Dynamics of functional status of classical university students of military training faculty driven by sportizated physical education
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Dr.Hab., Associate Professor, Head of the Physical Education and Health Department E.A. Cherepov1
Trainer-instructor of the Physical Education and Health Department R.G. Shaikhetdinov1
Postgraduate student of the Theory and Methods of Physical Culture and Sports Department A.S. Khafizova1
1South Ural State University (National Research University), Chelyabinsk
Keywords: sportizated physical education, classical university students, applied professional physical training, applied military and sporting competences, Military Training Faculty (MTF), functional status of students.
Introduction. The third-generation Federal State Educational Standards of Higher Vocational Education, as well as the Ministry of Defenсe of the Russian Federation - the main requestor of reserve officer training, - specify requirements to the level of formation of professional competences of a military specialist, which among other things include the ability to keep physically fit [4]. In our publications we have substantiated and presented in a structured fashion a complex of applied military and sporting competences, the possession of which is the result of physical education of students acquiring extended education at the military training faculty. We have loosely organized these competences into the following blocks: cognitive, functional-adaptive, athletic and personality-mental [5]. In turn, and it is also practically assured, a high competency of a military specialist is largely determined by his physical fitness and physical working capacity, which are determined by the activity and dynamics of the body's functional reserves, psychophysiological qualities and ability to mobilize the body reserves when needed.
In the field of muscular activity physiology, it is well recognized that physical training has a general stimulating effect on the functional status of the internal organs and, above all, the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. At the same time, according to the researchers, the traditional system of university physical education cannot provide a training effect, and as a result, the set-up of adaptation mechanisms in the student body. The idea of converting the sports training technology in the interests of physical education proposed by Professor V.K. Bal’sevich and substantiated in numerous publications by the scientist and his followers [1, 3], otherwise speaking, in favor of active implementation of sports activities, competitions and other elements of sports during the educational process, which aims to form the students’ sports culture, is meant to solve the problem of increasing the effectiveness of university physical education and, in particular, physical education at the military training faculty. Such a transition from the traditional conditioning classes to the classes in chosen sports is also significant when mastering professionally applied nature of the future profession. As we see it from the works of V.K. Bal’sevich and L.I. Lubysheva, the innovation and ideological basis of sportizated physical education consists in designing conditions that would exclude the possibility of undifferentiated mastering by students of physical culture values, and would simultaneously show the immediate prospects of their qualitative and quantitative physical improvement, according to personal motives, personal characteristics and level of aspiration of an individual student [13].
Objective of the study was to analyze the dynamics of the functional status of students during their studies at the military training faculty of the classical university, taking into account the use of sportizated physical training forms and conditions.
Methods and structure of the study. The study was carried out at the premises of the Military Training Faculty and Physical Education and Health Department of South Ural State University (National Research University). The experimental group was made of the 2nd-4th-year students enrolled in the military registration specialty 420200 "Operation and maintenance of basic machinery of armored vehicles", a total of 60 people (n=60). The reference group consisted of cadets of the branch of Military Educational and Scientific Center of Air Force "Air Force Academy" in Chelyabinsk, a total of 60 people (n=60). The subjects of the experimental group got a medical and psychological screening before entering the military training faculty. The subjects of the reference group, being the military university cadets, underwent an annual medical examination.
The study lasted from February, 2014, through July, 2016 (which corresponded to the military training course duration).
The functional status of the subjects of both groups was assessed using the conventional methods: Harvard step test, Stange’s and Genche’s tests, measurement of HR at rest. Additionally, the ergospirometric testing was conducted in the experimental group: the subjects performed pedaling exercises on a bicycle ergometer at the pedaling speed of 60-65 rpm; the exercise intensity constantly increased by 25 W per minute (Bruse protocol) until the students’ heart rate reached 170 bpm (PWC170 test) [5].
During the data processing we singled out the key parameters characterizing the cardiorespiratory system performance and functionality: HR at rest, PWC170 test, VO2max/kg (maximal oxygen consumption, ml/min/kg), VEmax (maximal ventilatory equivalent, l/min).
