Pre-conscription-age men's physical education model efficiency in context of Russian physical culture and sports "Ready for Labour and Defence" (GTO) complex tests
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Postgraduate A.A. Rayzikh1
Dr.Hab., Professor, RANS Academician P.K. Petrov1
1Udmurt State University, Izhevsk
Keywords: pre-conscription-age men, test standards, Russian Physical Culture and Sports GTO Complex.
Background. The ongoing Russian education system reformation concept sets new requirements to the physical education system applied at the national general education establishments. Presently physical education and sport (PES) specialists give increasingly high priority to the innovation methods applicable to the school Physical Education discipline. The educational potential of physical education, particularly in terms of the young people’s physical education, has always been high. Therefore, the education process should be designed and managed in a most efficient format to encourage the young people’s psychological, social and cultural development by creating, among other things, due conditions to facilitate the habitual healthy needs for physical practices being formed to advance their physical fitness standards.
Objective of the study was to rate the pre-conscription-age men’s physicality and theoretical background in the context of the Russian Physical Culture and Sports “Ready for Labour and Defence” (GTO) Complex tests.
Methods and structure of the study. The study was performed at the general education schools of Izhevsk city. Subject to the study were 60 pre-conscription-age men (aged 16-17 years that is the GTO Class V qualification age) split up into Study Group (n=31) and Reference Group (n=29). The subjects’ physical fitness and theoretical knowledge in the Physical Education discipline were tested prior to and after the model-testing educational experiment. The physical fitness was rated by four obligatory and two optional tests compatible with the GTO Class V tests.
The subjects’ theoretical knowledge in Physical Education was tested using a special application software for the 1-11-graders of the general education establishments designed to offer a few optional responses to every knowledge-testing question, the software being easily applicable at personal computers or at information science lessons within the relevant client-server design [1, 2].
The Study Group has been trained for an academic year as required by the logics and content of the physical education model of our own design that includes the following four components: goal-setting; substantive; process management and resultant components [3], the model being intended to improve the physical fitness by sets of multi-purpose physical exercises and knowledge in the school Physical Education discipline to make the subjects fit for the Russian Physical Culture and Sports GTO Class V tests. The Reference Group was trained as required by the standard physical education program for the 10-11-graders designed in compliance with the relevant Federal State General Secondary (Full-time) Education Standard (FSGSES) [4].
Study results and discussion. Given in Table 1 hereunder are the physical fitness test data for the 16-17-years-old subjects of the Study Group versus Reference group, the tests performed prior to and after the educational experiment.
Table 1. Physical fitness test rates for the 16-17-years-old (pre-conscription-age) subjects, at the start and the end of the experiment, for the Study Group (SG) versus Reference Group (RG)
|
Test |
Stage |
Group |
n |
|
t |
p |
|
|
actual |
crit. |
||||||
|
Obligatory tests |
|||||||
|
100 m sprint, s |
Start |
RG |
29 |
14,2±0,15 |
0,58 |
2,01 |
>0,05 |
|
SG |
31 |
14,3±0,14 |
|||||
|
End |
RG |
29 |
14,1±0,15 |
2.3 |
2,01 |
<0,05 |
|
|
SG |
31 |
13,7±0,11 |
|||||
|
3 km race, min
|
Start |
RG |
29 |
14,04±0,23 |
0,22 |
2,01 |
>0,05 |
|
SG |
31 |
14,10±0,14 |
|||||
|
End |
RG |
29 |
13,20±0,21 |
2,5 |
2,01 |
<0,05 |
|
|
SG |
31 |
12,58±0,14 |
|||||
|
Pull-ups on horizontal bar, times
|
Start |
RG |
29 |
8,2±0,88 |
0,4 |
2,01 |
>0,05 |
|
SG |
31 |
7,8±0,65 |
|||||
|
End |
RG |
29 |
9,1±0,94 |
2,3 |
2,01 |
<0,05 |
|
|
SG |
31 |
11,9±0,78 |
|||||
|
Standing bends forward, cm |
Start |
RG |
29 |
10,9±1,88 |
0,30 |
2,01 |
>0,05 |
|
SG |
31 |
11,3±1,58 |
|||||
|
End |
RG |
29 |
11,8±1,26 |
2,1 |
2,01 |
<0,05 |
|
|
SG |
31 |
14,4±1,36 |
|||||
|
Optional tests |
|||||||
|
Standing long jump, cm
|
Start |
RG |
29 |
224,5±2,46 |
1,5 |
2,01 |
>0,05 |
|
SG |
31 |
219,2±2,56 |
|||||
|
End |
RG |
29 |
228,3±2,01 |
2,6 |
2,01 |
<0,05 |
|
|
SG |
31 |
235,5±1,89 |
|||||
|
Crunches, reps per min |
Start |
RG |
29 |
49,1±1,40 |
0.82 |
2,01 |
>0,05 |
|
SG |
31 |
47,7±1,09 |
|||||
|
End |
RG |
29 |
55,9±1,30 |
2.8 |
2,01 |
<0,05 |
|
|
SG |
31 |
60,8±1,27 |
|||||
The prior tests showed the Study and Reference Group subjects being virtually the same in the physical fitness standards and theoretical background. The study found many of the pre-conscription-age young men being fit for the age-specific GTO tests to qualify for the GTO gold, silver or bronze badges, albeit a significant part of the subjects failed the tests, particularly the strength tests (pull-ups on horizontal bar). The model-testing educational experiment was designed to give a top priority to the deficient physical qualities and abilities identified prior to the experiment.
