Informational and didactic information technologies applied for physical education at economics university
Фотографии:
ˑ:
S.Y. Vitko1
PhD, Associate Professor K.E. Stolyar1
E.G. Stadnik1
M.Y. Tochigin1
1Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, Moscow
Keywords: innovation, information technology, higher education, physical education, sport, health.
Background. Presently the education process design in the elective academic physical education and sport disciplines is complicated by the free choice of indoor facilities by the students – as the education process may not always be efficiently controlled and progress efficiently verified by the interim and final progress assessments to rate the education process success and the competences acquired by the students. Therefore, a high priority was given to the local electronic education and information environment (EEIE) development project to offer the relevant theoretical and practical materials with efficient progress control, assessment and test tools [7].
Objective of the study was to develop a system of information technologies to redesign on a more efficient basis the academic physical education and sports.
Methods and structure of the study. The innovative process management and didactic technologies were developed and implemented in the following few stages: we analysed the theoretical and practical experience of information technologies implementation projects at Physical Education departments; selected the most efficient ones; developed an educational website “Electronic Journal” in 2015-2016; procured the programmed testing ESTECK System Complex for health tests; and developed a few interactive education technologies such as the “reverse class”, individually controlled education, case technologies and conference lectures geared to ensure a high degree of student’s involvement in the education process. The innovations have been implemented in the period of 2016-2017.
Study results and discussion. Presently the education process at Plekhanov Russian University of Economics (RUE) is designed on a modular basis. The academic Physical Education discipline (taking 72 hours and rated by 2 credit units) is offered in 4 modules in the first academic year. Each module includes lectures, workshops, master classes and studies using the programmed testing ESTECK System Complex, research conferences, electronic tests and examinations. The core mission of this discipline (and the key objective of the education process) is to form health management skills in the students, improve their mental and physiological health rates and physical working capacity by a variety of tools including highly efficient new fitness and sporting practices. The Physical Education department is staffed by highly knowledgeable and skilful academic personnel having research degrees and qualifications. The education process is finalised by the Students Research Conference “Sport Science”. The winners and runner-ups of the contests in the conference successfully contribute to international student congresses and qualify for grant projects. As a result, students are much more determined in the education process, successful in the academic progress tests and exams and demonstrate excellent progress in the general cultural competency building.
The university also offers the academic Elective Physical Education Disciplines taking 328 hours in three academic years and designed in 12 modules including practical trainings in gyms, overall physical fitness tests and exams.
Two of the above disciplines are supported by electronic Academic Progress Logbooks designed using the standard Excel toolkit, with the outcome lines and columns including the relevant formulae and programmable inserts designed in a user-friendly format. The networking Logbook service is available in every indoor sport facility of the University and includes an attendance registration service for the academic elective sport disciplines. For example, training sessions are scheduled on Monday and Wednesday by the general schedule. A student may opt for a gym on Monday and swimming pool on Wednesday. His/her attendance of each of the sport facilities is fixed in the relevant electronic insert, with the current credits being added up to the total credits for the prior sessions. The headline of the Logbook indicates the name of the educator in charge of the group sessions and gives contact details of the group leader. Insert “Yearly Account” provides summarised information on individual attendance, test results, competitive record and current sport ranking. This insert is designed only for data consolidation and cannot be edited by the educator in charge: see Figure 1.
The academic physical education disciplines may be elected (recommended) based on the test data generated by the programmed testing ESTECK System Complex: see Figure 2. The express test procedure takes only 6 minutes and produces the following express body test data: digital bio-impedometric data, digital pulse wave data, digital heart rate variability data and skin galvanometric response data. The test results are displayed to present the overall body status data classified into the following 10 groups: blood pressure, hemodynamics, CV components, systolic time, arterial rigidity, sudoscan test, sympathetic NS, parasympathetic NS, О2 indices and fat mass. The test data are calculated in points on a 100-point scale. As a result, individual recommendations on the physical activity and nutrition are generated.
