Electronic education guiding system application in academic "Sport Metrology" discipline under MOODES system
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Associate Professor, PhD O.B. Dmitriev1
Udmurt State University, Izhevsk
Keywords: e-learning, Electronic Education Guiding System (EEGS), MOODES (Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Education System), sport metrology, bachelor education.
Background/ It was in the early 1990ies that the education system computerization concept was formulated, and by the end of 1990ies the e-learning vector was shaped up and theoretically developed and the first e-learning system was implemented. One of such systems is the MOODES (Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Education System) designed by a team of educators and programmers. The ongoing computerization of the education system and the new “reality created by modern innovations” in the latter call for the new e-learning tools and the relevant components being actively implemented in every domain of the education process [3].
As things now stand in the national physical culture and sports sector, however, practical applications of e-learning technologies are presently very limited if any. Therefore, initiatives to develop high-quality e-learning resources (ELR) including discipline-specific Electronic Education Guiding Systems (EEGS) are ranked among the top priorities by the sector community.
As provided by the State Standard GOST Р 55751-2013 [2] “Electronic Education Guiding System (EEGS)”, the EEGS means the structured integrity of electronic education regulating documents, electronic learning resources, education process and progress control tools having interrelated content and designed for combined application to ensure the education subjects, disciplines, courses and their components being learnt in the most efficient format. The EEGS may be designed to facilitate learning in specific education disciplines, education modules and sets of disciplines and for success of the combined education curricula on the whole.
Objective of the study was to design and test an Electronic Education Guiding System (EEGS) for the academic Sport Metrology discipline based on the virtual education toolkit called MOODES (Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Education System).
Methods and structure of the study. The newly designed Electronic Education Guiding System for the academic Sport Metrology discipline includes the following components:
- Electronic textbook “Sport metrology: materials for lectures”, see Figure 1;
- Electronic “Sport metrology manual”, see Figure 2; and
- Differentiated Qualification Test.
As argued by L.B. Aksenov [1], the clipped thinking increasingly typical for modern young people is gradually suppressing and replacing the natural logical thinking that provides a basis for the traditional education models and may be critical for the education process efficiency. The education contents of the new EEGS are offered in a few education modules. The modules were designed and filled with didactic materials selected with due consideration for the clipped thinking and perception typical for the modern students and to ensure their logical thinking skills being activated and developed. To ensure the students’ attention being kept up in the work with the modules/ paragraphs, we structured the content in portions taking 2-3 screens.
Given in Figure 1 hereunder is the front page and frame structure of the electronic textbook “Sport metrology: materials for lectures”. The education material in the textbook is somewhat clipped (to a reasonable degree) though otherwise mostly structured as a traditional textbook. The textbook content was put together based on the valid Sport Metrology curriculum and presented in paragraphs.

Figure 1. Front page and frame structure of the electronic textbook
Given in Figure 2 is the front page and frame structure of the electronic “Sport metrology manual” with the following key components:
1. General unspecific introductory component presenting the front page of the course, news forum and contacts of the correspondent e-learning course administrator from Udmurt State University (USU), abstract and Differentiated Qualification Test for the student’s progress rating.

Figure 2. Front page and frame structure of the electronic “Sport metrology manual”
Theme 2: Laboratory work 1: Variation ranges of metering data
1.1. One-dimensional range of direct metering data
1.2 Integrated range of metering data
1.3. Integrated range design algorithm
2. Introduction to the academic Sport Metrology discipline. The section outlines the subject, goals and stages of a statistical study.
3. Thematic modules: for example “Laboratory work 1: Variation ranges of metering data”. Every module includes paragraphs that brief the reader on the topic with examples and tasks.
To test the students’ progress by the study tasks, we offered a hierarchical bank of questions [3] that may be classified as follows:
Class 1: questions that offer multiple optional responses;
Class 1: matching requiring questions;
Class 3: digital response requiring questions, i.e. the student must solve a task and give the digital result.
The Class 1 and Class 2 questions are designed for the theoretical knowledge test, and Class 3 questions – for the practical skills test.
