Peculiarities of development of higher mental functions in athletes
Фотографии:
ˑ:
Professor, Dr.Sc.Psych. V.I. Strelkov
Associate Professor, Dr.Sc.Psych. O.I. Mironova
Associate Professor, PhD A.V. Romanova
Associate Professor, PhD V.V. Trubnikov
Russian state social university, Moscow
Keywords: higher mental functions, training, pre-season mental conditioning, idea.
Introduction. For several years now, Russian athletes have been attacked by the World Anti-Doping Agency that monitors the usage of various banned substances aimed to enhance physical and mental state of those involved in sport. This wreaks havoc on domestic athletes, and, most of all, on the authority of the State that, on top of everything else, is squeezed financially and politically. We argue that various performance-enhancing drugs displace pre-season mental conditioning tools, where raised demands are placed upon the psyche of athletes who strive to reach the top of their sport skills.
Theoretical treatment. We should start with the formulation of the law of development of higher mental processes by L.S. Vygotsky - a forecaster of the conceptual approach in sports: "Every mental function comes on the scene of life twice: first, externally, i.e. socially, in terms of externalization, then internally, i.e. psychologically, in terms of internalization" [1, p. 145]. The law makes it possible to consider common learning field of the athletes’ activity as the one shared between them and their coaches (Fig. 1).
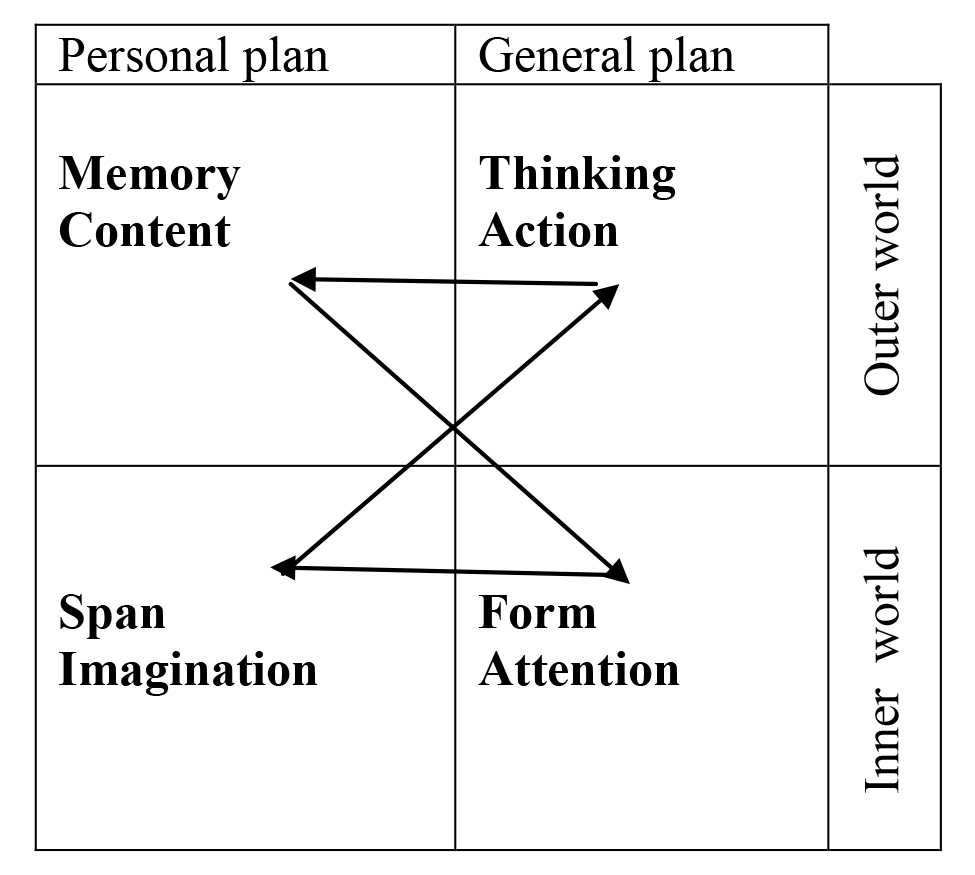
Fig. 1. Structure of learning field of activity of athlete and coach
According to the law of development of higher mental functions, this field is divided into two vertical zones: general - for the coach, and personal - for the athlete. However, such distribution adjoins something that akins the subjects of the training process, namely, common inner world which confronts the outer one. The true "masters of the situation" in the mindset displayed are higher mental functions (HMF) - memory, attention, imagination and thinking distributed between the brain areas. Their object of activity is idea defined by such features as content, span, form and effect directly related to HMF [6, 7, 8].
