Personality qualities of students engaged in active sports in context of sportization of physical education
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Associate Professor, PhD N.V. Peshkova
Surgut State University, Surgut
Keywords: university students, personality traits, sportization of physical education, elective courses.
Introduction. An increased focus has been recently placed on the issue of updating the approaches and means of search for new up-to-date technologies of physical education of students, which, on the one hand, is associated with a decrease in the public health indicators, and on the other – with the fact that the stage of university studies is actually the last period in an individual's life, when it is possible to solve within the framework of the educational system the problems of formation of an integral system of knowledge in the sphere of physical culture, motivation for self-training, teaching commitment to a healthy and athletic lifestyle. As proved by numerous studies, the traditional educational process does not make it possible to accomplish the target goals and objectives in real life. Thus, there is a need to implement in the university environment the innovative educationa technologies that would be up to the contemporary challenges. Among these technologies is sports-oriented physical education, which various aspects of realization in the university environment are highlighted in the works of M.V. Bazilevich, L.I. Lubysheva, S.V. Radaeva, K.B. Tumarov, V.G. Shil'ko et al. [1-4, 6, 7].
It should be noted that sportization of physical education consists in the organization of students’ motor activity within the framework of elective courses, which young people choose themselves, and further on, while getting involved in the training process, improve their sports skills, which involves their participation in competitive activities. With reference to the above mentioned, there arises a necessity for severization of the requirements applied to the training process design, improvement of its effectiveness, which largely depends on the psychological component, namely a teacher’s ability to apply his knowledge of personality traits of those involved, understanding of the specifics of setting goals and objectives depending on the prevailing trends in the achievement motivation and level of subjective control.
Objective of the study was to explore specific manifestations of the personality traits of the students attending elective courses within the frame of sportization of academic physical education – to help improve the academic education and training process efficiency.
Methods and structure of the study. The study was performed at Surgut State University in the 2015-16 academic year. Subject to the tests under the study were 149 second-year students including 86 young men and 63 women majoring in the non-sporting bachelor training disciplines and going in for different sports as encouraged by the elective physical education courses such as volleyball, fitness aerobics, body-building, football and swimming. The following methods of psycho-pedagogical diagnostics were used in the study: Method of success aspiration and fear of failure assessment by A.A. Rean; Self Control Rating method by Y.F. Bazhin, Y.A. Golynkina, L.M. Etkind; and Eysenck Personality Inventory (EPI).
Results and discussion. Figures 1-2 illustrate the data obtained by the MSF method.
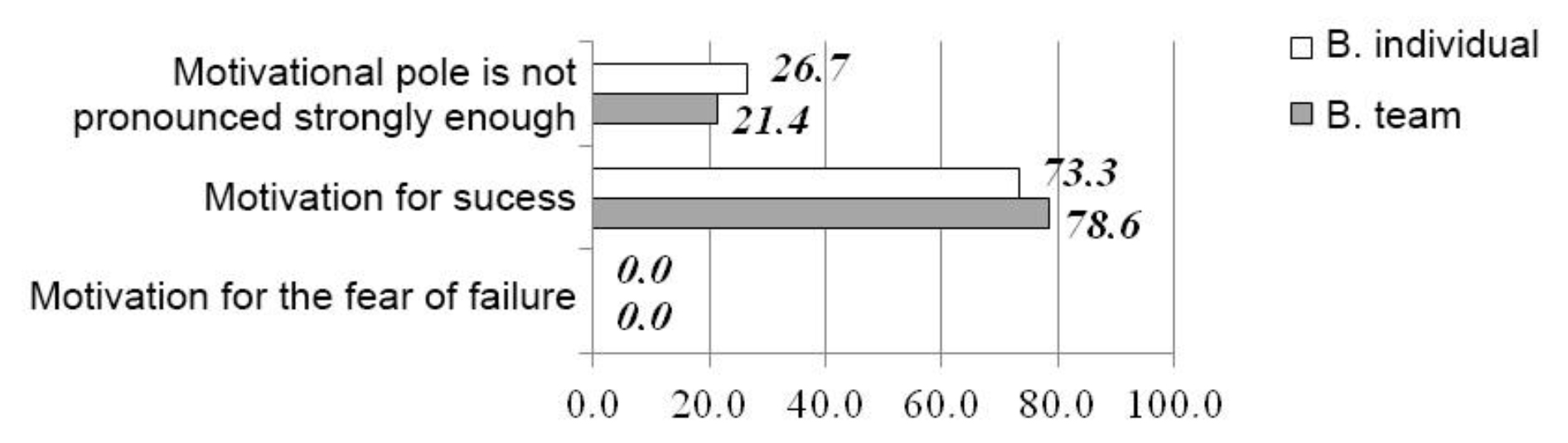
Fig. 1. MSF test rates of boys, %
As follows from the survey results, boys engaged in both team (volleyball, football) and individual (artistic gymnastics, swimming) sports demonstrate similar results. The motivational pole is not pronounced strongly enough in 21.4% of male respondents in the first instance or in 26.7% in the second one. It is motivation for success that predominates in the testees, which may suggest that students are persistent enough in achieving the set goals, strive to set themselves challenging tasks. People with such motivation are believed to direct their activity to the achievement of constructive, positive results, and their personal activity depends on the need to achieve success.
