Continuous college-to-university physical education technology: case study of Physical Education and English Language disciplines
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Dr.Hab., Associate Professor R.S. Nagovitsyn1
Dr.Hab., Professor A.V. Tutolmin1
PhD, Associate Professor Y.G. Maksimov1
Senior lecturer P.B. Volkov1
1Glazov State Pedagogical Institute named after V.G. Korolenko, Glazov
Keywords: physical education, pedagogical education, continuous physical education, individualized education, networking, clustering, education trajectory.
Background. The continuous physical education specialist training technology shall be designed based on a broad cooperation of education establishments, departments and institutes offering a wide range of education services. The continuous college-to-university physical education technology is the most common today. The Bologna and Turin education models implemented in the national vocational and higher education systems give a high priority to the initiatives to step up the competitiveness of the national education institutions and system on the whole on the global markets. The growing demand for the academic human resource and the need to comply with the new higher education standards including the new requirements to increase the shares of foreign students at national universities, urged the sector to develop and implement new cluster-technology-based education trajectories. A special priority in this context is given to a strategic partnership system to secure a close cooperation of the relevant colleges, universities, their departments, employers and local government agencies for success of the initiatives.
The frame continuous college-to-university physical education specialist training model in application to professional training in the academic Physical Education and English Language disciplines was designed to fulfill the following missions set forth by the Federal Target Education System Development Program for the Period of 2016-2020: implement the integrated systemic projects under the Program to establish new university models and new education curricula with the implementation technologies; implement a set of pilot projects to upgrade the regional vocational education systems; encourage cluster-type associations of vocational education establishments under the relevant universities; implement the key requirements of the Bologna and Turin education models in the national vocational training and higher education systems; and step up the competitiveness of the national educational establishments and system on the whole on the global markets.
Objective of the study was to develop a frame continuous college-to-university physical education specialist training model in application to the academic Physical Education and English Language disciplines – to offer an individualized continuous education system for physical education specialists.
Methods and structure of the study. Methodologically, the frame model design was based on the studies of the physical education theory and practices by V.K. Bal’sevich [1], M.Y. Vilenskiy, L.I. Lubysheva [5], L.P. Matveyev, S.D. Neverkovich, Y.M. Nikolaev and others; conceptual design of the foreign language curricula for physical education universities by N.V. Bagramova, M.K. Kalkova, Z.V. Perepelkina [7] and others; and ideas of systemic continuous education systems by Y.P. Belozertsev, B.S. Gershunskiy, Y.P. Kargapolov [2], V.V. Krayevskiy, I.K. Latypov, [4], V.A. Slastenin, Y.P. Sokolnikov, G.P. Shchedrovitskiy, A.G. Yudin and others.
Having analyzed and summarized the available materials on the subject, we have found the key inefficiencies in the bilingual physical education specialist training systems to set a logical framework for our further research and to develop the relevant programmatic, regulatory and practical provisions for the continuous physical education specialist training system [6]. Our theoretical study with analyses of the existing regulatory framework [8, 9, 10] and Concept of the Federal Target Education System Development Program for the Period of 2016-2020 [3] gave us a foothold for the frame continuous college-to-university physical education model design: see Figure 1 hereunder.