By definition, "an idea is a unity of essential properties, connections and relationships of objects or phenomena reflected in the mind as a result of thinking; a thought or a system of thoughts, outlining and consolidating the objects of a certain class by definite common and object-specific features" [5].
With HMF and an idea in the primitive basis, it is possible to build the model of the category "Information" (Table 1), where things move from form to span, then - to action, and finally - to content (Fig. 1). The procedures undertaken conform to the law of development of HMF by L.S. Vygotsky.
Table 1. "Information" category model
|
Understanding |
span – way of thinking |
|||
|
syncret |
category |
complex |
||
|
form-logic |
comparison |
1. signal |
2. feature |
3. cell |
|
classification |
2. stimulus |
3. sense |
1. group |
|
|
definition |
3. sign |
1. meaning |
2. image |
|
|
creation |
1. symbol |
3. word |
2. community |
|
Herein, HMF start developing when attention replaces imagination, which in turn sidelines thinking. The latter, consequently, starts to dominate in the position of memory, which has no choice but to move into the area previously occupied by attention.
The next stage is the development of each higher mental function. In this case, attention involves four linear units: comparison, classification, definition, creation. Accordingly, imagination includes three volumetric units: syncret, category, complex. In turn, thinking is limited to one unit - understanding. Finally, memory develops into the content of twelve units.
When it comes to the development, it is the concept of "zone of proximal development" introduced by L.S. Vygotsky that is appropriate here. In our case, it is associated with the order of inclusion of definite HMF: attention, imagination, thinking, memory. They are opposed to lower, physical functions.
Objective of the study was to analyze the athletes’ higher mental functions dynamics over the academic year.
Methods and structure of the study. Subject to the study were sports class graduates of comprehensive school (30 people), team coaches in various fields (30 people), future psychologists going into further full-time education following a yearly crash program (30 people). The study was conducted in autumn and spring. The participants were tested using four methods of study of higher mental functions - memory, attention, imagination and thinking. At the same time, the psychologists involved into the yearly further education system were trained based on the conceptual modeling technology aimed to develop higher mental functions [2; 4; 5].
The following methods were used:
Memory. Short-term visual memory span is assessed by means of the "Mnemotest" block as part of the microprocessor hardware complex for psychophysiological testing developed by All-Union Scientific Research Institute of Medical Instruments and Equipment (Moscow) [E.V. Nadezhdin, L. N. Zuev, A.I. Vishnyakov, 1991]. The testee sits in front of a console with a matrix split into squares 7x7 and holds a special probe in his/her arms. Separate cells on the matrix randomly light up and go off 5 sec after. The testee is to remember the lit cells and touch them with the probe. The task complexity increases from three lit cells to eleven. The microprocessor-based measurement enables to get a printed integral indicator of success of the testee's activity, taking into account recognition time, task complexity, number of errors and omissions.
Attention. Attention span is estimated using the "Gorbov-Schulte tables" method (1990). The technique is 6 matrices consisting of 25 cells (5 vertically and 5 horizontally). Each cell contains a random number from 1 to 25. The task is to find the numbers on each of the six matrices as quickly as possible. The average time of reading the six matrices is determined.
Imagination. Ingenuity of an idea is determined by means of the tests for creative thinking (P. Torrance, 1995). The essence of the study is to perform the following tasks: "Picture construction", "Drawing completion", "Synthesis of lines."
Abstract-logical thinking. The "Raven's Progressive Matrices" E-IQ test (N.P. Chumakova, V.I. Suslov, 1992). The testees are offered to solve 12 tasks of increasing complexity consisting in analyzing the figures on the main image and subsequent "assembly" of the missing figure part by part (it is analytical and synthetic mental activity that is activated). Each correct solution is a score. Total scores are counted and reduced to standard points. The study results are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Analysis of higher mental functions in athletes, coaches and psychologists
|
Experimental variables |
Groups of subjects |
|||||
|
Athletes |
coaches |
psychologists |
||||
|
Autumn |
spring |
autumn |
spring |
autumn |
spring |
|
|
Memory (integral indicator) |
4.45+1.19 |
3.92+1.08 |
|
|
6.34+1.11 |
5.48+2.33 |
|
Attention (ms) |
90.00+23.49 |
90.25+23.72 |
|
74.09+25.67 |
75.09+22.86 |
65.10+22.31 |
|
Imagination (total points) |
79.60+34.08 |
65.00+14.72 |
|
85.67+25.01 |
71.77+19.23 |
89.29+15.59 |
|
Abstract-logical thinking (stens) |
77.19+12.07 |
71.93+14.30 |
|
92.23+9.35 |
55.00+20.06 |
73.93+12.33 |
Results and discussion. The analysis has revealed that athletes have an advantage over psychologists only in memory performance. At the same time, an increase in the absolute values of memory improvement seems to be more pronounced in psychologists than in athletes.