The results were evaluated using the SCHILLER CARDIOVIT AT-104 PC Ergo-Spiro device. The stationary ergospirometric workstation – SCHILLER, (Switzerland) – is a functional diagnostic method that analyzes breathing gases in the inspiratory and expiratory phases, which reveals respiratory, cardiac, circulatory and metabolic systems interaction. Ergospirometry provides an objective non-invasive measurement of the functional capacity of the cardiovascular system, as well as an accurate determination of the individual aerobic/anaerobic threshold. Mathematical and statistical data processing was performed using the computerized programs. The significance of differences was at the level of 95% (p<0.05) and was determined by Student’s t-test.
During the experiment to form applied military and sporting competences, we designed, developed and introduced into practice a system of applied military physical training for students of civilian higher education institutions, the model of which is presented in Figure 1.
As related to the system functioning, it appears relevant to us to detail its technological component, each element of which, as a university subdivision, is characterized by the corresponding sportizating feature, which is, on the one hand, component-specific but, on the other, supplements the functions of the rest of the system elements and enhances their common developmental effect.
Physical Education and Sports Club provides qualified coaching in various kinds of sport of applied military orientation, creates conditions for staffing sports teams, thereby strengthening the inter-faculty communications and promoting a sporty (healthy) way of life, including sports of applied military orientation in the Spartakiad of SUSU.
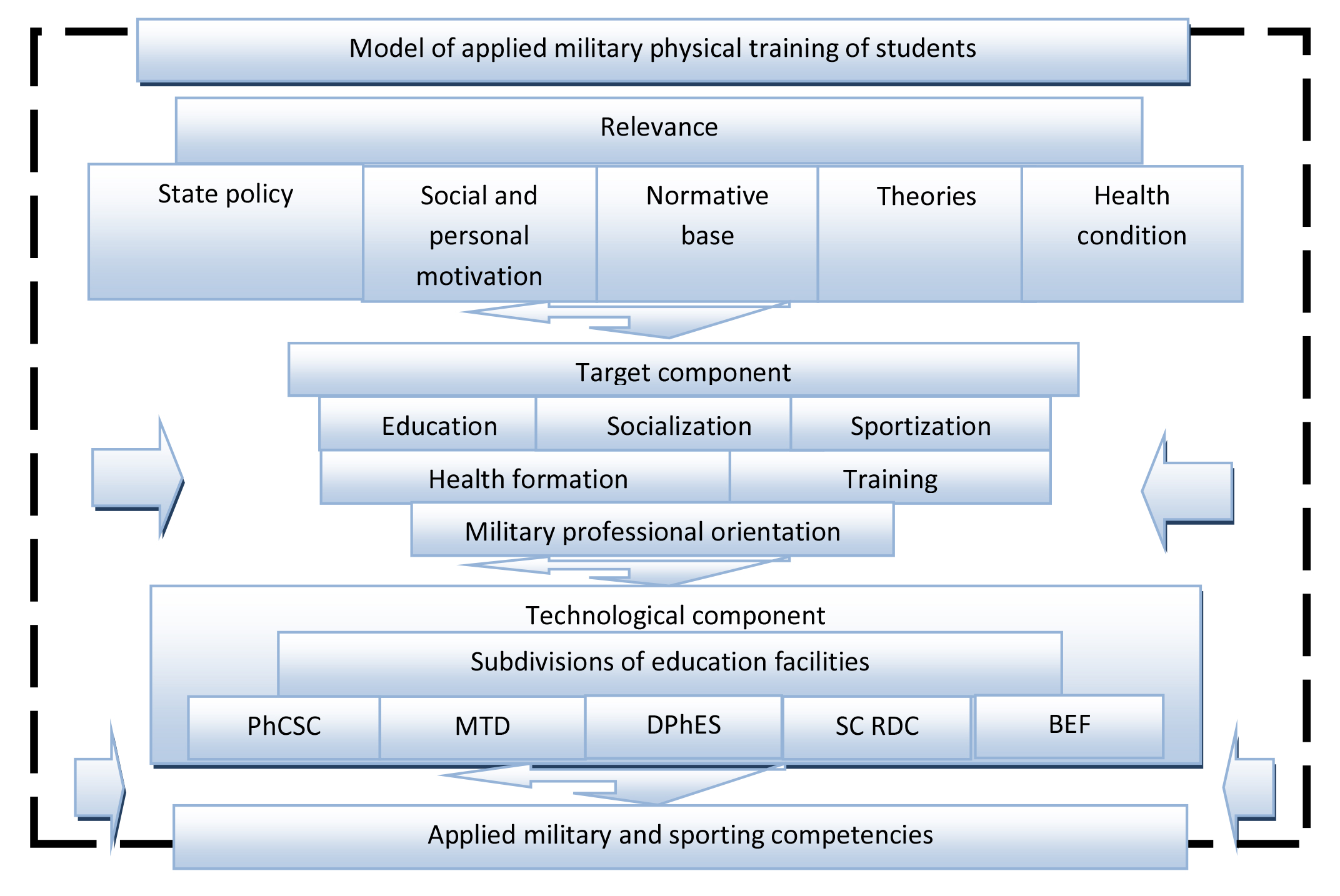
Figure 1. Model of applied military physical training of students
Military Training Faculty enables to acquire a second profession, supplies with training workshops, training grounds and laboratories that contribute to the professional military competences building; stimulates training via supplementary military honorary, requires from students performance and practicing of exercises, techniques and qualifying standards defined by the statutes, manuals and guidelines, fulfillment of other combat training tasks and acquisition of experience in performing professional duties.
The Physical Education and Health Department provides qualified professorial-teaching staff, supplies with the sports grounds and halls to conduct core educational program classes, offers the studies for the qualification of a physical education and health-improving technologies instructor in the health and fitness technologies center, thus facilitating the formation of general cultural and professional competences that would ensure practical application of knowledge during the training process.
