nutrition, water schedule and volume of motor activity.
The initial and final results of the functional, motor and monthly dynamics of heart rate and control pause of the female first-year students of the Kursk branch of RSTEU are adduced in the tables 1-2 and patterns 1-2.
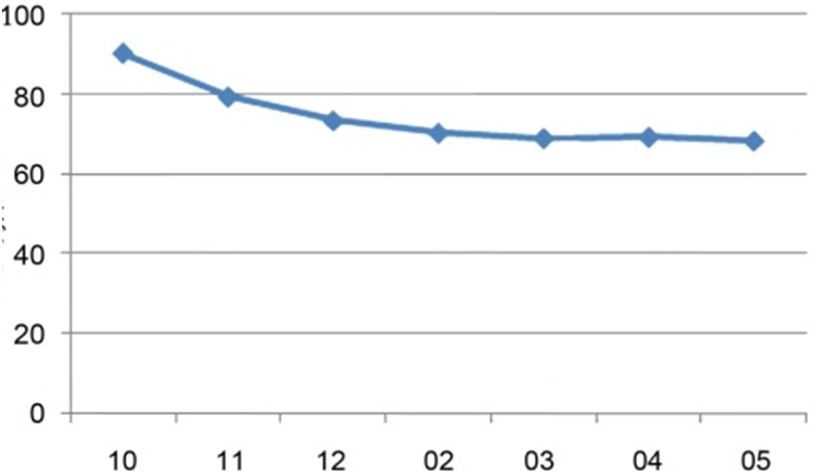
Pattern 1. The mean decrease of the students’ heart rate indices within the research was noticeable (pattern1) and amounted to 16,3% (P<0,001), testifying to the more effective work of the cardiorespiratory system
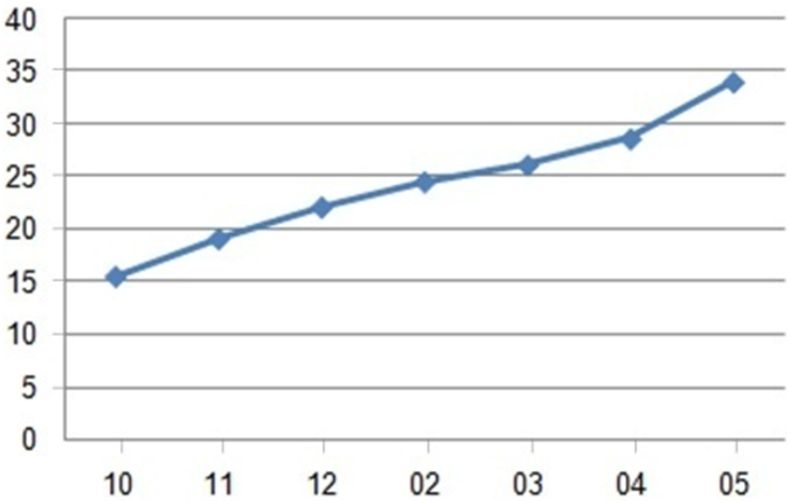
Pattern 2. The control pause (pattern 2) of the female students has increased by 119% on the average (P <0,001) in the course of the academic year
Table 1. Functional indices of female students of basic medical group
|
Indices |
n |
M±m |
M±m |
||||||
|
September 2010 |
May 2011 |
||||||||
|
Body length (sm) |
24 |
161,5±0,80 |
162,8±0,83 |
||||||
|
Body weight (kg) |
24 |
54,9±1,60 |
56,2±1,51 |
||||||
|
VC due (ml³) |
24 |
3175±16,04 |
3244±21,39 |
||||||
|
VC actual (ml³) |
24 |
2458±45,45 |
2633±48,12 |
||||||
|
Shtange’s test (s) |
24 |
26,8±1,44 |
37,7±2,41 |
||||||
|
Genchi’s test (s) |
24 |
17,9±1,39 |
27,6±1,71 |
||||||
|
Heart rate (str/min) |
24 |
88,3±3,90 |
82,4±3,64 |
||||||
|
Hand dynamometry (kg) |
24 |
19,4±0,61 |
22,2±0,51 |
||||||
|
Fat tissue % |
24 |
14,5±0,92 |
20,9±0,83 |
||||||
Table 2. Fitness indices of female students of basic medical group
|
Indices |
n |
M±m |
M±m |
||||
|
September 2010 |
May 2011 |
||||||
|
Sit-up (reps) |
24 |
33,3±1,9 |
47,6±2,2 |
||||
|
100-m run (s) |
24 |
18,0±0,36 |
16,9±0,32 |
||||
|
2000-m run (s) |
24 |
760±19,2 |
638±18,0 |
||||
|
Long jump s/m (sm) |
24 |
145±4,28 |
157±4,28 |
||||
Research results. Proceeding from the questionnaire, most of the students evaluate their health and fitness levels as 4-5 (68% of testees). The rest estimate these indices as 3 (32%). 71% of the testees failed to estimate their level of physical development, whereas 29% considered it as 4. 77% of the testees were proved to perceive consciously and with interest the classes of physical culture by the breathing technology. 20% do not take it as a method of improvement of human health and 3% of the respondents are passive to the occupations of physical education.