It is of interest to note that, in terms of other HMF, the athletes’ indicators decreased over the academic year, whereas those in the psychologists increased significantly at the level of P≥0.05. With that, the coaches, who were surveyed in spring only, had an average level of attention and imagination, but were absolute leaders in terms of thinking. However, the most significant data were typical for imagination - the most subtle tool of information processing, at which the athletes totally failed, whereas the psychologists demonstrated the largest increase in the function values.
Conclusion. The experimental data indicate that in the long view physical training focused on motor functions reaches its limits giving way to mental training. Of all HMF it is imagination that undergoes the most significant transformation as the most sophisticated tool of mental conditioning. HMF are activated under the influence of the idea, which, being planted in the mental training process, acts as a subject-substitute for the acquired during sports training centering around small matrices.
References
- Vygotskiy L.S. Sobranie sochineniy: V 6 t. T. 3. Problemy razvitiya psikhiki [Collected Works. In 6 vol. Vol. 3. Problems of psychogeny]. Moscow: Pedagogika publ., 1983, 368 p.
- Ilyin E.P. Psikhologiya sporta [Sports Psychology]. St. Petersburg: Piter publ., 2008, p. 74.
- Oshanin D.N. Kontseptsiya operativnosti otrazheniya v inzhenernoy i obshchey psikhologii [Concept of efficiency of reflection in engineering and general psychology]. Inzhenernaya psikhologiya. Teoriya, metodologiya, prakticheskoe primenenie [Engineering psychology. Theory, methodology, practical applications]. Moscow: Nauka publ., 1977, pp. 134-149.
- Rodionov A.V. Psikhologicheskaya podgotovka basketbolista na osnove mentalnogo treninga [Mental conditioning of basketball player based on mental training]. Available at: http://www.vst-basket-lesgaft.ru/content/view/30/7/ (Accessed: 02.12.2016)
- Strelkov V.I. Psikhologiya personalnogo obrazovaniya [Psychology of personal education]. Arkhangelsk: Pomor state university publ., 2003, 423 p.
- Strelkov V.I., Safoshin A.V., Barankin S.Y. Volya: innovatsionny podkhod [Will; innovative approach]. Saarbrucken: LAP «Lumbert Academic Publ., 2015, 180 p.
- Strelkov V.I., Zavarzina O.O., Barankin S.Y., Safoshin A.V. Tekhnologiya soderzhatelnogo modelirovaniya v sisteme vysshego obrazovaniya Rossii [Meaningful simulation technology in Russian higher education system]. Moscow: ARTKRAS publ., 2017, 72 p.
- Knyazeva N., Gryaznukhin A.G., Kislyakov P.A., Esaulov V.I., Kekteeva Y.I., Polivara Z.V. (2016). Psychological and managerial problems of modern higher education. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6 (1), pp. 47-52.
Corresponding author: StrelkovVI@rgsu.net
Abstract. As of today, pre-contest mental conditioning of Russian athletes is still the weakest aspect of their sports activity. The article presents the results of the study of the domestic athletes’ higher mental functions dynamics over the academic year. Subject to the study were sports class graduates of comprehensive school, team coaches in various fields, and future psychologists. The following research methods were used: estimation of the short-term visual memory span by means of the "Mnemotest" block as part of the microprocessor hardware complex for psychophysiological testing; determination of the attention span using Gorbov-Schulte tables; Torrance test for creative thinking; "Raven's Progressive Matrices" E-IQ test. The experimental data indicate that it is imagination that undergoes the most significant transformation as the most sophisticated tool of mental conditioning. Higher mental functions are activated under the influence of the idea, which, being planted in the mental training process, acts as a subject-substitute for the acquired during sports training.