By the end of the educational experiment, the Reference Group showed an insignificant growth of the test rates (t=0.4 at p>0.05) versus the Study Group test rates that showed significant growth in every test (p<0.05) that was interpreted as indicative of the pre-conscription-age men’s physical training model being efficient in its design and content. Given on Figure 2 hereunder is the variation of the knowledge rating test data in the school Physical Education discipline.
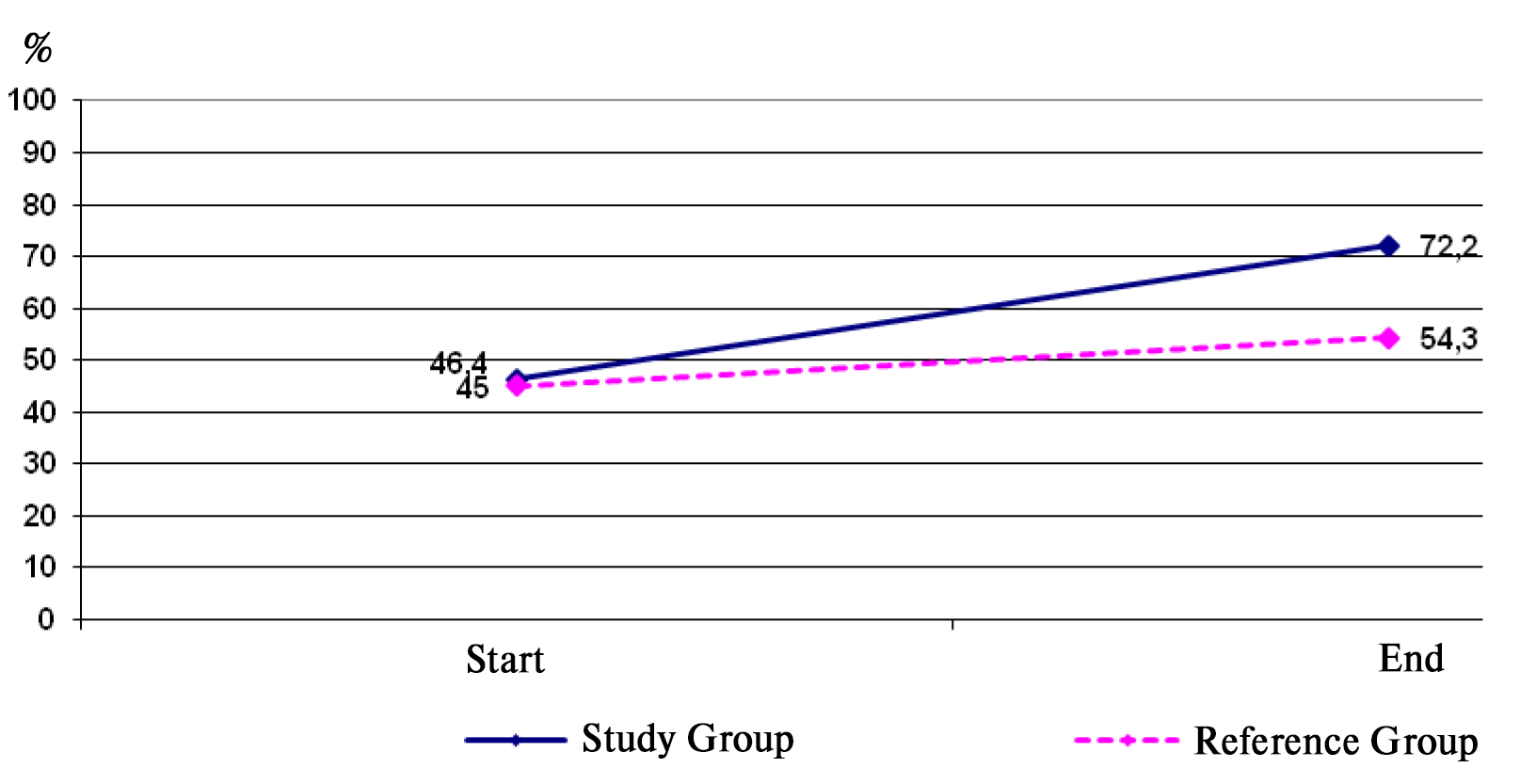
Figure 1. Variation of the knowledge rating test data for the school Physical Education discipline prior to and after the educational experiment
Prior tests showed the Study and Reference Group subjects being virtually the same in the physical fitness and theoretical background. The Study Group has been trained for a school year as required by the physical education model of our own design including the relevant information and communication technologies [3] geared to build up the trainees’ physical education knowledge. The education material was designed as provided by the Federal State Education Standard for the school Physical Education discipline and the knowledge test standards under the Russian Physical Culture and Sports “Ready for Labour and Defence” (GTO) Complex [as provided by regulatory document] #540 of 11.06.2014. The successful GTO test rates after the educational experiment accounted for 54.3% in the Reference Group versus 72.2% in the Study Group.