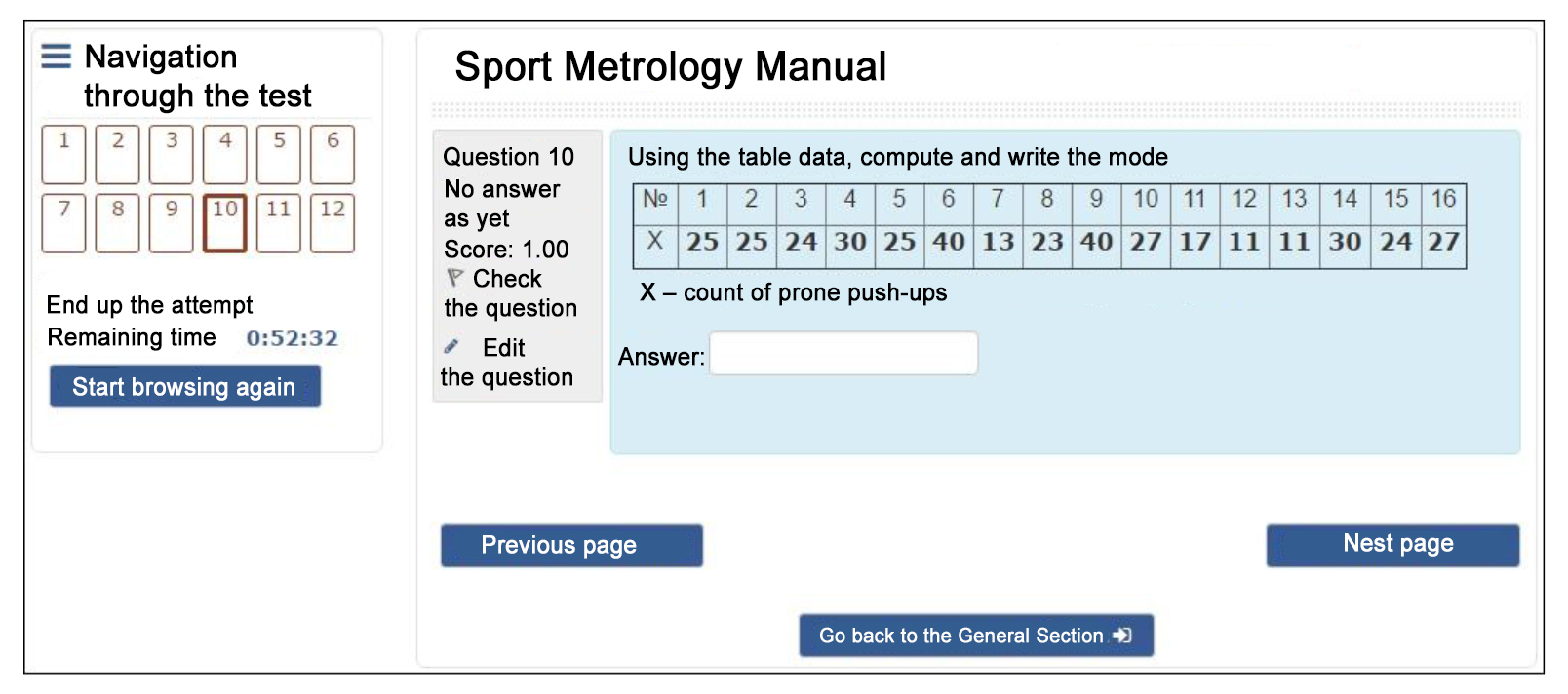
Figure 3. Window of the Differentiated Qualification Test
The Differentiated Qualification Test (Figure 3) includes 12 questions including six Class 1, three Class 2 and three Class 3 questions. Questions in every class are selected randomly and, therefore, the test is newly generated for every test session. The 100-point scale is used to rate the test success (as the most convenient for the student’s knowledge rating and ranking), the test rates being convertible to the traditional 5-point school system convenient for the teachers and students; and then – to the qualified/ failed status (i.e. the final result scoring).