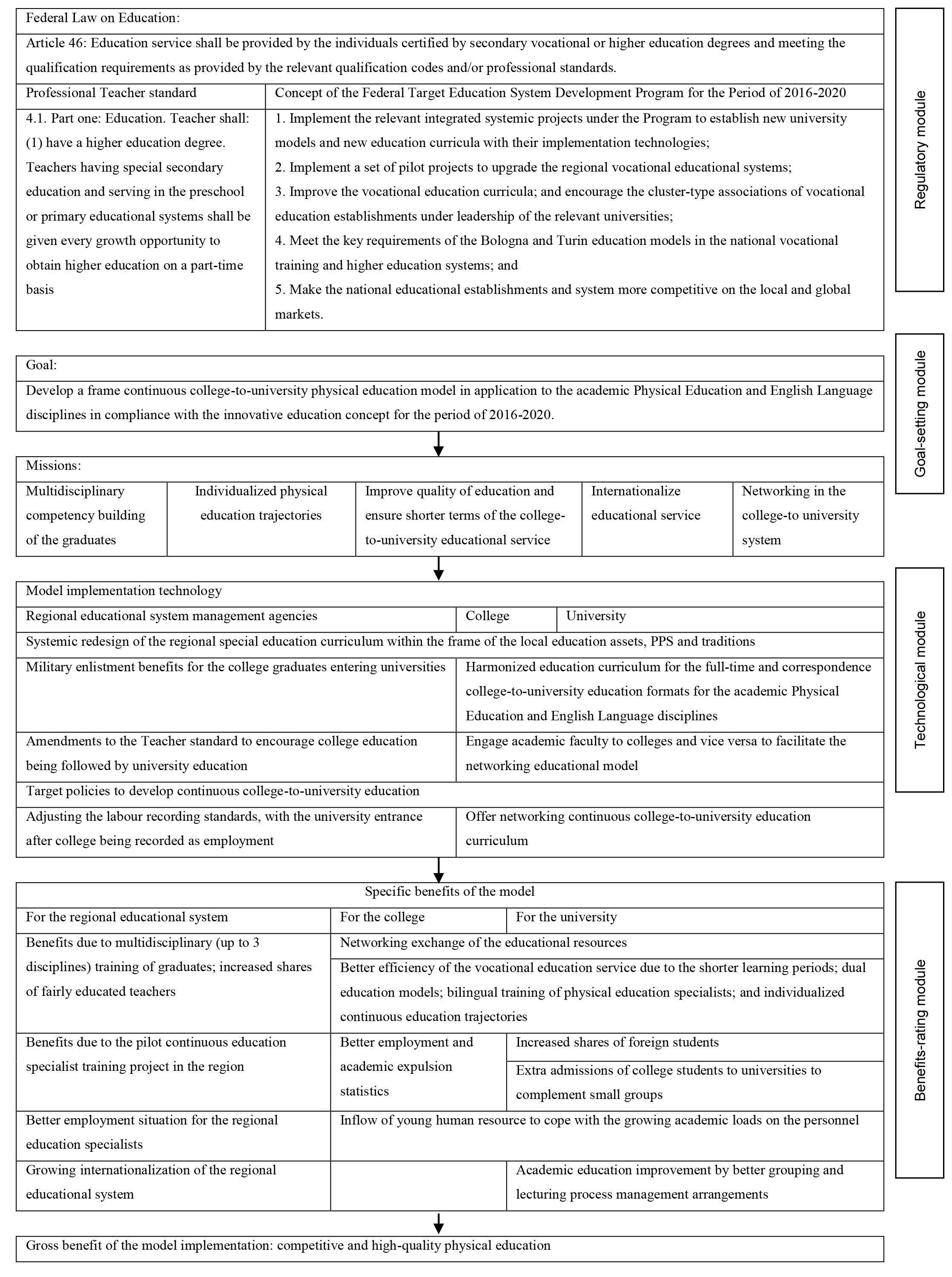
Figure 1. Frame continuous college-to-university physical education specialist training model
Study results and discussion. Based on the analysis of the competency of the physical education specialist training system for the internationalization of the physical culture and sporting contacts and services, we found the academic Physical Education and English Language disciplines being of highest demand and priority for the sector: see Table 1 hereunder.
Table 1. Individualized continuous physical education system for the academic Physical Education and English Language disciplines
|
Academic Pedagogical Education trajectory upon graduation from a teacher training college |
Education term |
Total academic load |
Base part |
Variable part in PE discipline |
Variable part in X discipline |
Variable part in Y discipline |
Elective courses |
Practice |
SAC |
Qualification |
|
Bachelor of PE |
1,5 |
75 |
19 |
27 |
|
|
12 |
11 |
6 |
Physical education specialist |
|
Bachelor of English Language |
2 |
113 |
19 |
|
53 |
|
24 |
11 |
6 |
Physical education and English language specialist |
|
Bachelor of PE and English Language |
2,5 |
150 |
19 |
27 |
53 |
|
34 |
11 |
6 |
Physical education and English language specialist |
|
Bachelor of PE, English Language and X |
3 |
188 |
19 |
|
53 |
53 |
46 |
11 |
6 |
Physical education, English language and X specialist |
Note: X means any specialty under the academic Pedagogic Education discipline including Preschool Education, Primary School Education, Life Safety, Music, Biology, Russian Language etc.
