Acmeological support for professional coaches' progress in advanced professional education system
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Dr.Hab., Professor V.G. Tyutyukov1
PhD, Associate Professor G.V. Safonova2
1Far Eastern State Academy of Physical Culture, Khabarovsk
2Far Eastern Federal University, Vladivostok
Keywords: coach, advanced education, professional career, professional competency, aсmeological support.
Background. Presently there is still a gap between the high priority given to physical education and sports in the school and academic education process and the deficiencies in the theoretical knowledge of the psychological and educational aspects of the key actors of the process i.e. physical education teachers/ coaches. This situation calls for further integrated studies to facilitate the professional competency building process in this professional category including aсmeological support for their professional progress. The aсmeological support system may be described as a specific form of educational activity with the acmeo-specific practical toolkit being applied to facilitate productive personality growth and professional competency building process. This practical toolk33it makes a special emphasis on the acmeological technologies of constructive effects on the self-assessment, self-discovery and self-development components plus an acmelogogical monitoring to obtain objective data to rate the effects of the acmeological technologies on the education process actors [1].
Objective of the study was to contribute to the coaches’ professional competency building process in the advanced education (skills improvement) process by the acmeological support system.
Methods and structure of the study. We have developed and implemented an acmeological support system to secure professional progress of coaches in the advanced education courses taking 144 hours in form of evening classes. The system was designed to support the trainees in their efforts to conscientiously manage their own progress zones within individual, social, professional and technological domains. Subject to the study were 44 coaches having 5-10-year practical coaching experiences, with some of the group (n=22) trained at Far Eastern State Academy of Physical Culture and the other part at Arts, Culture and Sports School under Far Eastern Federal University, both of the training programs being the same. The progress rating procedures under the study implied the progress rates being averaged both in the coaches’ progress tests and self-rating procedures.
The acmeological support of the advanced education course was designed on an integrated basis, with analyses of the professional development benefits in the process; mindset and acmeological trainings, coaching and game modelling sessions; progress assessment procedures and analyses; and individual portfolio quality ratings. Given on Figure 1 hereunder is the frame diagram of the acmeological support system.
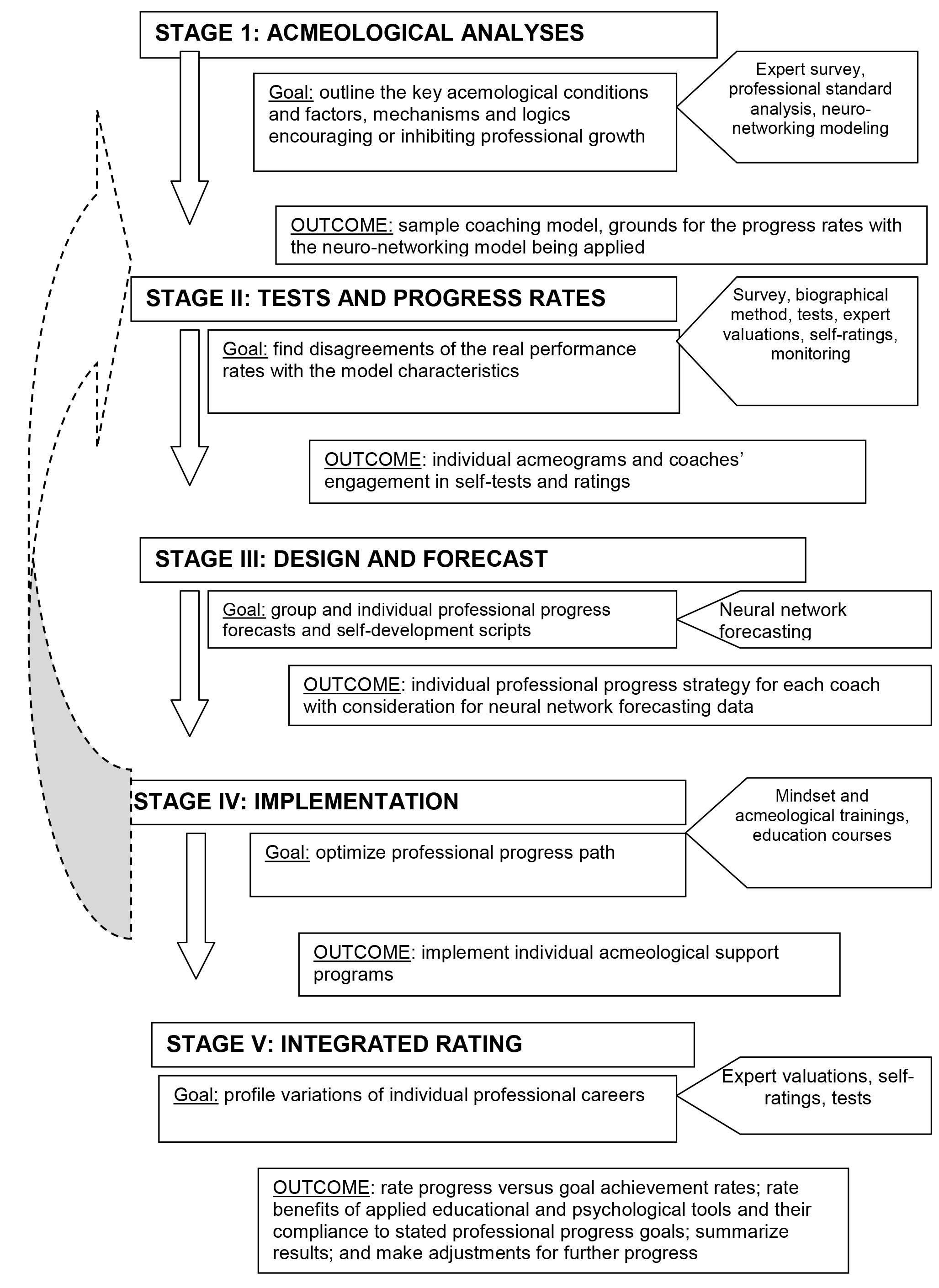
Figure 1. Frame diagram of the acmeological support system applied in the coaches’ advanced education courses and further professional careers
Stage I Acmeological Analyses as a component of the acmeological support process was designed to identify the key acemological conditions and factors, mechanisms and logics encouraging or inhibiting professional growth. Stage I resulted in a sample coaching model designed in compliance with the valid professional standard as verified by the relevant progress rating indicators using the neural network forecasting tools. The latter give the means to set the key progress rates - to rate the qualities, traits, abilities and competences of the trainees that are most important for their professional growth.