Basic education faculties conduct Olympiads on the subjects related to applied military competences, ensure educational program introspection, hold up the faculty traditions, encourage students’ sports achievements.
Research and Development Center enables the students to participate in scientific researches, provides a detailed monitoring of their physical working capacity and functional status.
Results and discussion. At the beginning of the experiment, we detected a statistically significant difference between all the studied indicators of the functional status of the university students and cadets (Table 1). We assume this is due to the greater efficiency of their learning and employment activities, including physical training of cadets of military higher education institutions. In addition, cadets of military universities are, as a rule, characterized by sustained motivation to military activities, train to hit the physical fitness qualifying standards to be admitted to military higher education institutions, as well as systematically exercise to form applied military skills throughout the first year of studies.
Table 1. Functional status indicators in students
|
|
|
At the beginning of the experiment |
|
At the end of the experiment |
|
||
|
Indicators |
Units of measurement |
Value (х+m) |
p |
Value (х+m) |
p |
||
|
RG |
EG |
RG |
EG |
||||
|
Harvard step test |
Points |
93.21±1.79 |
88.79±1.77 |
<0.05 |
96.37±1.83 |
95.22±1.82 |
>0.05 |
|
Stange’s test |
Sec |
60.32±1.39 |
56.65±1.38 |
<0.05 |
62.77±1.45 |
62.13±1.43 |
>0.05 |
|
Genche’s test |
Sec |
34.24±1.25 |
31.09±1.27 |
<0.05 |
39.07±1.26 |
38.19±1.31 |
>0.05 |
|
HR at rest |
Bpm |
72.63±1.39 |
75.21±1.41 |
>0.05 |
68.38±1.41 |
69.62±1.46 |
>0.05 |
At the end of the experiment, the EG subjects graded up to their RG peers in terms of the functional status indicators (p>0.05). During the experiment, the following dynamics of the functional status of the young men was recorded: Harvard step test RG - 3.33%, EG - 8.16%; Stange’s test - RG - 3.34%, EG - 11.01%; Genche’s test RG - 13.18% and EG - 20.5%. Accordingly, the increase in the functional status indicators in the experimental group was more pronounced.
Alongside the improvement of the physical working capacity, a negative chronotropic effect was observed in the experimental group, which was manifested in a decrease of HR rate at rest by 10.48%. Apparently, this change was due to the growth of the respiratory system reserves, improvement of both ventilation and oxygenation, so the body reduced the "stress level" of the cardiovascular system.
