Ural region’s municipalities: sport infrastructure state analysis
ˑ:
M.A. Kocheryan1
I.V. Vashlyaeva1
T.V. Volovik1
1Ural State Economic University, Yekaterinburg
Keywords: physical education and sport, municipalities, sport infrastructure, depreciation rate
Background. Physical education and mass sports are ranked high on the list of the national priorities due to their health, physical progress and socializing benefits [1]. Modern physical education and sport service is considered beneficial for recreation and professional, physical, intellectual and ethical progress [2]; and that is the reason why rural and urban municipalities take special efforts to support systemic, well-designed and managed physical education and sport services in their areas, with the service quality and supply largely dependent on the available municipal sport assets and infrastructure [4].
Objective of the study was to analyze the sport infrastructure in the Sverdlovsk Oblast municipalities.
Methods and structure of the study. Subject to the study was the municipal sport infrastructure in the Sverdlovsk Oblast, with the key data for the study mined in the annual reports of the municipal governments on the physical education and sport service infrastructure development, supply and demand.
Results and discussion. Active population of region widely use the municipal sport facilities to satisfy the natural need for the modern physical education and sport / health practices, with the Sverdlovsk Oblast government reporting the actively sporting population at above 1 million at present. The public demand is met by more than 4 thousand municipal physical education and sport groups in the Sverdlovsk Oblast. Given on Figure 1 is the municipal physical education and sport group activity growth statistics.
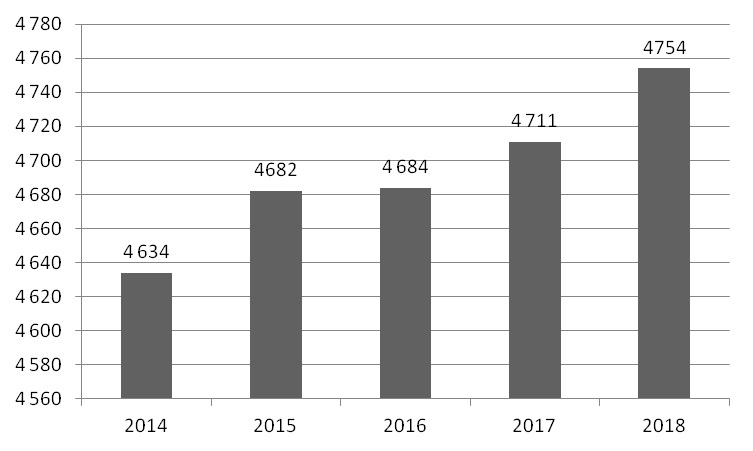
Figure 1. Municipal physical education and sport / heath group growth statistics of 2014-2018, numbers
As demonstrated by the Figure above, the physical education and sport / health groups had grown in numbers by 102.5% for the period. Given on Figure 2 is the Sverdlovsk Oblast municipal sport assets development statistics for the same period.
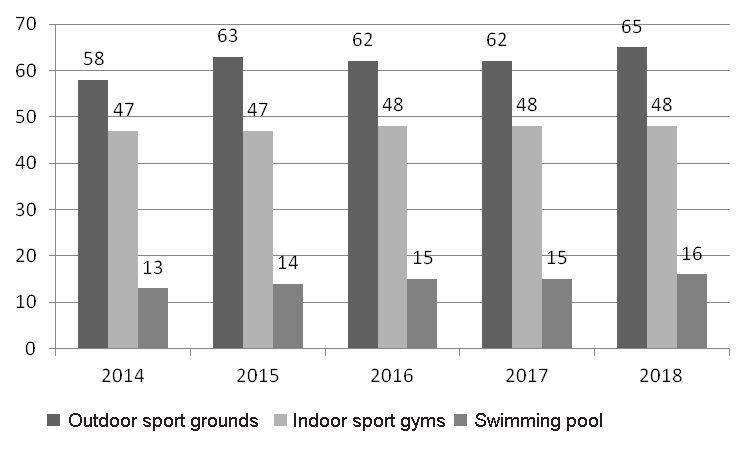
Figure 2. Municipal physical education and sport / heath assets development statistics for 2014-2018
Outdoor sport grounds Indoor sport gyms Swimming pool
Actual supply of the sport infrastructure for the last 5 years has remained virtually the same, with the shortest supply and highest demand reported for the swimming pools. Given on Figure 3 hereunder is the Sverdlovsk Oblast municipal sport infrastructure depreciation statistics.