The body length and weight indices have changed incidentally by the level of physical development and functional indices (table 1) for the 8 months of trainings – 0,8-2,4%(P >0,05). The authentic changes occurred in the VC indices (due and actual) by 2,2-7,1% (P <0,05). The Shtange’s and Genchi’s test indices increased essentially (40,7 and 54,2% correspondingly; P <0,001), testifying to the considerable improvement of exercise performance of the breathing system by the developed diaphragm, intercostal muscle and pelvic girdle power indices. The mean decrease of the students’ heart rate indices within the research was noticeable (pattern1) and amounted to 16,3% (P<0,001), testifying to the more effective work of the cardiorespiratory system. The level of power indices grew by 24,7% on the average (P<0,001), positively affecting the improvement of the students’ results in power, speed and speed-power exercises. Thus in 100-m speed run (table 2) it has improved by 6,5% (P<0,05). The indices in endurance run (2000 m) have improved by 19,1% (P <0,001) for 8 months of occupations. The average increase of the female students’ speed-power indices authentically was equal to 14% in long jump and by 43% in sit-up. The control pause (pattern 2) of the female students has increased by 119% on the average (P <0,001) in the course of the academic year.
Conclusions:
1. The level of the students functional and motor (physical) preparedness on the initial research stage was proved to correspond to 1-2 by the estimation of the current curriculum on physical culture for students [12], negatively affecting their attitude to the subject.
2. The technique has been worked based on the use of the VLDB method in studies, promoting improvement of functional and motor preparedness of students of the basic medical group. The total volume of physical load for the term of the research (134 hours) amounted to: race walk – 6 hours; graduated slow run – 20 hours; work by the VLDB method – 13 hours; breathing exercises – 24 hours; related flexibility and stretching exercises – 7 hours.
Bibliography
1. Alekseev, A.A. Integrative (system) connective medicine: V.1 – V.4, Moscow: Lenard, 2005. - 2134 P. (In Russian)
2. Amosov, N.M. Contemplation on health. - Moscow: Molodaya gvardiya, 1987.-102 P. (In Russian)
3. Ashmarin, B.A. Theory and methods of physical education.- Moscow: Prosveschenie, 1990.-287 P. (In Russian)
4. Бутейко К.П. The theory of the pathogenesis of diabetes / K.P. Buteyko // Izobretatel’ i ratsyonalizator. -1962. - №5. - P. 7. (In Russian)
5. Buteyko, K.P. Buteyko’s method: experience of introduction into medical practice. Collection / Comp. by K.P. Buteyko.- Odessa: Titul, 1991.- 232 P.
6. Vilunas Yu.G. Sobbing breath cures in a month. – St.-Petersburg: Piter, 2009.- 224 P. (In Russian)
7. Zheleznyak, Yu. D., Petrov, P.K. The basis of scientific and methodological work in physical culture and sport: study guide for university students. - Moscow: Academia, 2002. - 264 P. (In Russian)
8. Zakonschikov, K. F. Adaptation. Hypoxia. Health // Moscow: 1996.- 121 P. (In Russian)
9. Lubysheva, L.I. Scientific-practical congress "National health and mass sport." / L.I. Lubysheva // Teoriya i praktika of fizicheskoy kultury.- 2008.- № 3.- P. 79-80. (In Russian)
10. Small Medical Encyclopedia: in 6 volumes. Academy of Medical Sciences the USSR. Ed.-in-ch. V.I. Pokrovsky.- Moscow: V.2, 1991.- P. 223-225. (In Russian)
11. Obolochkov, S.G. Methods software of classes with junior female students of teacher’s college from special medical group / S.G. Oblolochkov // Fizicheskoe vospitanie studentov. - 2010. - №2. - P. 48-50. (In Russian)
12. Sample program for universities of physical culture. Ministry of Education RF, 2000. (In Russian)
13. Shatalova, G.S. Choosing the way. - Moscow: Litur, 2002. - 240 P. (In Russian)
14. Schetinin, M.N. A.N. Strelnikova’s breathing exercises. - Moscow: Metafora, 2008.- 368 P. (In Russian)
Author’s contacts: ac-1945@mail.ru



 Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE
Журнал "THEORY AND PRACTICE