Stage II Tests and Progress Rates were designed to compare the progress rates of the coaches with the model characteristics to find disagreements in the data arrays. The testing and rating procedures widely applied psychological tests, biographical analysis, self-ratings and expert valuations to profile progress in the professionally important qualities and competences additionally verified by the practical professional accomplishments.
State III Design and Forecast in the acmeological support process were geared to forecast group and individual professional progress paths and produce their scripts.
Stage IV Implementation implied the coaches’ professional progress paths being optimised by the relevant group and individual acmeological technologies applied. This stage included a set of individual and group acmeological trainings, game modelling and coaching sessions.
Stage V Integrated Rating was designed to rate the overall progress versus the goal achievement rates; rate benefits of the applied educational and psychological tools and their compliance with the stated professional progress goals; summarize the results; and make adjustments for further progress.
Study results and discussion. Since it is a combination of the behavioural and performance transformations and new competences acquired by students that may be viewed as a practical product of an educator’s labour; and the modern physical education and sport functionality includes a variety of cultural, educational, health improvement and competitive functions; a coach’s success will be rated with due account of the trainees’ individual transformations as verified by the relevant culture, knowledge and physical development test rates and individual athletic accomplishments [2, 4].
The above progress tests (rated on a 5-point scale) yielded the following rates in the health improvement domain: 3.2 points prior to the advancement course versus post-course 3.6 points (one year after). In the education quality domain, the progress rates were 4.1 and 4.4 points, respectively; and in the cultural progress domain the rates were estimated at 3.8 and 4.3 points, respectively. Rated highest was the competitive progress of the trainees, with the primary rate of 4.2 versus the final rate of 4.5 points. The summarised professional progress of the coaches was rated by 3.8 and 4.2 points, respectively. The increments in the progress rates were found statistically significant with p<0.05 (х² criterion).
The prior and final professional competence rates of the coaches who took the advanced education course supported by the pilot acmeological system, as verified by the professional competences rating tests (using an adapted version of the M.E. Inkov’s method [3]) were indicative of the highest progress in psychological, educational, design, research, analytical and acmeological competencies (see Figure 2). As demonstrated by the study data, the most demanded prior to the advancement course were the following advanced education modules: new trends in the modern athletic training systems; biomedical provisions for sporting activity including nutrition and rehabilitation components; and athletic training process standardisation. The least demanded were the modules including self-development, professional progress aspects and own resource assessments, plus the tests and research technologies applicable in sports. Upon completion of the advanced education course, the coaches were found to give a higher priority to own professional resource discovery, individual self-development and progress profiling issues.