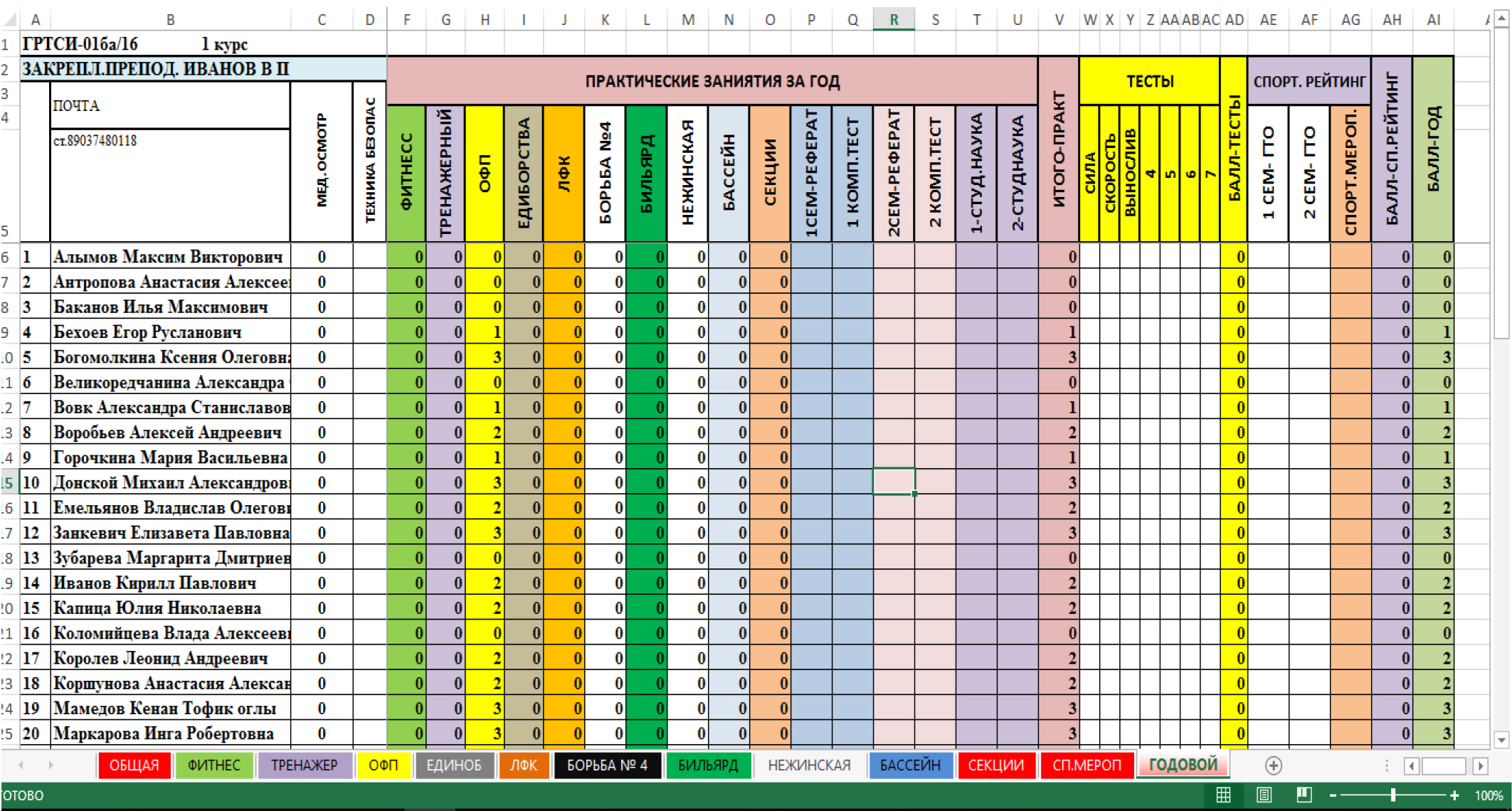
Figure 1. Screenshot of the electronic Academic Progress Logbook
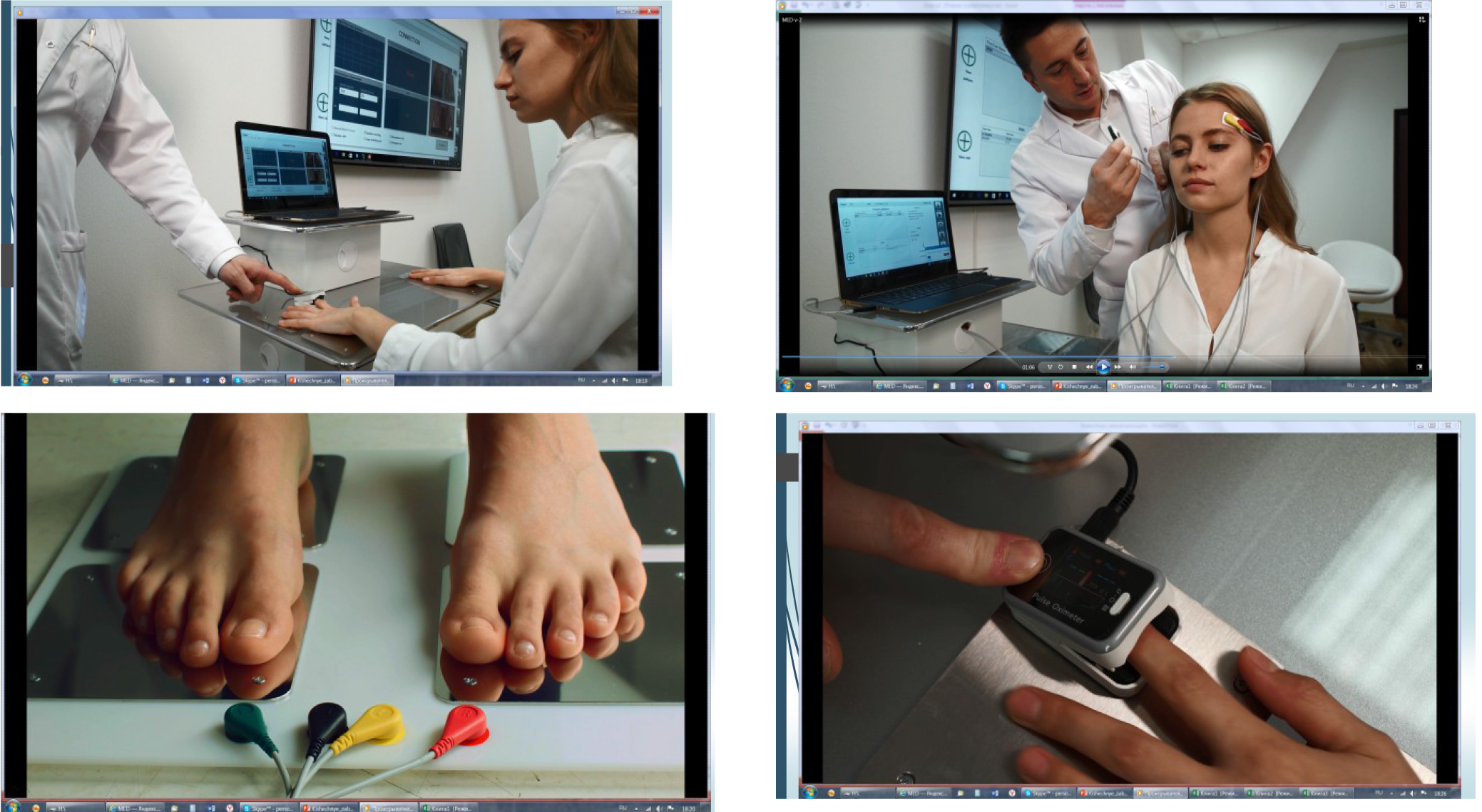

Figure 2. Programmed testing ESTECK System Complex
A mobile application “Physical education” was designed to ensure a permanent access to the above electronic Logbook to give students the means to keep track of their education progress; with the application scheduled for implementation in the academic year of 2017-2018.