Table 2. Functional status indicators in subjects of experimental group (EG) according to ergospirometry
|
Indicators |
Units of measurement |
At the beginning of the experiment Value (х+m) |
At the end of the experiment Value (х+m) |
p |
|
PWC170 |
Watt |
176.56±6.95 |
198.37±7.12 |
<0.05 |
|
VO2max/kg |
ml/min/kg |
32.51±1.32 |
39.35±1.32 |
<0.05 |
|
VЕmax |
l/min |
56.37±4.75 |
69.15±4.45 |
<0.05 |
The ergospirometry test results also indicate that implementation of the sportization driven system of applied military physical training of students had a significant influence on the key parameters of their cardiorespiratory system and, consequently, physical working capacity (Table 2). In particular, according to the PWC170 test, the subjects of the experimental group had a considerable (11.63%) dynamics in adaptation to physical loads. Probably, the key factor determining this change was not the enhancement of strength endurance of the lower limb muscles, but a set of physiological changes in the external respiration function (an increase in the maximal ventilatory equivalent under exercise (VEmax) by 19.04% and tissue respiration - an increase in the maximal oxygen consumption by 20.36%).
Conclusion. The study findings suggest for the conclusion that the sportization of physical education of the military training faculty students in a classical university promotes positive dynamics of the functional status of their cardio-respiratory system. Adaptation of the body to exercise, as well as formation of positive personality traits and temperamental attributes during sports training, will enable students to develop the required level of applied military and sporting competences and comply fully with the professional requirements imposed on military officers of the Russian Federation.
References
- Bal'sevich V.K., Natalov G.G., Chernyshenko Y.K. Konversiya osnovnykh polozheniy teorii sportivnoy podgotovki v protsesse fizicheskogo vospitaniya [Conversion of main provisions of sports training theory in physical education process]. Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury, 1997, no. 6, pp. 15-25.
- Isaev A.P., Rybakov V.V., Erlikh V.V., Potapov V.N., Polozkova N.F., Ivanov E.B. Strategiya formirovaniya adaptatsionnoy reaktsii u sportsmenov [Athletes' adaptation reaction formation strategy]. Osnovy adaptatsii i zakonomernosti ee formirovaniya v sporte vysshikh dostizheniy [Fundamentals of adaptation and patterns of its formation in elite sport]. Vestnik YuUrGU seriya «Obrazovanie, zdravoohranenie, fizicheskaya kultura», 2014, vol. 12, no. 21, pp. 46-56.
- Lubysheva L.I. Konversiya vysokikh sportivnykh tekhnologiy kak metodologicheskiy printsip sportizirovannogo fizicheskogo vospitaniya i "sporta dlya vsekh" [Conversion of sports high-technology as methodological principle of sportizated physical education and "sport for all"]. Fizicheskaya kultura: vospitanie, obrazovanie, trenirovka, 2015, no. 4, pp. 6-8.
- Shaykhetdinov R.G., Gromov V.A. Dostizhenie vypusknikom universiteta psikhofizicheskoy gotovnosti k professionalnoy deyatelnosti [University graduate's psychophysical vocational fitness: methods of achievement]. Teoriya i praktika fizicheskoy kultury, 2016, no. 3, pp. 26-28.
- Cherepov E., Shaikhetdinov R., Khafizova A. Applied military and sporting competence of students оf military training faculty in classic university. INTED2017 Proc. 11th International Technology, Education and Development Conference. Valencia, Spain. March 6th-8th, 2017, pp. 0927-0933. ISBN: 978-84-617-8491-2. ISSN: 2340-1079.
Corresponding author: cherepov.e@mail.ru
Abstract. The article presents the author's model of the experimental physical education system for students acquiring extended education at the military training faculty of South Ural State University (National Research University). This innovation educational system is based on the idea of using the sportizated physical training forms and conditions meant to improve the applied military and sporting competences of students. The obtained data on the statistically significant positive changes in the cardiorespiratory system of students (Harvard step test, Stange’s test, Genche’s test, HR at rest, PWC170 test, VO2max / kg (maximal oxygen consumption) and VEmax (maximal ventilatory equivalent, l/min), testifying to the formation of the long-term adaptation mechanisms and concentration of a cumulative training effect, prove the effectiveness of the sportizated physical education model in training of the contingent under study.



