The Influence of Physical Education Classes in University on Quality of Life Related to Health in Students of Middle Ob Region
Фотографии:
ˑ:
M.A. Rodionova, postgraduate student
M.V. Shutova
V.A. Rodionov, associate professor, Ph.D.
Surgut State University, Surgut
Keywords: health-related quality of life, female students of Middle Ob region, university physical education, survey, physical health component, mental health component.
The relevance of the study is that the current model of education poses the qualitatively new challenge for higher education institutions: not only to protect health of students, but to teach them how to manage and fully realize their personal capacities.
Considering the category of "health" and following of the principles of healthy lifestyle as a reserve of students' adaptation to the changing conditions of life, it is advisable to investigate such a category as quality of life (QOL). The health related study of the QOL is a new advanced methodology of health protection that helps assess the results of the formation of the quality of life of a person in the social environment, including educational activity [4].
According to the findings of V.K. Balsevich, L.I. Lubysheva et al., a close relationship is marked between the level of sports activity, vital activity of an individual and health of adolescents [1].
The purpose of the study was to estimate the level of physical and mental components of the quality of life of higher school students attending and not attending physical education classes in a university.
Materials and methods. The survey was carried out at the premises of Surgut State University.
The study involved 40 1-3-year female students aged 18-20 years. 20 girls attended an elective course where they could choose a type of physical activity, while the other 20 girls (with the low level of physical activity) did not attend physical education lessons at the university and were not engaged in any sports.
The survey was carried out with the help of the Russian version of the standard questionnaire of health-related quality of life SF-36 v.2 in March-April 2014. The SF-36 Health Status Survey is one of non-specific questionnaires used to assess quality of life (QOL), it is widespread in the US and Europe and is used for the study of quality of life. The results are presented in the form of ratings in points based on 8 scales drawn up in such a way that a higher score indicates a higher level of QOL. The scales are grouped into two indicators "physical health component" and "mental health component". The value of 50 ± 10 points was considered the norm in each scale of the survey SF-36v.2.
Statistical analysis of the findings was carried out with the use of the software Statistica, 6.0. The calculated parameters were as follows: sample size (n), mean value (x), minimum, maximum, standard deviation (σ), standard error. The statistical significance of differences was determined by the non-parametric U-Mann-Whitney test and the parametric Student's t-test. Differences were considered significant at the significance level of p <0.05.
Results and discussion. As seen from the study, the rate of "physical functioning” (PF), which reflects to which extent physical condition limits physical activity (self-care, walking, climbing stairs, carrying heavy loads, etc.) in female students leading active lifestyle and attending the elective course on physical education in the university, on average, is significantly higher than that of female students who are not engaged in: 95 ± 5 points versus 69 ± 9 points respectively.
In terms of "role-physical” (RP) and "general health” (GH) the situation was the same: the results of female students who attended practical classes of physical education were higher than those of students who did not attend classes for medical reasons (69 points versus 56 points and 69 points versus 51 points respectfully for the two indicators). No significant differences were marked in the mean values of "pain intensity".
If we are to consider the group of mental health indicators, we should mention the presence of minor differences in the scoring values of the two groups. So, in terms of "vitality” (VT) and "social functioning” (SF) the differences in the mean values were up to several points: 54 points versus 58 points and 78 points versus 81 points in female students with low PA and in female students attending physical education classes, respectively.
More significant differences (of ten points) were observed in the "role-emotional” indicator. There should also be noted the predominance of average score values in most indicators of the mental health component.
The total index of the physical health component (PCS) was 53 and 45 points in the group of girls attending the elective course and for those not engaged in physical education lessons, respectively.
The total index of general mental health (MCS) in girls of both groups was close to the lower limit of normal - 42-43 points. The summary data for both subject groups is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. The distribution of the scoring values of physical and mental health components between the female student groups:
|
Indicators
Groups |
Physical health component in points |
Mental health component in points |
||||||
|
physical functioning (PF) |
role functioning determined by physical condition (RP) |
pain intensity (PI) |
general health (GH) |
vitality (VA) |
|
social functioning (SF), role-functioning determined by emotional state (RE) |
Mental health (MH) |
|
|
Students not attending physical education lessons |
69 |
56 |
72 |
51 |
54 |
78 |
50 |
57 |
|
Students attending physical education lessons |
95 |
69 |
73 |
69 |
58 |
81 |
60 |
62 |
A more descriptive distribution of score values is shown in Figure.