Regarding the results demonstrated by girls (see Fig. 2), it should be noted that, just like in boys, there were no statistically significant differences in the achievement motivation tendencies in various kinds of motor activity. Nevertheless, the percentage of girls, whose motivational pole is not pronounced strongly enough, is higher than that of boys by more than 20%. Moreover, 2.2% of female representatives involved in individual sports have the motivation for the fear of failure. The results obtained suggest that separate students are in need of extra psychological follow-up in the training process in view of their attitude towards own achievements and failure.
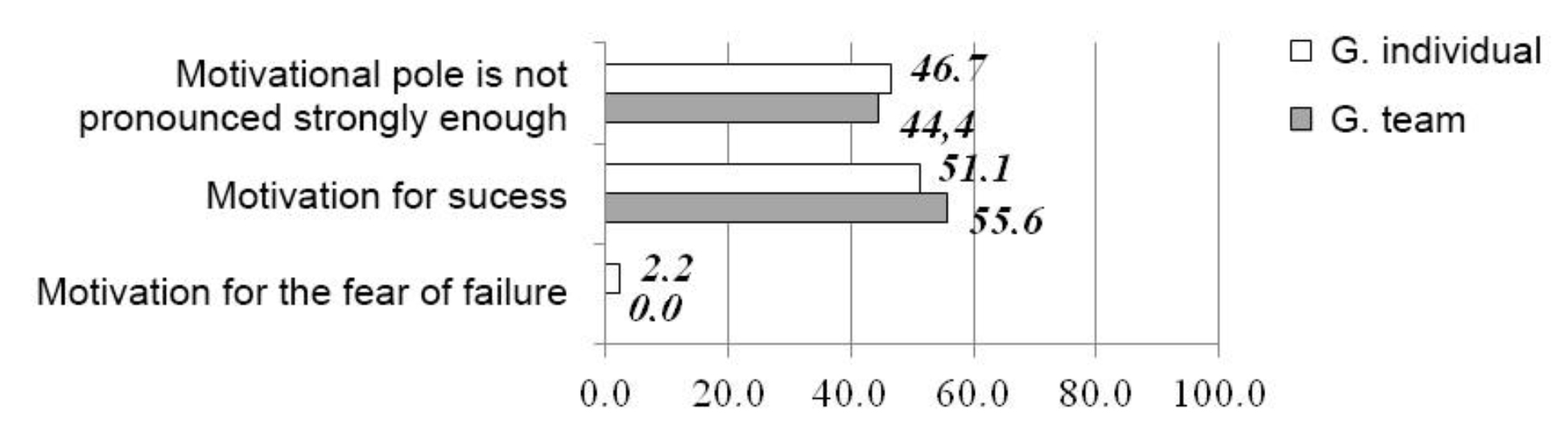
Fig. 2. MSF test rates of girls, %
Fig. 3 illustrates the results of the questionnaire survey of students obtained by the SCL test method. The authors of the given methodology believe that people differ in how and where they localize their control over the meaningful events. There are two polar types of such localization: external and internal. In the first instance, man believes that everything happening to him is caused by external forces – opportunity, other people, etc., in the second – the meaningful events are interpreted as a result of own activities. Any individual has a propensity for a certain mindset in the continuum from the external type to the internal one.