The EEGS was tested on the third-year full-time and correspondent course students of the Physical Culture and Sports Institute (PCSI) of Udmurt State University. For every laboratory session, each student was given the e-learning material on the subject from the Electronic “Sport metrology manual”. In their preparations for the Differentiated Qualification Test, the students additionally could use the electronic textbook. Upon completion of the course in the discipline, the students were tested by the final e-tests. As of the study completion date, 290 tests were performed.
Study results and discussion. The test results were rated satisfactory in 232 (80%) of the cases and unsatisfactory (failed) in 58 (20%) of the cases, with 84% of unsatisfactory test rates scored by the correspondent course students. Given in Figure 4 is a part of the final table of the students’ progress test rates. The upper window 1 “Isolated groups” gives the group list of the successful (qualified) students, and window 3 gives the personal test data and scores of every student.
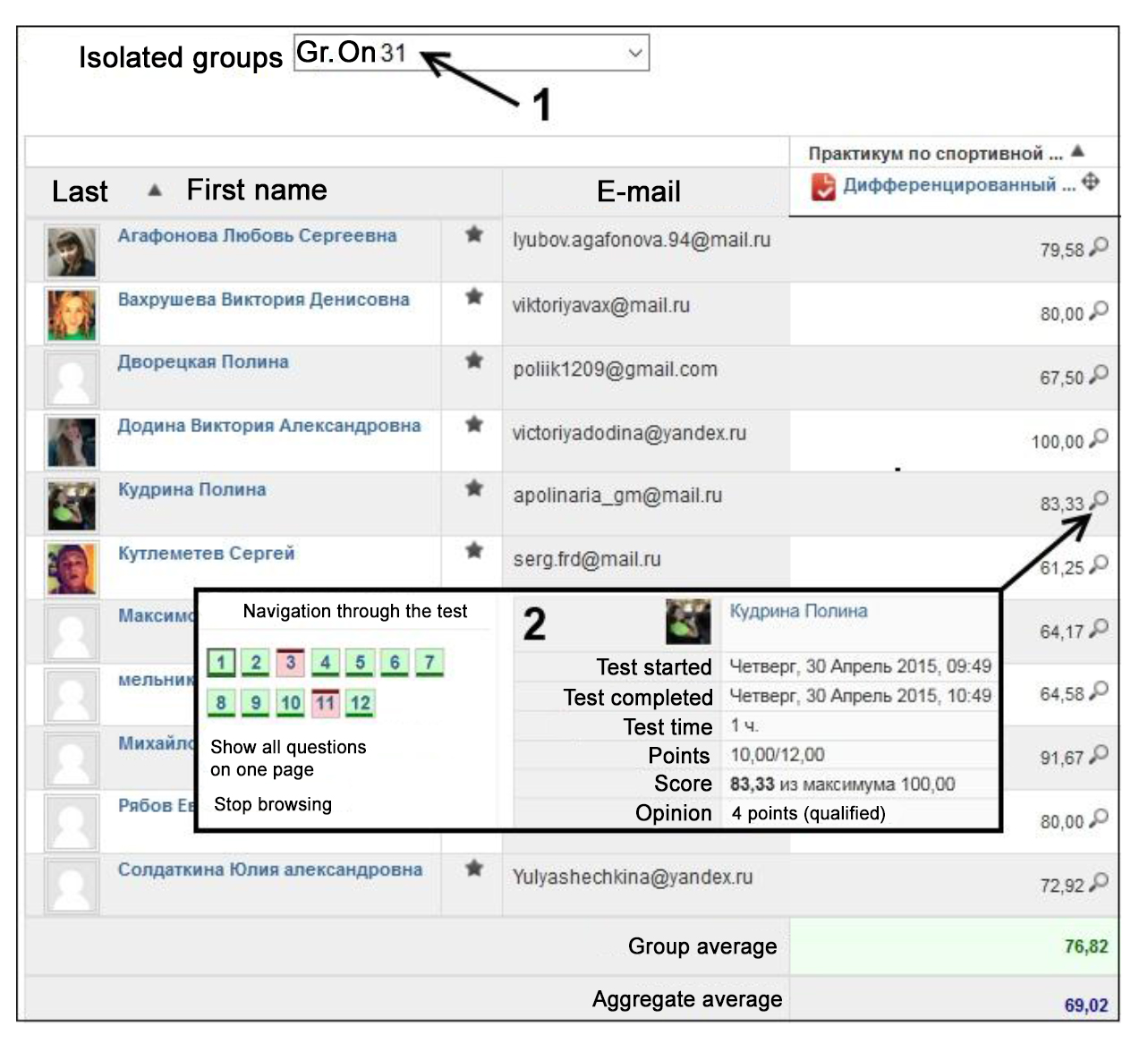
Figure 4. Final “Test report” table
Furthermore, we analyzed the full-time students’ test data for validity (information quality). The Spearman rank correlation coefficient for the sample was estimated at 0.74 that is indicative of a strong correlation and high validity of the test data. Therefore, the education process test was found to be an efficient and convenient tool for the students’ competency and knowledge level rating in the academic Sport Metrology discipline; and it is also beneficial that the test secured a comfortable psychological environment during the qualifications and examinations.
Conclusion. The project to implement and test the EEGS in the educational process of the full-time and correspondence course students of the Physical Culture and Sports Institute (PCSI) of Udmurt State University was found highly beneficial.
References
- Aksenov L.B. Klipovoe myshlenie – genialnost ili dementsiya [Mosaic thinking - genius or dementia]. Mat. 4y mezhdunar. nauch.-prakt. konf "Sovremennoe mashinostroenie. Nauka i obrazovanie" [Proc. 4th Int. res.-practical conf. "Modern engineering. Science and Education"]. St. Petersburg: Pub. h. of Polytechn. un-ty, 2014. P. 3–9.