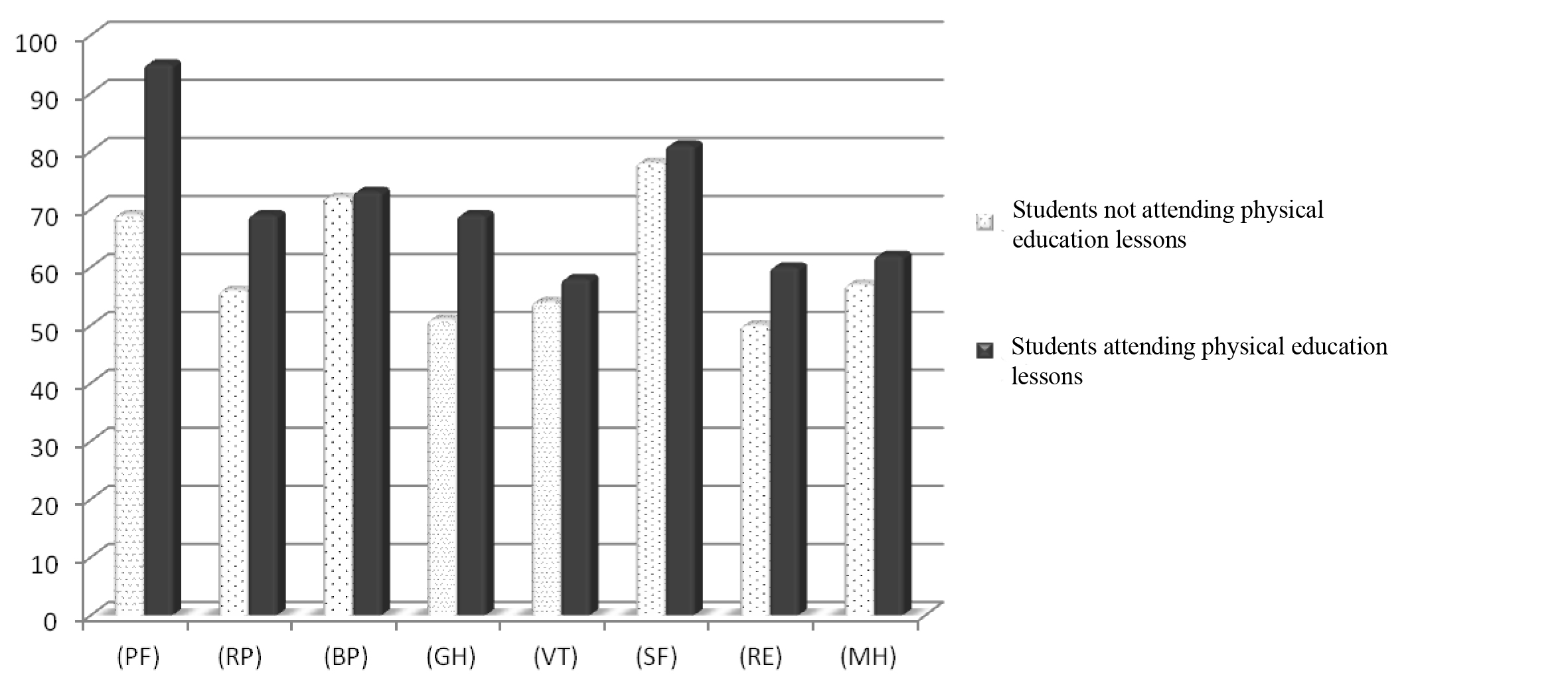
Figure. A comparison of score values of physical and mental components of health in the groups of students
The findings resulted in the following conclusions:
Since the state of health of students of Russian universities is getting worse year after year and the number of students attributed to special medical groups is increasing steadily, it is of particular interest to study the health-related quality of life.
There is a disparity in the level of physical and mental health and the quality of life of female students attending and not attending physical education lessons in the university. The indices of life quality of female 1-3-year students of the Middle Ob region were predominantly up to the norm, but the values were closer to its lower limit (40 points).
At the same time the scoring values of individual indicators of the physical health component of the students attending the elective course on "Physical Education" were significantly higher than those in females not attending such lessons, which suggests a considerable role of physical activity for improvement of the quality of life of students.
References
- Balsevich, V.K. Physical Culture: Youth and modernity / V.K. Balsevich, L.I. Lubysheva // Teoriya i praktika fizicheskoy kul'tury. – 1995. – № 4. – P. 2–7. (In Russian)
- Galai, O.I. Physical education of students of the special department in Yugra State University / O.I. Galai, N.I. Sannikova, S.I. Eremeyev // International journal of experimental education. – 2011. – № 4. – P. 51–54. (In Russian)
- Esaulenko, I.E. The influence of the learning environment on students' health / I.E. Esaulenko, A.S. Faustov, I.I. Libina, O.I. Gubina // Vestnik VGU (Voronezh State University), Series: Problems of higher professional education. - Voronezh, 2009. – № 2. – P. 55–59. (In Russian)
- Kuvaldin, V.A. Analysis of the influence of physical and mental health components on the quality of life and study of students of Tyumen State Agricultural Academy and those who do not study / V.A. Kuvaldin // Teoriya i praktika fizicheskoy kul'tury. – 2010. – № 10. – P. 19–23. (In Russian)
- Litovchenko, O.G. Morphofunctional state of 7-20-year-old natives of the Middle Ob region / O.G. Litovchenko // Proceedings of the Internat. theor.-pract. conf. "Modern problems of ecological physiology", 2008. Almaty. – P. 93. (In Russian)
Corresponding author: apokin_vv@mail.ru