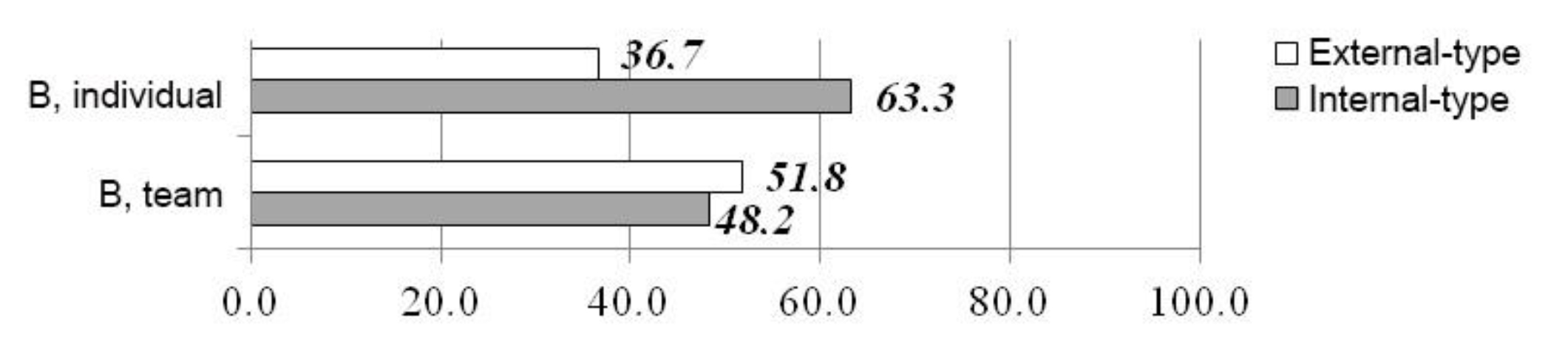
Fig. 3. SCL test rates of boys regarding achievements, %
Proceeding from the data in Fig. 3, it may be concluded that boys who choose individual sports explain their achievements by own efforts mostly, whereas in team sports there is no such clear tendency among students. Yet, the external locus of control slightly predominates. Girls (Fig. 4), doing both individual and team sports, are generally characterized by the internal locus of control; however, its predominance in the first instance is 15.6%, while in the second one – 66.6%.
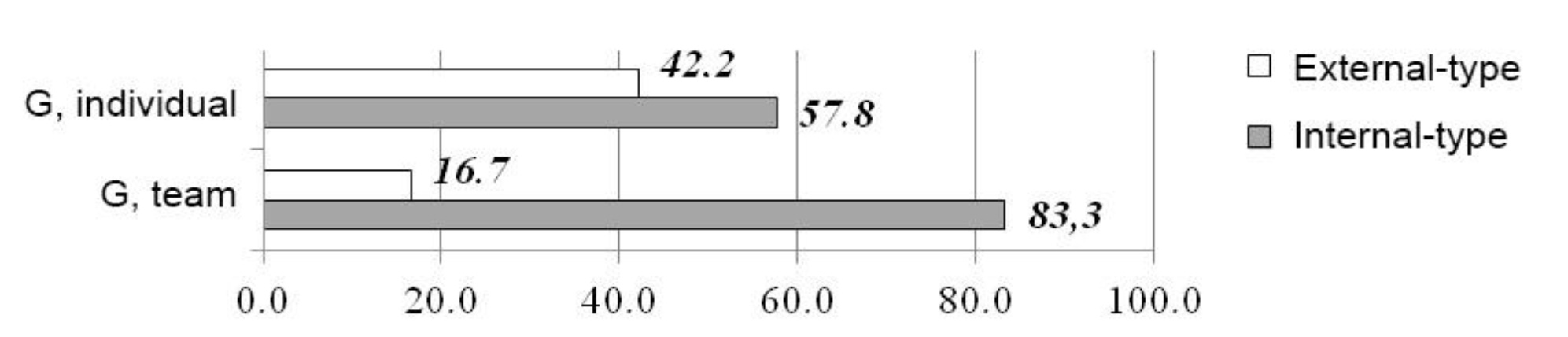
Fig. 4. SCL test rates of girls regarding achievements, %
These data differ significantly from those registered in boys. It can be concluded that girls engaged in team sports associate the results achieved with own efforts to a greater extent, they are able to successfully move towards the set goals in future.
The SCL testing of boys regarding own health and health problems on the “internality” scale (Fig. 5) shows that, unfortunately, it is the external type that prevails among the students of both groups, which can be manifested in shifting responsibility for own health to others or external circumstances.

Fig. 5. SCL test rates of boys regarding own health and health problems, %
By contrast to boys, girls are generally more responsible for own health (Fig. 6). In both team and individual sports, the percentage ratio of the external and internal types is almost the same, in the first instance it matches – 50%, while in the second one there is a 6.6% difference.