- GOST R 55751-2013. Informatsionno-kommunikatsionnye tekhnologii v obrazovanii. Elektronnye uchebno-metodicheskie kompleksy. Trebovaniya i kharakteristiki. Razrabotka GOST R [GOST R 55751-2013. Information and communication technologies in education. Electronic educational-methodical complexes. Requirements and specifications. GOST R Development]. Available at: http://www.rags.ru/gosts/gost/56132/. (Accessed: 26.09.2016).
- Dmitriev O.B. Elektronny uchebny kurs «Praktikum po sportivnoy metrologii» kak informatsionnaya predmetno-orientirovannaya sistema [E-learning course "Practical work on sports metrology" as an information object-oriented system]. Sbornik mat. vseros. nauch.-prakt. konf. «Informatsionno-telekommunikatsionnye sistemy i tekhnologii» [Proc. res.-practical conf. "Information and Telecommunication Systems and Technologies"]. T.F. Gorbachev Kuzbass state techn. un-ty. Kemerovo, 2015, 3 p. Available at: http://sibscience.ru/page/ITSIT-2015/ITSIT/files/Vyhodnye-dannye.html. – Published Online: 26.10.2015
Corresponding author: obdmit@mail.ru
Abstract
Objective of the study was to design and test an Electronic Education Guiding System (EEGS) in the academic Sport Metrology discipline based on the virtual education system called MOODES (Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Education System). A research project to design the electronic education system for Bachelors of Physical Culture and Sports training was designed and implemented. The virtual education environment created by the MOODES was used to design every element of the EEGS followed by the EEGS tests on the third-year full- and part-time students of the Physical Culture and Sports Institute (PCSI) of Udmurt State University. At every practical lab session, the students were offered the relevant electronic education materials on the study topic from the Sport Metrology Tutorial. The students could also use the relevant electronic textbook for preparations to specific exams. Upon completion of the education course in this discipline, the students were electronically tested. The project to implement and test the EEGS in the educational process of the third-year full-time and correspondence course students of the Physical Culture and Sports Institute (PCSI) of Udmurt State University was found highly beneficial.