Conclusion. The test data obtained after the model-testing educational experiment showed significant growth of the Study Group test rates in every practical tests (р<0.05) and notable improvement of the theoretical knowledge rates in Physical Education. The Reference Group showed some – albeit insignificant – growth (р>0.05) of some test rates. The comparative analysis of the pre-conscription-age men’s physical fitness and knowledge rating test data in the school Physical Education discipline for the Study Group versus Reference Group demonstrated the physical training model that we developed being efficient in its design and content as verified by the model-testing educational experiment within the frame of the Russian Physical Culture and Sports “Ready for Labour and Defence” (GTO) Complex implementation process.
References
- Novokreshchenov V.V., Petrov P.K., Akhmedzyanov E.R. Programmnoe obespechenie dlya kontrolya znaniy i vozmozhnosti ego ispolzovaniya dlya proverki znaniy i umeniy v komplekse GTO [Academic performance rating software and its use for knowledge and skills checks within GTO complex]. Vestnik IzhGTU, 2015, no. 4, pp. 112-115.
- Petrov P.K., Rayzikh A.A., Akhmedzyanov E.R. Analiz fizicheskoy i teoreticheskoy podgotovlennosti doprizyvnoy molodezhi 16-17 let na sootvetstvie normativnym trebovaniyam Vserossiyskogo fizkulturnogo kompleksa «Gotov k trudu i oborone» [Analysis of physical and theoretical competency of pre-conscription youth aged 16-17 years by the standards of Russian physical culture and sports complex "Ready for Labor and Defence"]. Sovremennye problemy nauki i obrazovaniya, 2015, no. 4. Available at: www.science-education.ru/127-21246 (Accessed: 23.08.2016).
- Petrov P.K., Rayzikh A.A. Modelirovanie fizicheskogo vospitaniya yunoshey doprizyvnogo vozrasta v usloviyakh vnedreniya Vserossiyskogo fizkulturno-sportivnogo kompleksa «GTO» [Modelling of physical education of pre-conscription males in context of introduction of Russian physical culture and sports GTO complex]. Vestnik Udmurtskogo universiteta, Seriya «Filosofiya. Psikhologiya. Pedagogika", 2016, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 119-123.
- Federalny gosudarstvenny obrazovatelny standart srednego (polnogo) obshchego obrazovaniya [Federal state educational standard of secondary (complete) general education]. Available at: http://fgosreestr.ru/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Primernaya-osnovnaya-obr... (Accessed: 25.08.2016)
Corresponding author: rayzikh@gmail.com
Abstract
Objective of the study was to rate the physicality and theoretical background of the pre-conscription-age men in the context of the Russian Physical Culture and Sports “Ready for Labour and Defence” (GTO) Complex tests. Subject to the study were 60 men aged 16-17 years split up into Study Group (n=31) and Reference Group (n=29). The subjects’ physical fitness was tested by the six standard Russian Physical Culture and Sports “Ready for Labour and Defence” (GTO) Complex Class V tests. The subjects’ theoretical background in the physical education domain was tested using special application software for the 1-11-graders of general education establishments. Prior tests showed the Study and Reference Group subjects being virtually the same in the physical fitness and theoretical background. By the end of the model-testing educational experiment the Reference Group showed an insignificant growth of test rates (p>0.05) versus the Study Group test rates that showed significant growth in every test (p<0.05) that was interpreted as indicative of the pre-conscription-age men’s physical training model being efficient in its design and content.