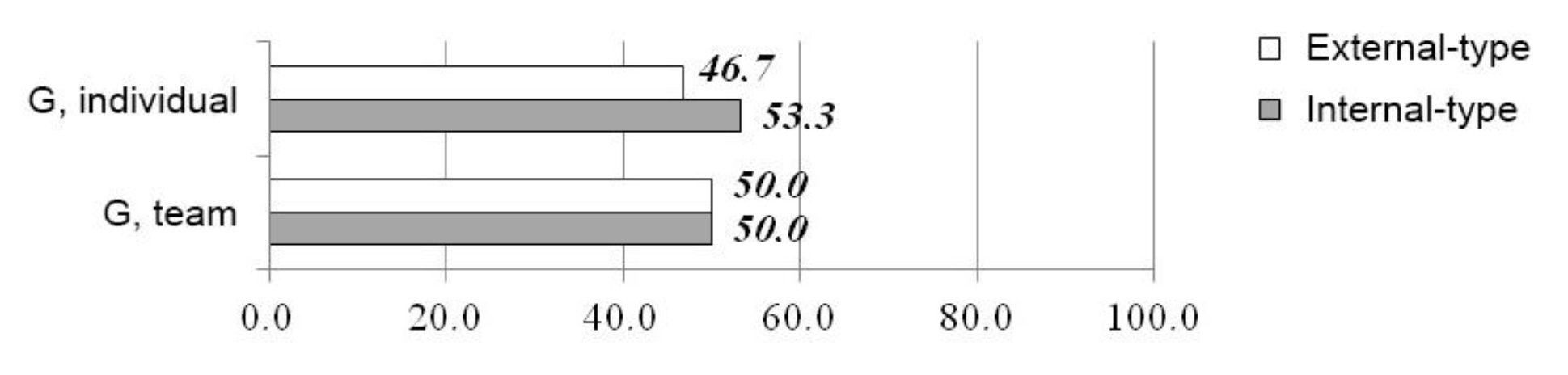
Fig. 6. SCL test rates of girls regarding own health and health problems, %
As follows from the results obtained, the subjective control rates may rise; however, it is noted that the internals mostly prefer non-directive methods as opposed to the externals who are more satisfied with behavioral methods [5].
The results of the H. Eysenck questionnaire survey of students are indicated in Fig. 7.
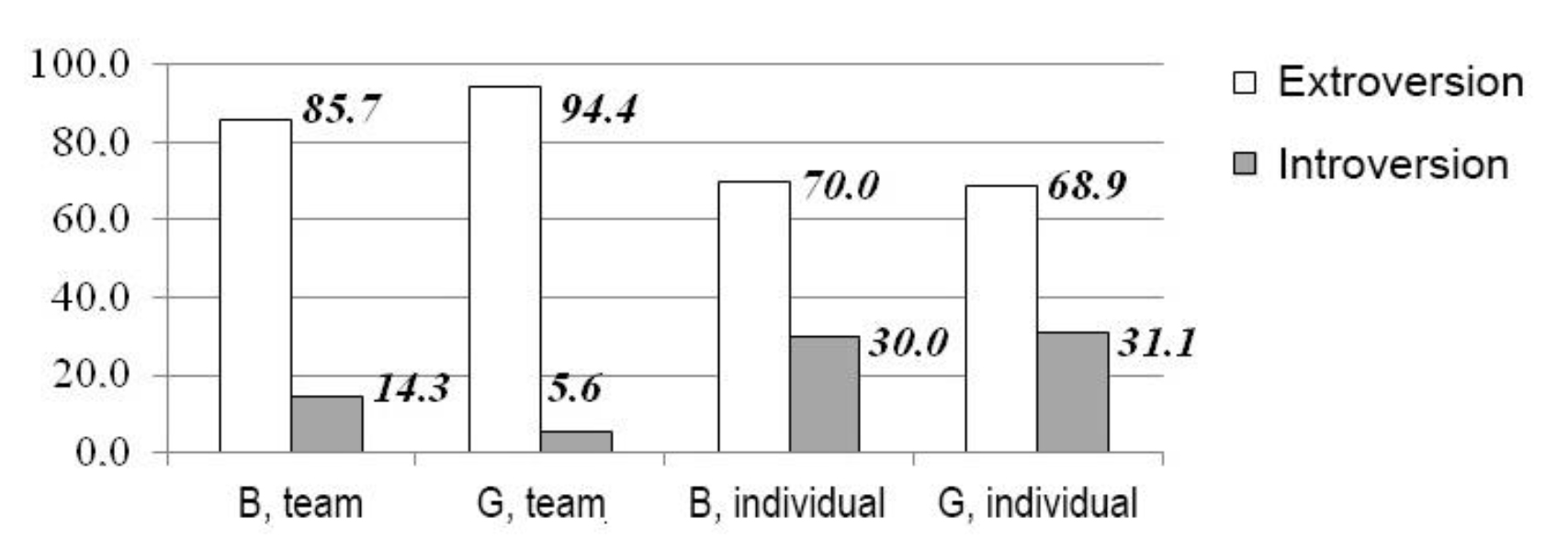
Fig. 7. Eysenck personality inventory results of students, %
Following on from the data submitted, it should be noted that in team and individual sports extroversion is characterized by significantly high values in both boys and girls, approaching the value of 94.4%, whereas introversion is more pronounced in students engaged in individual sports (31.1% and 30.0%, respectively). In our view, this kind of distribution is quite logical, as team sports require a person to possess well-developed communication skills, display such qualities as sociability and extrospection, be able to interact with other team members, while in individual sports, where the result depends on an individual only, there is mostly a tendency for introspection, more detailed framing of an action plan, increased individual responsibility for the result achieved.