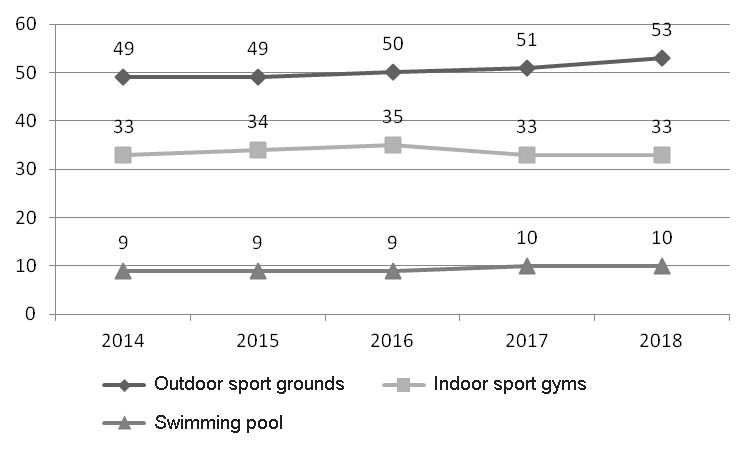
Figure 3. Sverdlovsk Oblast municipal sport infrastructure depreciation statistics for 2014-2018, %
Outdoor sport grounds Indoor sport gyms Swimming pool
The average depreciation rate is reported at 30% for the local sport facilities, with the outdoor sport grounds reported to have depreciated by more than 50%: see Figure 3. This natural growth needs to be countered by high investments in the operation and maintenance to meet the relevant O&M requirements and standards. These issues need to be negotiated and decided upon in the municipal budgeting process. It is not unusual that the municipal budgets report insufficient financing of some sport disciplines versus the over-financing (and non-disbursements) on some other items of the municipal physical education and sport budgets.
Conclusion The analysis found some deficiencies and underdevelopments in the municipal physical education and sport asset design and management in the context of the formal progress goals set by the municipal governments in the Sverdlovsk Oblast. The analysis found the following: the local physical education and sport facilities and equipment are often obsolete and depreciated; the physical education and sport system requires additional financing to improve the operation and maintenance standards; and the physical education and sport infrastructure often fails to meet the communal demand in full. These and some other problems may explain the fact that the local communities are still relatively uninterested in the municipal physical education and sport services.
References
- Antipova E.V., Antipov V.A. Organizatsionno-upravlencheskie faktoryi razvitiya ozdorovitelnoy i adaptivnoy fizicheskoy kultury po mestu zhitelstva naseleniya [Organizational and managerial factors in development of domiciliary recreational and adaptive physical education]. Diskurs. 2017. no. 3. pp. 6-15.
- Berezhnoy A.V., Vanetsyan L.I. Sozdanie usloviy dlya razvitiya fizicheskoy kultury i sporta v munitsipalnom obrazovanii [Efforts to create conditions for development of municipal physical education and sports]. Ekonomika i upravlenie: aktualnye voprosy teorii i praktiki. 2017. pp. 18-23.
- Bratanovskiy S.N., Vulakh M.G., Bratanovskaya M.S. Sistema munitsipalnogo upravleniya fizicheskoy kulturoy i sportom v Rossii: pravovye osnovy organizatsii i deyatelnosti [Municipal management of physical education and sports management system in Russia: legal framework of organization and activities].2007 [znanium.com/catalog/author/cc314f58-f6d8-11e3-9766-90b11c31de4c].
- Shabunova A., Leonidova G., Moskvina E. Razvitie munitsipalnoy infrastruktury: fizicheskaya kultura i sport [Development of Municipal Infrastructure: Physical education and Sports]. 2017. Litres.
Abstract
Physical education and mass sports are ranked high on the list of the national priorities due to their health, physical progress and socializing benefits. Municipal governments are responsible for local communities being duly supplied by and having a free access to the municipal physical education and sport facilities – since good versatile physical/ sporting activity is considered a prime prerequisite for a physically and intellectually fit personality development missions. Every municipality is responsible to hold, develop and secure free access to the physical education and sport service facilities within its area for the local communities. Objective of the study was to analyze the sport infrastructure in the Ural Region’s municipalities. Basic data for the analysis were mined in the annual reports of the municipal governments on the physical education and sport service infrastructure development, supply and demand.
The analysis revealed some deficiencies and underdevelopments in the municipal physical education and sport asset design and management in the context of the formal progress goals set by the municipal governments in the Sverdlovsk Oblast. The analysis found the following: the local physical education and sport facilities and equipment are often obsolete and depreciated; the physical education and sport system requires additional financing to improve the operation and maintenance standards; and the physical education and sport infrastructure often fails to meet the communal demand in full. These and some other problems may explain the fact that the local communities are still relatively uninterested in the municipal physical education and sport services.