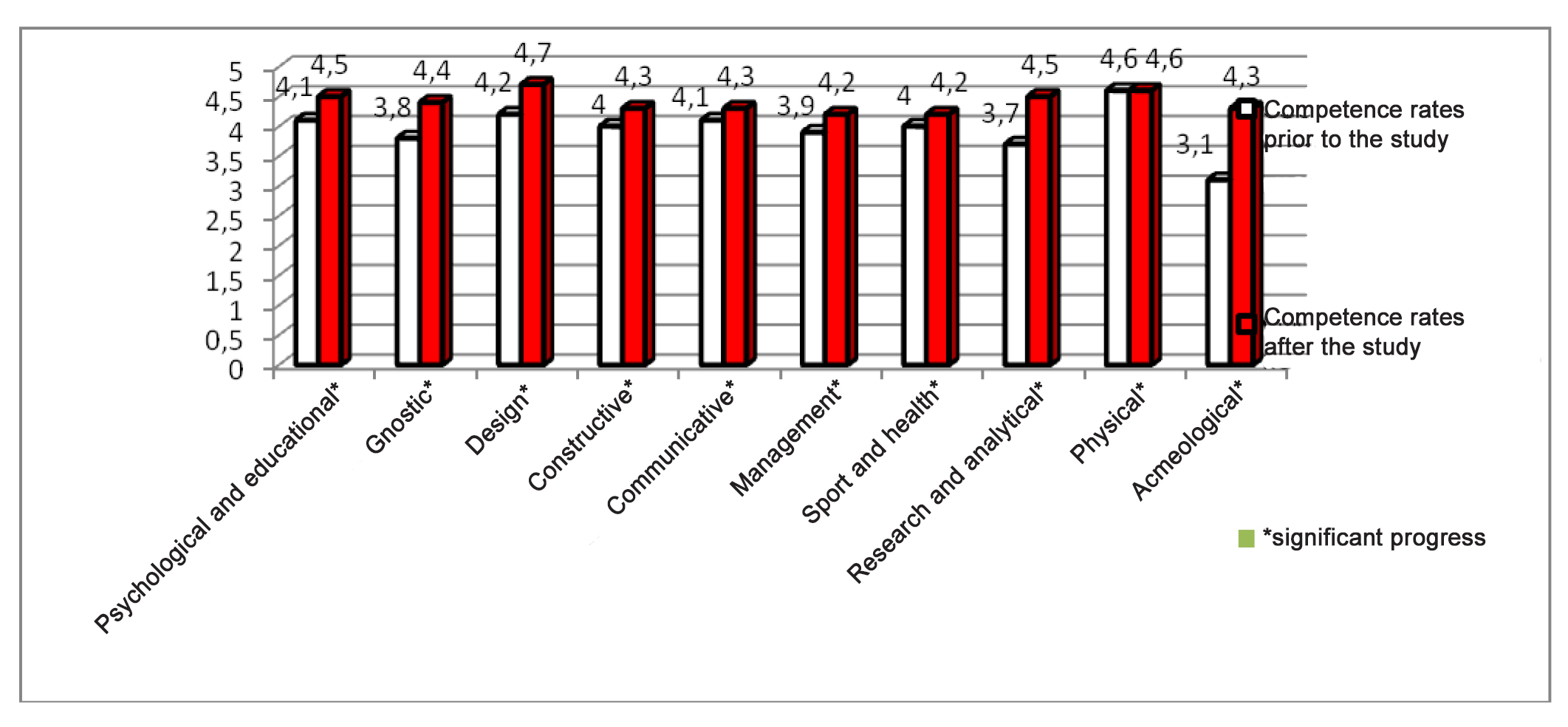
Figure 2. Coaches’ professional competences test rates prior to and after the supported advanced education course
Conclusion. The study data and analyses showed that the proposed aсmeological support system to ensure progress of coaches in the periods of advanced professional education is beneficial as verified by the objective tests and the trainees’ personality development and professional progress rates; with the professional competences tested to qualitatively improve, the progress being verified by the professional accomplishments plus the positive transformations in the individual agendas with a higher priority given to the constant professional and educational progress in professional career.
References
- Derkach A.A. Metodologo-prikladnye osnovy akmeologicheskikh issledovaniy [Applied methodological basics of acmeological research]. Moscow: RACS publ., 1999, 392 p.
- Nikolaev A.N. Psikhologiya trenera v detsko-yunosheskom sporte [Coach's psychology in children's and youth sports]. St. Petersburg: GAPPO publ., 2005, 344 p.
- Inkov M.E. Diagnostika professionalnoy kompetentnosti uchiteley v usloviyakh povysheniya kvalifikatsii. Dis. kand. ped. nauk [Diagnostics of teacher's professional competency in conditions of advanced training. PhD. diss.]. Rostov-on-Don, 2009, 149 p.
- Tyutyukov V.G. Akmeologiya fizicheskoy kultury i sporta. Uchebnik dlya vuzov fizicheskoy kultury [Acmeology of physical culture and sports. Textbook for physical culture universities]. Khabarovsk: FESAPC publ., 2006, 349 p.
Corresponding author: doctor_tyutyukov@mail.ru
Abstract
The study generated the key data to summarise the practical academic experience of aсmeological support to ensure progress of coaches in the periods of advanced professional education. The authors have developed and implemented an acmeological support system to secure professional progress of coaches in the advanced education courses taking 144 hours in form of evening classes. The system was designed to support the trainees in their efforts to conscientiously manage their own progress zones within individual, social, professional and technological domains. Subject to the study were 44 coaches having 5-10-year practical coaching experiences. The aсmeological support under the advanced education program was designed based on an integrated analysis of individual professional experiences and included psychological and aсmeological trainings, coaching, game modelling tools, analyses and pre-graduation skills-rating exercises and content analyses of the trainees’ portfolios.
The study findings demonstrated progress of the subjects as verified by the growth of the key competences and professionally important qualities and abilities in the coaches upon the advanced education courses with a special emphasis on the education component designed to help them acquire conscientious management skills to manage their own professional progress zones.