Conclusion. The results obtained during the study proved the necessity for considering students’ personality traits, knowledge and understanding of which should be reflected not only in the specifics of setting goals and objectives depending on the prevailing trends in the achievement motivation and level of subjective control, but also in the employed means and methods of teacher-student communication.
References
- Bazilevich M.V. Modelirovanie sportivno-orientirovannogo fizicheskogo vospitaniya v vuze : dis. ... kand. ped. nauk (Simulation of sports-oriented physical education in university: PhD thesis) / M.V. Bazilevich. – Surgut, 2009. – 164 p.
- Lubysheva L.I. Sportizatsiya obrazovaniya ot nauchnoy idei k innovatsionnoy praktike (Sportization of education from scientific ideas to innovative practice) / L.I. Lubysheva // Nauchno-pedagogicheskie shkoly v sfere sporta i fizicheskogo vospitaniya (Scientific-pedagogical schools in the field of sport and physical education): Proc. of I res.-practical conf. with intern. participation. – Moscow: RGUFKSMiT, 2016. – P. 32-42.
- Peshkova N.V. Sportizatsiya fizicheskogo vospitaniya kak uslovie razvitiya studencheskogo sporta v vuzakh nesportivnogo profilya (Sportization of physical education as a condition for development of university sports in non-sports universities) / N.V. Peshkova, L.I. Lubysheva, A.A. Peshkov // Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury. – 2013. – # 12. – P. 88-90.
- Radaeva S.V. Fizicheskoe vospitanie studentov nefizkul'turnogo vuza na osnove sportivno-orientirovannykh tekhnologiy: avtoref. dis. … kand. ped. nauk (Physical education for non-sports university students based on sports-centered technologies: PhD thesis abstract) / S.V. Radaeva. – Krasnoyarsk, 2008. – 24 p.
- Rogov E I. Nastol'naya kniga prakticheskogo psikhologa v obrazovanii (School psychologist's handbook in education): study guide / E.I. Rogov. – Moscow: Vlados, 1996. – 235 p.
- Tumarov K.B. Soderzhanie i organizatsiya lichnostno orientirovannogo fizicheskogo vospitaniya studentov na osnove mini-futbola: dis. ... kand. ped. nauk (Content and organization of futsal-based personality-centered physical education of students: PhD thesis) / K.B. Tumarov. – Naberezhnye Chelny, 2012. – 247 p.
- Shil'ko V.G. Fizicheskoe vospitanie studentov na osnove lichnostno orientirovannogo so-derzhaniya fizkulturno-sportivnoy deyatel'nosti (Physical education of students based on personality- centered content of physical culture and sports activity) / V.G. Shil'ko. – Tomsk, 2003. – 363 p.
Corresponding author: peshkova_ffk@mail.ru
Abstract
The article is focused on the issue of the academic education and training process efficiency improvement in the context of the sport-centered academic physical education. The author notes that one of the ways to solve the issue is to help teachers make more emphasis on the process individualization tailored to the personality traits of the trainees so as to formulate the process objectives and goals more specifically depending on the prevailing trends in the trainees’ motivations and self-control levels.
Objective of the study was to explore specific manifestations of the personality traits of the students attending elective courses within the frame of sportization of physical education – to help improve the academic education and training process efficiency. The study was performed at Surgut State University in the 2015-16 academic year. Subject to the tests under the study were 149 second-year students including 86 young men and 63 women majoring in the non-sporting bachelors’ training disciplines and going in for different sports as encouraged by the modern sport-advancing academic physical education. The following methods of psycho-pedagogical diagnostics were used in the study: Method of success aspiration and fear of failure assessment by A.A. Rean; Self Control Rating method by Y.F. Bazhin, Y.A. Golynkina, L.M. Etkind; and Eysenck Personality Inventory (EPI) mental test. The study data and findings demonstrated the need for the students’ personality traits being duly taken into account in the academic education and training process design for the elective groups classified by the motor activity types.



