Club format of physical culture, sporting and health activity in Yakut (Sakha) Republic
Фотографии:
ˑ:
PhD, Associate Professor S.S. Gulyaeva
Churapcha State Institute of Physical Culture and Sports, Churapcha, Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
Keywords: Yakut (Sakha) Republic, physical culture, health and fitness clubs, public outreach, sociological questionnaire survey.
Background. Progress of the national physical culture and mass sports is highly important for the public health and life quality assurance agenda and, hence, has always been considered among the key priorities of the policies to secure sustainable social and economic development of the country. The top priority national policies in the mass physical culture and sports domain were spelled out in the Federal Program “Physical Culture and Sports Development” and the target Federal Program “Physical Culture and Sports Development in the Russian Federation in the Period of 2006-2015” that mostly address the mass sport sector [2]. Physical culture and health activity is interpreted herein as the initiatives to design and manage special regular physical training system with an emphasis on its health aspects, the system implying a set of specific training forms applicable in due succession [4].
Government policies in the sector at present are geared, among other things, to lure the economically active population to the mass sports albeit the existing institutional framework is still insufficient for that. In this context, the initiatives to revitalize the once popular physical training and sport associations are considered quite relevant, feasible and promising [1]. The physical culture, sport and health projects focused on the local communities are to be supported by a sound legal and regulatory framework including the relevant federal and republican laws and regulations of the RF Government and the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) government [3, 5, 6].
Health and fitness clubs are a key element of the mass physical culture movement in the country. It is fairly clear now for the decision-makers that a network of health and fitness clubs needs to be established to meet the natural human need for physical improvement and healthy lifestyle and to encourage the most efficient forms of the initiatives.
Objective of the study was to make a sociological analysis of the most promising formats of the mass physical culture, sporting and health activity in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) based on the relevant local clubs and associations.
Methods and structure of the study. The sociological survey was performed in 2016 in the Republic with support from the Ministry of Sports of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia). Subject to the questionnaire survey were 42 managers and leading specialists of the relevant physical culture and sports sector management offices and departments of 22 rural municipal governments within the Sakha Republic (Yakutia); with 82% of men and 18% of women in the sample. The subjects were offered a set of questions to obtain their age-, gender- and social-status-specific data plus the basic information on the local health and fitness clubs and associations in their areas of residence and the core physical activity forms, regularity, training experiences and numbers of the activists.
Study results and discussion. Given on Figure 1 hereunder are the outcome data of the survey showing the physical activity forms presently popular and habitual for the Sakha population.
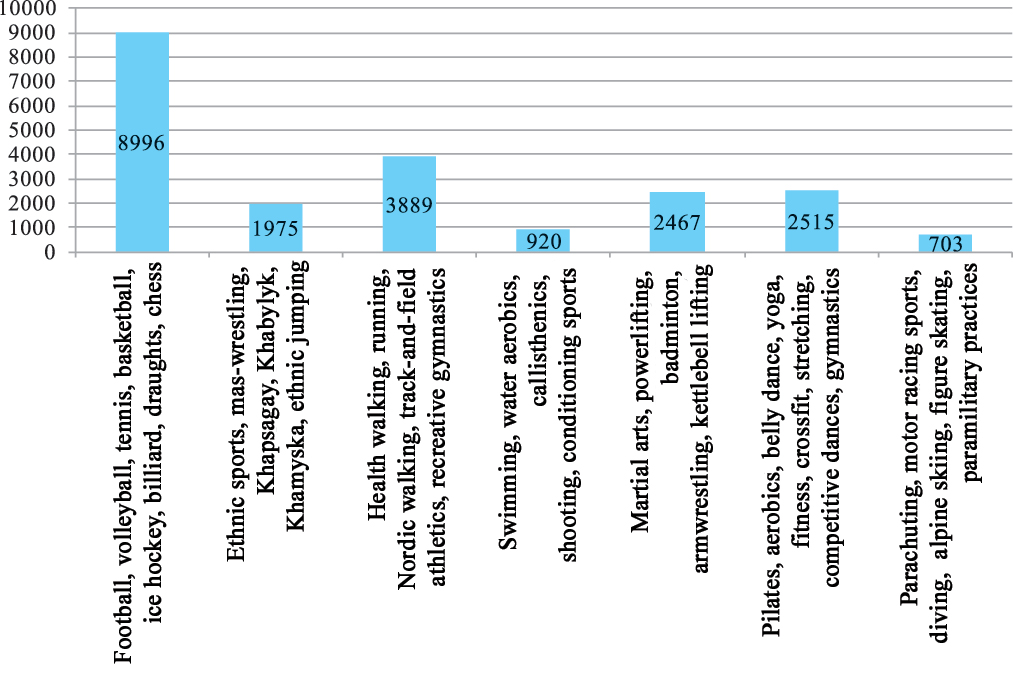
Figure 1. Physical activity forms and types popular and habitual in the 22 municipal areas of the Yakut (Sakha) Republic
Reports and surveys of the existing health and fitness clubs and associations were used to mine the following data:
- 23,924 people are presently engaged in the club activity including 32.1% women and 67.9% men;
- As things now stand, operating in the subject municipal districts of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia)– as far as allowed by the local climatic, areal and social conditions – are 58 health and fitness clubs, 67 physical culture, sport and health groups, 45 communal associations; 15 sport federations; and 19 young people’s communal organisations;
- The club and public association activists are 18 to 65 years old;
- The physical activity of the sampled people varies around 2-3 training sessions per week each taking some 1.5 hours;
- The young and middle-age people surveyed prefer team sports, fitness and crossfit;
- Most popular among the elderly and senior people surveyed are Nordic and health walking practices, running, intellectual sports and table games;
- Most of the subject municipal governments take efforts to promote and develop the ethnic sports and games traditional for the Sakha people;
- Most popular in the industrial uluses (districts) are different extreme sports including parachuting, motorsports, diving etc.; and
- The local communities are lured into the systemic physical and sport activities both by the local health and fitness clubs and the young people’s and/or sporting associations, veterans’ unions and sport federations.