Conclusion. The proposed multilevel physical education specialist training model will secure: on the individual level – the educational process individualization in terms of the professional education service content and scope customizable to meet the relevant intellectual, social, international and economic needs; on the regional educational system level – training of interdisciplinary graduates in shorter terms to meet the system demand for the high-quality human resource; and on the academic (college and university) staff level – systemic fulfillment of the relevant networking, research, educational process and social missions.
The study was supported by the RSRF grant financing for Project #16-16-18003
References
- Bal’sevich V.K., Popov K.I., Sannikova N.I. Nepreryvnoe fizkulturnoe obrazovanie [Continuous physical education]. Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury, 2004, no. 12, pp. 10-13.
- Kargapolov E.P. Organizatsionno upravlencheskie osnovy nepreryvnogo fizkulturnogo obrazovaniya. Avtoref. dis. dokt. ped. nauk [Organizational and management basics of continuous physical education. Doctoral diss. abstract (Hab.)]. Moscow, 1992, 49 p.
- Kontseptsiya Federalnoy tselevoy programmy razvitiya obrazovaniya na 2016 – 2020 gody [The Concept of the Federal Targeted Program for Development of Education for 2016-2020]. Available at: http://minobrnauki.rf/dokumentyi/4952/fayl/3922/ PRAVITEL'STVO_ROSSIISKOI_FEDERACII_FCPRO.doc.
- Latypov I.K. Nepreryvnoe professionalnoe obrazovanie v sfere fizicheskoy kultury: sostoyanie, problemy i perspektivy [Continuous professional education in the field of physical education: state, problems and prospects]. Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury, 2004, no. 6, pp. 5-10.
- Lubysheva L.I. Kontseptsiya fizkulturnogo obrazovaniya: teoriya i metodika [Physical education concept: theory and methodology]. Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury, 1996, no. 1, P. 2.
- Lubysheva L.I., Magin V.A. Kontseptsiya modernizatsii protsessa professionalnoy podgotovk spetsialistov po fizicheskoy kulture i sportu [The concept of physical education and sports specialist vocational training process modernization]. Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury, 2003, no. 12, pp. 13-16.
- Perepelkina J.V. Formirovanie gotovnosti k ispolzovaniyu inostrannogo yazyka v protsesse podgotovki spetsialista po fizicheskoy kulture. Dis. kand. ped. nauk [Formation of readiness to use foreign language in physical education specialist training process. PhD. diss.]. St. Petersburg, 1997, 151 p.
- Professionalny standart pedagoga [Professional standard of teacher]. Available at: http://fgosvo.ru/uploadfiles/profstandart/01.001.pdf
- Federalny gosudarstvenny obrazovatelny standart. 44.03.05 –«Pedagogicheskoe obrazovanie» [Federal State Educational Standard. 44.03.05 - "Pedagogical Education"]. Available at: http://fgosvo.ru/uploadfiles/fgosvob/440305.pdf
- Federalny zakon ob obrazovanii Rossiyskoy Federatsii [Federal Law on Education in the Russian Federation]. Available at: http://zakon-ob-obrazovanii.ru/46.html
Corresponding author: romanagovitsin@rambler.ru
Abstract
The study analyses benefits of the continuous college-to-university physical education technology tested on an individualized education model designed to train a physical education specialist. The frame continuous college-to-university physical education specialist training model includes regulatory, goal-setting, technological and benefits-rating modules and tests solutions for the following process missions: multidisciplinary training of a physical education specialist; individualized continuous physical education technology; education quality improvement; time saving on the college-to-university education route; higher educational service internationalization; and networking/ clustering of the college-to-university education process. New cluster-technology-based education trajectories were offered to meet the modern requirements to the education specialist’s competency including the federal standards on the whole and the academic system management standards in particular – in relation, among other things, to the foreign students’ educational service. To facilitate implementation of the continuous physical education technology, the study offers a special curriculum for the remote training of the education specialists majoring in the academic Physical Education and English Language sub-disciplines of the Pedagogical Education discipline.