Conclusion. The local electronic education and information environment (EEIE) implemented at the Physical Education Department may be described as a special innovative space that includes a networking electronic Academic Progress Logbook to keep track of the attendance of the sport facilities; mobile application; and express test system for health tests. The didactic content of the new education model includes a few interactive communication technologies such as “reverse class”, individually controlled education, case technologies and conference lectures geared to ensure a high degree of the student’s involvement in the education process. It should be noted that the interactive education models and methods are considered an obligatory component of the FSHES implementation in the academic education process and ranked among the top priority innovative technologies to activate the learning and self-education activity of students.
References
- Averyasova J.O., Aliev T.D. Formirovanie prostranstva fizicheskoy kultury v sisteme professionalnoy podgotovki studentov [Formation of physical education space in vocational training system]. Moscow: TR-print publ., 2015, 170 p.
- Beletskiy S.V. Vliyanie informatsionnykh tekhnologiy na formirovanie kompetentsiy po teoreticheskim osnovam fizicheskoy kultury [Building competences on theoretical foundations of physical education influenced by information technologies]. Vestnik Rossiyskogo ekonomicheskogo universiteta im. G.V. Plekhanova, 2015, no. 4 (82), pp. 14–22.
- Beletskiy S.V. Informatsionnaya kompyuternaya podderzhka v formirovanii kompetentnosti zdorovyesberezheniya u studentov bakalavriata [Information computer support in building health protection competency in undergraduates]. Pedagogicheskoe masterstvo i pedagogicheskie tekhnologii, 2015, no. 3 (5), pp. 326–328
- Beletskiy S.V., Antonova I.N., Kondratyev P.A. Obuchayushchee kompyuternoe testirovanie v prepodavanii fizicheskoy kultury sovremennogo vuza [Educative online testing in physical education teaching skills in modern university]. Interaktivnaya nauka, 2016, no. 1.
- Vitko S.Y., Vnukova E.Y., Makarenkova T.I., Antonova I.N. Fizicheskoe vospitanie kak osnova razvitiya, sovershenstvovaniya i garmonizatsii cheloveka v usloviyakh tekhnicheskogo progressa [Physical education as basis for development, improvement and harmonization of man within technological progress]. Mater. VII Mezhdunar. nauch.-prakt. konf. "Aktualnye napravleniya nauchnykh issledovaniy: ot teorii k praktike" [Proc. VII Internar. res.-pract. conf. "Actual guidelines of scientific research: from theory to practice"]. Cheboksary: Interaktiv plyus, 2016, no. 1 (7), pp. 103–106.
- Stolyar K.E., Vit'ko S.Y., Pikhaev R.R., Kondrakova I.V. Organizatsionno-metodicheskie podkhody k kompleksnoy otsenke fizicheskoy podgotovlennosti studentov [New institutional and practical system for students' integrated physical fitness rating]. Teoriya i praktika fiz. kultury, 2016, no. 9, pp. 9-11.
- Federalny zakon ot 29.12.2012 goda no. 273-FZ «Ob obrazovanii v Rossiyskoy Federatsii» [Federal Law dated December 29, 2012 no. 273-FL "On Education in the Russian Federation"].
Corresponding author: andryushenko-lil@mail.ru
Abstract
The article overviews the newly developed electronic education and information environment (EEIE) including an electronic Academic Progress Logbook, mobile application “Physical education” and a programmed testing ESTECK System Complex.
The electronic Academic Progress Logbook was designed using the standard Excel toolkit, with the outcome lines and columns including the relevant formulae. The networking Academic Progress Logbook service covers every sport facility of the University and includes an attendance registration service for every academic elective sport discipline.
The programmed testing ESTECK System Complex generates (in only 6 minutes) the following express body test data: digital bio-impedometric data, digital pulse wave data, digital heart rate variability data and skin galvanometric response data.
A mobile application “Physical education” was designed to ensure a permanent access to the above electronic Academic Progress Logbook to give students the means to keep track of their education progress.
The didactic content of the new education model includes a few interactive communication technologies such as “reverse class”, individually controlled education, case technologies and conference lectures geared to ensure a high degree of the student’s involvement in the education process.
It should be noted that the interactive education models and methods are considered an obligatory component of the FSHES implementation in the academic education process and ranked among the top priority innovative technologies to activate the learning and self-education activity of students.