Conclusion. Most of the health and fitness clubs and associations running their operations in the Republic are still in need of formal government registrations and legal statutory documents.
Many municipalities under the study reported being in need of competent specialists to design and manage mass physical culture initiatives and in need in the relevant informational, advocacy and consulting services to the elderly and senior population groups in the Republic. The sport and health system in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia)is to be designed with due regard to the climatic, geographic and weather conditions of this Far Northern region to satisfy the communal demand for modern sport infrastructure and to encourage broad masses of the local population being involved in the physical training process on a systemic and habitual basis, with a special emphasis on the most beneficial forms of physical training practices and theoretically grounded technologies of outdoor physical activities reasonably designed and managed to improve the respiratory and cardiovascular systems of the trainees by a variety of tools including body tempering practices.
References
- Vystuplenie V.V. Putina na zasedanii Soveta po razvitiyu fizicheskoy kultury i sporta v mezhdunarodnom forume «Rossiya – sportivnaya derzhava» [V.V. Putin's speech at a meeting of the Council for Development of Physical Culture and Sports at the international forum "Russia - Country of Sports"]. Available at: http://kremlin.ru/events/president/news/53070.
- Doklad o rezultatakh raboty v 2015 godu i osnovnykh napravleniyakh deyatelnosti Ministerstva sporta Rossiyskoy Federatsii na 2016-2018 gody [Report on the results of work in 2015 and the main guidelines of the Ministry of Sports of the Russian Federation in 2016-2018]. Available at: http://www.minsport.gov.ru/press-centre/speeches/28895/.
- Zakon Respubliki Sakha (Yakutiya) ot 18 iyunya 2009 g. 696-Z # 327-IV «O fizicheskoy kulture i sporte» [Law of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) June 18, 2009 696-W, no. 327-IV «On Physical Culture and Sports"].
- Nekrasova V.V., Kuznetsov V.P. Fizkulturno-ozdorovitelnaya i sportivno-massovaya rabota v vuze [University physical culture and sports activities]. Sb. mater. Vseros. nauch.-prakt. konf. "Fizicheskaya kultura, sport i zdorovye studencheskoy molodezhi v sovremennykh usloviyakh" [Proc. res.-pract. conf. "Physical education, sports and health of students today"] Orel: Orel SAU publ., 2013, p. 30.
- Postanovlenie Pravitelstva Rossiyskoy Federatsii ot 11 yanvarya 2006 g. # 7 «O Federalnoy tselevoy programme «Razvitie fizicheskoy kultury i sporta v Rossiyskoy Federatsii na 2006 – 2015 gody» [Russian Federation Government Resolution dated January 11, 2006 № 7 "On the Federal Target Program "Development of Physical Culture and Sports in the Russian Federation for 2006 - 2015"].
- Rekomendatsii po sozdaniyu sportivnykh klubov [Sports clubs establishment-related recommendations]. Available at: http://vertigosports.ru/business/experience.
Corresponding author: ssvjakutija@yandex.ru
Abstract
The study was designed to analyze the most promising formats of the physical culture, sporting and health activity in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia). Subject to the study was the adult population of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia). A sociological survey was applied to obtain gender- and age-specific data of the subjects and find their favourite physical practices and habitual physical exercises. The study data and analyses showed that most of the popular health and fitness clubs and associations operating in the Republic are still in need of formal governmental registrations and legal statutory documents. Many municipalities under the study reported being in need of competent specialists to design and manage the mass physical culture initiatives and in need of the relevant informational, advocacy and consulting services to the elderly and senior population groups in the Republic. The sport and health system in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) is to be designed with due regard to the climatic, geographic and weather conditions of this Far Northern region to meet the communal demand for modern sport infrastructure and to encourage broad masses of the local population being involved in the physical training process on a systemic and habitual basis.




